(Press-News.org) A team of University of Alberta researchers has discovered a way to use 3-D bioprinting technology to create custom-shaped cartilage for use in surgical procedures. The work aims to make it easier for surgeons to safely restore the features of skin cancer patients living with nasal cartilage defects after surgery.
The researchers used a specially designed hydrogel--a material similar to Jell-O--that could be mixed with cells harvested from a patient and then printed in a specific shape captured through 3-D imaging. Over a matter of weeks, the material is cultured in a lab to become functional cartilage.
"It takes a lifetime to make cartilage in an individual, while this method takes about four weeks. So you still expect that there will be some degree of maturity that it has to go through, especially when implanted in the body. But functionally it's able to do the things that cartilage does," said Adetola Adesida, a professor of surgery in the Faculty of Medicine & Dentistry.
"It has to have certain mechanical properties and it has to have strength. This meets those requirements with a material that (at the outset) is 92 per cent water," added Yaman Boluk, a professor in the Faculty of Engineering.
Adesida, Boluk and graduate student Xiaoyi Lan led the project to create the 3-D printed cartilage in hopes of providing a better solution for a clinical problem facing many patients with skin cancer.
Each year upwards of three million people in North America are diagnosed with non-melanoma skin cancer. Of those, 40 per cent will have lesions on their noses, with many requiring surgery to remove them. As part of the procedure, many patients may have cartilage removed, leaving facial disfiguration.
Traditionally, surgeons would take cartilage from one of the patient's ribs and reshape it to fit the needed size and shape for reconstructive surgery. But the procedure comes with complications.
"When the surgeons restructure the nose, it is straight. But when it adapts to its new environment, it goes through a period of remodelling where it warps, almost like the curvature of the rib," said Adesida. "Visually on the face, that's a problem.
"The other issue is that you're opening the rib compartment, which protects the lungs, just to restructure the nose. It's a very vital anatomical location. The patient could have a collapsed lung and has a much higher risk of dying," he added.
The researchers say their work is an example of both precision medicine and regenerative medicine. Lab-grown cartilage printed specifically for the patient can remove the risk of lung collapse, infection in the lungs and severe scarring at the site of a patient's ribs.
"This is to the benefit of the patient. They can go on the operating table, have a small biopsy taken from their nose in about 30 minutes, and from there we can build different shapes of cartilage specifically for them," said Adesida. "We can even bank the cells and use them later to build everything needed for the surgery. This is what this technology allows you to do."
The team is continuing its research and is now testing whether the lab-grown cartilage retains its properties after transplantation in animal models. The team hopes to move the work to a clinical trial within the next two to three years.
INFORMATION:
The research was supported by grants from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, Alberta Cancer Foundation, Canadian Foundation for Innovation, University Hospital Foundation, Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada and Edmonton Civic Employees Charitable Assistance Fund.
The study, "Bioprinting of human nasoseptal chondrocytes?laden collagen hydrogel for cartilage tissue engineering," was published in The FASEB Journal.
Metallacages prepared via coordination-driven self-assembly have received extensive attention because of their three-dimensional layout and cavity-cored nature. The construction of light-emitting materials employing metallacages as a platform has also gained significant interest due to their good modularity in photophysical properties, which bring emerging applications in fields as diverse as sensing, biomedicine, and catalysis.
However, the luminescence efficiency of conventional luminophores significantly decreases in the aggregate state because they encounter unfavorable aggregation-caused quenching (ACQ). Therefore, it was quite a challenge to fabricate light-emitting metallacages with high luminescence efficiency in various physical states.
In 2001, Tang's group ...
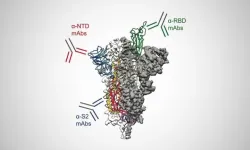
The most complete picture yet is coming into focus of how antibodies produced in people who effectively fight off SARS-CoV-2 work to neutralize the part of the virus responsible for causing infection. In the journal Science, researchers at The University of Texas at Austin describe the finding, which represents good news for designing the next generation of vaccines to protect against variants of the virus or future emerging coronaviruses.
Previous research focused on one group of antibodies that target the most obvious part of the coronavirus's spike protein, called the receptor-binding domain (RBD). Because the RBD is the part of the spike that attaches directly to human cells and enables the virus to infect them, ...
New York, NY (May 4, 2021) - A powerful, long-term study from WCS adds scientific backing for global calls for conserving 30 percent of the world's ocean. The studied no-take marine protected areas (MPAs) increased the growth of fish populations by 42 percent when fishing was unsustainable in surrounding areas, achieving the benefits of stable and high production of fish populations for fishers, while protecting threatened ecosystems.
The study recorded fish catches for 24-years across a dozen fish landing sites within two counties in Kenya, which allowed scientists to evaluate the long-term impacts of two different fisheries management methods. While one county ...
Harsh prison sentences for juvenile crimes do not reduce the probability of conviction for violent crimes as an adult, and actually increase the propensity for conviction of drug-related crimes, finds a new study by economists at UC Riverside and the University of Louisiana. Harsh juvenile sentences do reduce the likelihood of conviction for property crimes as an adult. But the increase in drug-related crimes cancels out any benefit harsh sentences might offer, researchers found.
"Juvenile incarceration is a double-edged sword which deters future property crimes but makes drug convictions more likely in adulthood. Thus, it's hard to make firm policy recommendations ...
Scientists believe a stomach-specific protein plays a major role in the progression of obesity, according to new research in Scientific Reports. The study co-authored by an Indiana University School of Medicine researcher, could help with development of therapeutics that would help individuals struggling with achieving and maintaining weight loss.
Researchers focused on Gastrokine-1 (GKN1) -- a protein produced exclusively and abundantly in the stomach. Previous research has suggested GKN1 is resistant to digestion, allowing it to pass into the intestine and interact with microbes in the gut.
In the Scientific Reports study, researchers show that inhibiting GKN1 produced significant differences in weight and levels of body fat in comparison to when the protein was expressed.
"While ...
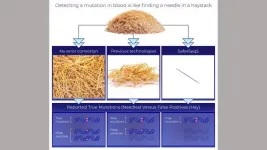
Next-generation gene sequencing (NGS) technologies --in which millions of DNA molecules are simultaneously but individually analyzed-- theoretically provides researchers and clinicians the ability to noninvasively identify mutations in the blood stream. Identifying such mutations enables earlier diagnosis of cancer and can inform treatment decisions. Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center researchers developed a new technology to overcome the inefficiencies and high error rates common among next-generation sequencing techniques that have previously limited their clinical application.
To correct for these sequencing errors, the research team from the Ludwig Center and Lustgarten Laboratory at the Johns Hopkins ...
ROCHESTER, Minn. -- A pair of Mayo Clinic studies shed light on something that is typically difficult to see with the eye: respiratory aerosols. Such aerosol particles of varying sizes are a common component of breath, and they are a typical mode of transmission for respiratory viruses like COVID-19 to spread to other people and surfaces.
Researchers who conduct exercise stress tests for heart patients at Mayo Clinic found that exercising at increasing levels of exertion increased the aerosol concentration in the surrounding room. Then also found that a high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) device effectively filtered out the aerosols and decreased the time needed to ...
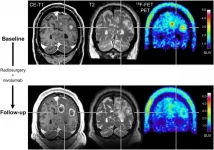
Reston, VA--For patients with brain metastases, amino acid positron emission tomography (PET) can provide valuable information about the effectiveness of state-of-the-art treatments. When treatment monitoring with contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is unclear, adding 18F-FET PET can help to accurately diagnose recurring brain metastases and reliably assess patient response. This research was published in The Journal of Nuclear Medicine.
Newer treatment options for patients with brain metastases--such as immune checkpoint inhibitors and targeted therapies--are effective, but can cause a variety of side effects. ...
The human immune system doesn't just protect our health, it reflects it. Each encounter with a potential disease-causing agent causes the body to produce specific immune agents -- proteins known as antibodies and T-cell receptors -- tailor-made to recognize and destroy the invader. Tasked with preventing re-infection, antibodies and T-cell receptors (TCR) from your previous encounters circulate throughout the body indefinitely, like a record of your personal medical history that you carry inside of you.
Clinical pathologist Ramy Arnaout, MD, DPhil, ...
WASHINGTON, DC -- A new case report, detailed in Annals of Emergency Medicine, is the first known case of a patient with VITT (vaccine-induced thrombotic thrombocytopenia) treated with a heparin alternative following the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) guidance.
An otherwise healthy female patient in her 40s came to the emergency department at UCHealth University of Colorado Hospital twelve days after receiving the Johnson & Johnson vaccine with a headache, dizziness, and vision changes. The patient was treated on April 13, 2021, the same day that the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) announced a pause in the administration of the Johnson & Johnson vaccine. CDC guidance recommended ...