(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON, May 4, 2021 -- Spinal fusion is frequently performed to restore spinal stability in patients with spinal diseases, such as spinal stenosis, vertebral fractures, progressive deformities, and instability. In the past two decades, there has been marked increase in the number of people over 65 years in age who have needed spinal fusion surgery.
While autogenous bone grafts have long been considered the reference standard for spinal fusion, painful pseudoarthrosis remains a leading cause of poor clinical outcomes. Many researchers have consequently focused on trying to create a biomimetic scaffold that induces vascularization to enable bone tissue regeneration and spinal fusion.
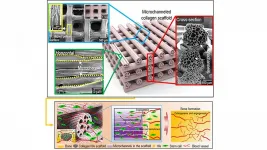
In Applied Physics Reviews, from AIP Publishing, researchers from Sungkyunkwan University in South Korea present a solution to address the challenge of fabrication of a biomimetic scaffold. The team designed a microchannel scaffold made of a collagen and hydroxyapitite combination, with each strut consisting of micrometer-scaled microchannels. The microchannels have induced growth of blood vessels in a mouse model.
"Since the fabrication of biomimetic scaffold is a challenging issue, the innovation of this study lies in adding extra hierarchy to the structure in the form of microchannels," said author Geun Hyung Kim. "This was achieved through a 4D printing strategy, where one-way shape morphing is used."
The researchers printed immiscible polymer blends that act as a double negative template in order to fabricate the the biomimetic collagen/hydroxyapatite hierarchical scaffold. They followed that by one-way shape morphing (4D printing) and coating processes.
Collagen is known as a hydrophilic material, and numerous in vivo studies have suggested it possesses excellent cellular activities. In the case of the microchanneled collagen/hydroxyapatite scaffold, the researchers noted significantly higher water-absorbing capability, compared to a conventional collagen scaffold, as a result of the capillary pressure supplied by the microchannels. Consequently, the in vivo studies have suggested excellent infiltration of cells into microchannels.
Going forward, the researchers will investigate enhancing the mechanical properties of the scaffold. Furthermore, controlling the mechanical properties of the scaffold would enable versatile applications of the microchanneled collagen/hydroxyapatite scaffold.
"I believe that the designed scaffold can have multiple applications with tubular structures such as muscle, tendon, and nerve," said Kim.
Skeletal muscle is a hierarchical organization where the muscle fibers are encapsulated in microchannels known as endomysium. Therefore, the designed scaffold could act as endomysium to enable the infiltration of muscle fibers into the channels.
INFORMATION:
The article "Bone tissue engineering via application of a collagen/hydroxyapatite 4D-printed biomimetic scaffold for spinal fusion" is authored by Hanjun Hwangbo, Hyeongjin Lee, Eun Ji Roh, WonJin Kim, Hari Prasad Joshi, Su Yeon Kwon, Un Yong Choi, In-Bo Han, and Geun Hyung Kim. The article will appear in Applied Physics Reviews on May 4, 2021 (DOI: 10.1063/5.0035601). After that date, it can be accessed at https://aip.scitation.org/doi/10.1063/5.0035601.
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
Applied Physics Reviews features articles on significant and current topics in experimental or theoretical research in applied physics, or in applications of physics to other branches of science and engineering. The journal publishes both original research on pioneering studies of broad interest to the applied physics community, and reviews on established or emerging areas of applied physics. See https://aip.scitation.org/journal/are.
WASHINGTON, May 4, 2021 -- Scientists from Texas A&M have developed an extension to an ordinary cellphone that turns it into an instrument capable of detecting chemicals, drugs, biological molecules, and pathogens. The advance is reported in Reviews of Scientific Instruments, by AIP Publishing.
Modern cellphones include high-quality cameras capable of detecting low levels of light and eliminating digital noise through software processing of the captured images. Recent work has taken advantage of this sensitivity to produce cellphone cameras that ...
SAN ANTONIO (May 4, 2021) - Risk-reducing mastectomy saves lives of women who, because of hereditary or other risk factors, may have a very high lifetime risk of developing breast cancer, according to two new journal articles written to guide physicians and patients. All of these women should also discuss with their physicians nonsurgical options such as screening and medications to reach the best, customized treatment strategy, the essays mention.
Both articles, published May 4 in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA), are by END ...
WHO Benjamin Rome, MD, Instructor of Medicine at Harvard Medical School and researcher in the Program On Regulation, Therapeutics, And Law (PORTAL) in the Division of Pharmacoepidemiology and Pharmacoeconomics, Brigham and Women's Hospital; corresponding author of a paper published in JAMA Network Open.
WHAT When drug manufacturers raise the list price for brand-name prescription drugs, do patients' out-of-pocket costs rise too? A new study published in JAMA Network Open by Dr. Benjamin Rome and colleagues in the Brigham's Division of Pharmacoepidemiology and Pharmacoeconomics finds that more than half of patients may experience increases in out-of-pocket spending when drug ...
BOSTON - Researchers from Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) appear to have solved the 120-year-old mystery surrounding the failing health of famed Antarctic explorer Sir Ernest Shackleton over the course of his daring expeditions to Antarctica in the early part of the twentieth century. In a paper published online in the END ...
Researchers have found that people who live beyond 105 years tend to have a unique genetic background that makes their bodies more efficient at repairing DNA, according to a study published today in eLife.
This is the first time that people with 'extreme longevity' have had their genomes decoded in such detail, providing clues as to why they live so long and manage to avoid age-related diseases.
"Aging is a common risk factor for several chronic diseases and conditions," explains Paolo Garagnani, Associate Professor at the Department of Experimental, Diagnostic ...
Studying protein changes in the kidneys as we age, as well as the transcription of genes into proteins, helps provide a full picture of the age-related processes that take place in these organs, says a study in mice published today in eLife.
Aging causes many changes in the body and in essential organs such as the kidneys, which function less efficiently later in life. Age-related changes in the kidneys have mostly been reported by looking at the transcription of genes - the process by which a segment of DNA is copied into RNA. The current study suggests that this approach, combined with studying changes in proteins, gives us a better understanding of age-related changes in the kidney and may point to new approaches for treating ...
TAMPA, Fla. (May 4, 2021) -- Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation, or rTMS, was FDA approved in 2008 as a safe and effective noninvasive treatment for severe depression resistant to antidepressant medications. A small coil positioned near the scalp generates repetitive, pulsed magnetic waves that pass through the skull and stimulate brain cells to relieve symptoms of depression. The procedure has few side effects and is typically prescribed as an alternative or supplemental therapy when multiple antidepressant medications and/or psychotherapy do not work.
Despite increased use ...
LONDON, ON - New findings from Ontario have shown that children born in Sarnia have a higher risk of developing asthma compared to neighbouring cities. A research team from Lawson Health Research Institute and Western University, using provincial data from ICES, found that higher air pollution exposure in the first year of life very likely contributed to this higher risk. Their results are published today in CMAJ Open.
Summary of study results:
-Children born in Sarnia in the 1990s and early 2000s were disproportionally at a higher risk of developing asthma in the first few years of life, compared to neighbouring cities.
-Air pollution exposure ...
Agência FAPESP – White-sand savannas are expanding in the heart of the Amazon as a result of recurring forest fires, according to a study published in the journal Ecosystems.
The study was supported by FAPESP, and conducted by Bernardo Monteiro Flores, currently a postdoctoral fellow in ecology at the Federal University of Santa Catarina (UFSC) in Brazil, and Milena Holmgren, a professor in the Department of Environmental Sciences at Wageningen University in the Netherlands.
“The edges of the Amazon Rainforest have long been considered the ...
FINDINGS
A new study by researchers at the UCLA Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center has identified a novel combination therapy to potentially help overcome resistance to immunotherapy in people diagnosed with advanced lung cancer. The combination approach uses immune checkpoint inhibitors with ATRA, a safe medication that is widely used to treat leukemia. The team found the combination therapy led to eradication of over 70% of tumors when tested in mice with LKB1-deficient lung cancer. It also generated durable tumor-specific immunity.
BACKGROUND
Immune checkpoint inhibitors have substantially ...