Researchers identify potential combination therapy for aggressive lung cancer
Preclinical study could help lead to better treatments for LKB1-deficient lung cancer
2021-05-04
(Press-News.org) FINDINGS
A new study by researchers at the UCLA Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center has identified a novel combination therapy to potentially help overcome resistance to immunotherapy in people diagnosed with advanced lung cancer. The combination approach uses immune checkpoint inhibitors with ATRA, a safe medication that is widely used to treat leukemia. The team found the combination therapy led to eradication of over 70% of tumors when tested in mice with LKB1-deficient lung cancer. It also generated durable tumor-specific immunity.
BACKGROUND
Immune checkpoint inhibitors have substantially improved the outcomes for people with lung cancer. The five-year survival rate for patients with advanced disease on this therapy is more than 13% compared to 5% in patients with conventional chemotherapy. Although immunotherapy has been successful for many patients, a majority of patients still do not respond to the therapy.
To help increase the number of patients who benefit from this therapy, researchers have sought to identify mechanisms for treatment resistance. The tumor suppressor gene LKB1 are found mutated in 20% of patients with non-small cell lung cancer and 30% of KRAS-mutant non-small cell lung cancers. It also is a major gene associated with resistance to immune checkpoint inhibitors. By identifying aberrant pathways caused by LKB1 mutation, researchers are figuring out a novel therapy that targets the pathway and sensitizes LKB1-deficient tumors to immunotherapy.
METHOD
To assess the response of the combination therapy, researchers tested the therapy in mice that were injected with LKB1-deficient lung tumors.
IMPACT
The study provides evidence that using ATRA in combination with checkpoint inhibitors could potentially help patients with advanced lung cancer who carry LKB1 mutation to have a positive response to immunotherapy.
AUTHORS
Lead authors are Rui Li, MD, PhD, currently a resident physician of internal medicine at UCLA, and Ramin Salehi-Rad, MD, PhD, a physician scientist in pulmonary and critical care medicine. The senior authors are Bin Liu, PhD, an adjunct professor of pulmonary and critical care medicine, and Steven Dubinett, MD, a professor of pulmonary and critical care medicine, pathology and laboratory medicine, and molecular and medical pharmacology at the Geffen School of Medicine and physician-scientist in the UCLA Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center.
JOURNAL
The study was published online in Cancer Research, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research.
FUNDING
The research was supported in part by funding from the National Cancer Institute, the National Heart Lung and Blood Institute and the Department of Veteran Affairs.
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-04
As nurseries and garden centers fill up with spring landscaping plants, home gardeners owe a lot to a technique called micropropagation, which has proven beneficial to many plants - perhaps soon to include cannabis, thanks to work by UConn researchers in the College of Agriculture, Health, and Natural Resources.
Micropropagation is a technique used for growing large quantities of new plants from fewer "parent" plants, yielding clones with the same, predictable qualities. The cannabis (Cannabis sativa) industry, however, has been largely left out of this beneficial technique, because this species of plant is extremely difficult to micropropagate.
Researchers from UConn - including Associate Professor Jessica Lubell-Brand, Ph.D. student Lauren Kurtz, and Professor Mark ...
2021-05-04
May 4, 2021 - From the very beginning of the AIDS epidemic in 1981, nurses have been at the forefront of patient care, advocacy, and research. But even in the age of antiretroviral therapy and pre-exposure prophylaxis, many challenges remain in reducing the impact of HIV and AIDS, according to the special May/June issue of END ...
2021-05-04
Relatives of the giant crocodile might have been kings of the waterways during the Cretaceous period, eating anything--including dinosaurs--that got a little too close to the water's edge, but the largest of these apex predators still started off small. Figuring out how these little crocs grew up in a world surrounded by giants is no small task. Now crocs fossils from Texas are shedding light on how these animals changed their diets as they grew, helping them find a place of their own in environments alongside their bigger, badder relatives.
According to the study, published by Cambridge University Press, the crocodiless in question are members of the Deltasuchus motherali and lived along the coastline of Texas 96 million years ...
2021-05-04
Scientists have shed light on why some people who have a stroke do not also have abnormal heart rhythms, even though their hearts contain similar scar tissue.
Their results, published today in eLife, could help identify the best treatments for people who might be at risk of recurrent stroke, new heart disorders, or both.
Strokes are often caused by abnormal blood flow resulting from rapid, irregular beating in the upper chamber of the heart. This is also called atrial fibrillation (AFib). But some people have strokes that appear to have been caused by the heart, ...
2021-05-04
Aachen, Germany and Hennigsdorf/Berlin, Germany, May 4, 2021 - German University Hospital Uniklinik RWTH Aachen ("Uniklinik RWTH Aachen") and diagnostics company SphingoTec GmbH ("SphingoTec") today announced that the endothelial function biomarker bio-ADM aids in the early risk stratification and management of patients suffering from severe COVID-19, in need for escalated intensive care treatment (1). A team lead by the clinical researchers at Uniklinik RWTH Aachen has shown that high bio-ADM levels indicate the severity of the acute respiratory distress ...
2021-05-04
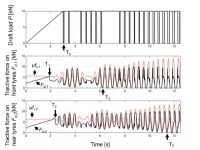
Tokyo, Japan - Researchers at Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology (TUAT) modeled the dynamic instability--the so-called "power hop"--that can cause uncontrollable bouncing and damage tractors when they plow dry ground. The team found that self-excited oscillations can arise when the tractor pushes against the ground.
Plowing a field on a tractor may seem like a serene occupation, but sudden vibrations can grow unexpectedly and threaten to topple you under certain conditions. The problem is that in nonlinear systems with coupled components, as with a mechanical tractor, ...
2021-05-04
A synthetic approach that improves absorber layers in perovskite solar cells could help them achieve their full potential and draw closer to the performance of leading gallium arsenide devices.
Solar cells that rely on perovskite thin films to capture sunlight are the fastest growing photovoltaic technology. Cheaper and easier to manufacture and incorporate into devices than conventional semiconductors, lead halide perovskites also effectively absorb visible light and display long charge carrier diffusion lengths -- an indicator of their ability to maintain light-induced electrons and holes separation and facilitate charge transport.
Performance ...
2021-05-04
A new Boston University School of Public Health (BUSPH) study has identified for the first time how the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR), an environmental chemical receptor, drives immunosuppression in oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC)--and that its removal from malignant cells can result in tumor rejection.
Published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, the study findings provide new insight into the biology of cancer immunosuppression, and identify a new target for cancer immunotherapy treatment.
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (immunotherapy drugs) are some of the most important treatments that have emerged for treating many cancers, including OSCC. Targeting immune checkpoint molecules such as PD-1, ...
2021-05-04
Measures to contain the Corona pandemic are the subject of politically charged debate and tend to polarize segments of the population. Those who support the measures motivate their acquaintances to follow the rules, while those who oppose them call for resistance in social media. But how exactly do politicization and social mobilization affect the incidence of infection? Researchers at the Max Planck Institute for Human Development have examined this question using the USA as an example. Their findings were published in Applied Network Science.
Limit crowds, keep a safe distance, and wear masks. Such non-pharmaceutical ...
2021-05-04
Cancerous tumors thrive on blood, extending their roots deep into the fabric of the tissue of their host. They alter the genetics of surrounding cells and evolve to avoid the protective attacks of immune cells. Now, Penn State researchers have developed a way to study the relationship between solid, difficult-to-treat tumors and the microenvironment they create to support their growth.
The method has the potential to act as a testbed for drugs and other anticancer treatments, according to Ibrahim T. Ozbolat, associate professor of engineering science and mechanics and biomedical engineering, who led the research. The details of the approach were published in Advanced Biology.
Using ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Researchers identify potential combination therapy for aggressive lung cancer
Preclinical study could help lead to better treatments for LKB1-deficient lung cancer