(Press-News.org) Cancerous tumors thrive on blood, extending their roots deep into the fabric of the tissue of their host. They alter the genetics of surrounding cells and evolve to avoid the protective attacks of immune cells. Now, Penn State researchers have developed a way to study the relationship between solid, difficult-to-treat tumors and the microenvironment they create to support their growth.
The method has the potential to act as a testbed for drugs and other anticancer treatments, according to Ibrahim T. Ozbolat, associate professor of engineering science and mechanics and biomedical engineering, who led the research. The details of the approach were published in Advanced Biology.
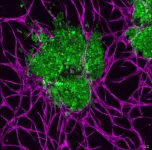
Using metastatic triple-negative breast cancer cells -- the most aggressive breast cancer, for which there are few treatments -- and specialized modeling techniques, the researchers cultivated tumor microenvironments.
"We brought together the tumor and its microenvironment and studied how the embedded tumor affects its surrounding matrix," said Madhuri Dey, first author on the paper and a doctoral student in the Department of Chemistry in the Eberly College of Science. "Then we asked if we could get any meaningful genetic information from this composite system."
Typically, researchers examine the genetic information of single cells in a system to understand which signals are being sent and received to encourage specific behaviors. However, Dey said, the individual actions may not reveal every facet of a composite system.
"We looked at the genome of the entire system," Dey said. "The result was a far more representative understanding of how cells talk to each other in the native conditions."
They found that the physiological changes in tumor behavior -- such as growth or movement -- are a direct result of cellular communication in the tumor's microenvironment. Cancer cells communicate with the cells lining blood vessels, called endothelial cells, that also control the exchange of materials between blood and the extracellular environment. Cancer also communicates with the cells that secrete collagen to produce the scaffolding of tissues, called fibroblasts.
"The cancer-endothelial cell crosstalk is equally important as the cancer-fibroblast crosstalk," Dey said, noting that each process can influence the other and change how the cancer grows.
To test their approach, the researchers 3D-bioprinted tumor models called spheroids in a microenvironment to see how distance might influence tumor growth.
"We asked, 'Can proximity increase cancer aggressiveness?' and we found that there is a critical distance," Dey said. "Tumors far apart don't affect each other, but endothelial cells from neighboring tumors can nourish each other and increase how aggressively the cancer spreads."
Next, the researchers plan to use the fabrication method to investigate how immune cells engineered to target cancer cells can be improved to penetrate solid tumors and limit their spread.
"We could also use this as a personalized tool to test treatment effectiveness for individual people -- that's a future goal," Ozbolat said. "There are so many ways in which we can apply this tumor microenvironment model."
INFORMATION:
Co-authors include Bugra Ayan, who earned his doctorate from Penn State in engineering science and mechanics in 2020 and is now a postdoctoral fellow at Stanford University; and Marina Yurieva and Derya Unutmaz, both with the Jackson Laboratory for Genomic Medicine and University of Connecticut Health Center. Ozbolat, Dey and Ayan are also affiliated with the Huck Institutes of the Life Sciences and the Materials Research Institute.
The National Cancer Institute and the National Science Foundation's Division of Civil, Mechanical and Manufacturing Innovation funded this work.
Despite human inventiveness and ingenuity, we still lag far behind the elegant and efficient solutions forged by nature over millions of years of evolution.
This also applies for buildings, where animals and plants, have developed extremely effective digging methods, for example, that are far more energy-efficient than modern tunnelling machines, and even self-repairing foundations that are unusually resistant to erosion and earthquakes (yep, we're talking about roots here).
Researchers from all over the world are therefore seeking inspiration in nature to develop the buildings of the future, and researchers from Aarhus University ...
Honeybees have a complex communication system. Between buzzes and body movements, they can direct hive mates to food sources, signal danger, and prepare for swarming - all indicators of colony health. And now, researchers are listening in.
Scientists based in Germany - with collaborators in China and Norway - have developed a way to monitor the electrostatic signals that bees give off. Basically, their wax-covered bodies charge up with electrostatic energy due to friction when flying, similar to how rubbing your hair can make it stand on end. That energy then gets emitted during communications.
"We were thrilled by the ...
The majority of top-rated fertility apps collect and even share intimate data without the users' knowledge or permission, a collaborative study by Newcastle University and Umea University has found.
Researchers are now calling for a tightening of the categorisation of these apps by platforms to protect women from intimate and deeply personal information being exploited and sold.
For hundreds of millions of women fertility tracking applications offer an affordable solution when trying to conceive or manage their pregnancy. But as this technology grows in popularity, experts have revealed that most of the top-rated fertility apps collect and share sensitive ...
T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) is a very aggressive type of blood cancer. It is relatively rare but still draws a lot of attention as it mostly develops in children under the age of 20. The standard treatment for T-ALL involves heavy chemotherapy procedures, which result in favorable outcomes with an overall survival of 75% after 5 years.
However, some patients do not respond to this treatment, or they only respond for a short period, after which the disease grows back. These patients therefore need alternative therapies.
Researchers from the Faculty of Health and Medical Sciences, University of Copenhagen, have now identified a combination treatment, which could potentially benefit patients ...
University of Bristol research into octopus vision has led to a quick and easy test that helps optometrists identify people who are at greater risk of macular degeneration, the leading cause of incurable sight loss.
The basis for this breakthrough was published in the latest issue of the Journal of Experimental Biology and describes new technology developed by lead researcher, Professor Shelby Temple, to measure how well octopus- which are colour-blind - could detect polarized light, an aspect of light that humans can't readily see. Using this novel technology, the research team showed that octopus have the most sensitive polarization vision system of any animal tested to date. Subsequent research ...
When COVID-19 patients began filling up ICUs throughout the country in 2020, health care providers faced difficult decisions. Health care workers had to decide which patients were most likely to recover with care and which were not so resources could be prioritized.
But a new paper from the University of Georgia suggests that unconscious biases in the health care system may have influenced how individuals with intellectual disabilities were categorized in emergency triage protocols.
The state-level protocols, while crucial for prioritizing care during disasters, frequently ...
(Boston)--If you come from a family where people routinely live well into old age, you will likely have better cognitive function (the ability to clearly think, learn and remember) than peers from families where people die younger. Researchers affiliated with the Long Life Family Study (LLFS) recently broadened that finding in a paper published in END ...
Brain implants are used to treat neurological dysfunction, and their use for enhancing cognitive abilities is a promising field of research. Implants can be used to monitor brain activity or stimulate parts of the brain using electrical pulses. In epilepsy, for example, brain implants can determine where in the brain seizures are happening.
Over time, implants trigger a foreign body response, creating inflammation and scar tissue around the implant that reduces their effectiveness.
The problem is that traditional implants are much more rigid than brain tissue, which has a softness comparable to pudding. Stress between the implant and ...
A new auroral phenomenon discovered by Finnish researchers a year ago is probably caused by areas of increased oxygen atom density occurring in an atmospheric wave channel. The speculative explanation offered by the researchers gained support from a new study.
Observations made by University of Helsinki researchers increased the validity of a speculative mechanism according to which a type of aurora borealis named 'dunes' is born. In the new study, photographs of the phenomenon taken by an international group of hobbyists in Finland, Norway and Scotland were compared to concurrent satellite data.
The rare type of aurora borealis was seen in the sky on 20 January 2016 and recorded in photos taken by ...
This overlay shows radio (orange) and infrared images of a giant molecular cloud called W49A, where new stars are being formed. A team of astronomers led by Chris DePree of Agnes Scott College used the National Science Foundation's Karl G. Jansky Very Large Array (VLA) to make new, high-resolution radio images of this cluster of still-forming, massive stars. W49A, 36,000 light-years from Earth, has been studied for many decades, and the new radio images revealed some tantalizing changes that have occurred since an earlier set of VLA observations in 1994 and 1995.
The ...