(Press-News.org) Metallacages prepared via coordination-driven self-assembly have received extensive attention because of their three-dimensional layout and cavity-cored nature. The construction of light-emitting materials employing metallacages as a platform has also gained significant interest due to their good modularity in photophysical properties, which bring emerging applications in fields as diverse as sensing, biomedicine, and catalysis.
However, the luminescence efficiency of conventional luminophores significantly decreases in the aggregate state because they encounter unfavorable aggregation-caused quenching (ACQ). Therefore, it was quite a challenge to fabricate light-emitting metallacages with high luminescence efficiency in various physical states.
In 2001, Tang's group discovered aggregation-induced emission (AIE) phenomenon that some nonluminous or weakly emissive materials in molecular state are highly emissive in aggregate state. The underlying mechanism accounting for the AIE effect was disclosed as restriction of intramolecular movements. So far, AIE has been a promising research field for more than 20 years, and brings a new opportunity to construct light-emitting metallacages with high luminescence efficiency.
In a recent review published in the Beijing-based National Science Review, scientists at the Shanghai Jiao Tong University in Shanghai, China, and at the University of Utah in Salt Lake City, United States, the latest advances in light-emitting self-assembled metallacages are summarized. The scientists presented the strategies for the rational design of light-emitting metallacages and highlighted the structural chemistry of AIE-active metallacages that display AIE, a novel photophysical phenomenon, as well as their emerging applications as chemical sensors, functional emissive materials, light-harvesting systems, and theranostic agents. These scientists likewise outline the potential future challenges in the development of light-emitting metallacages.
"The well-defined, highly tunable metallacage structures render them particularly attractive for investigating the properties of luminophores, as well as for inducing novel photophysical characters that enable widespread applications," they state in an article titled "Light-emitting self-assembled metallacages."
Studies on light-emitting metallacages stemmed from the use of rigid organic molecules as the building blocks for coordination-driven self-assembly. "Many of these molecules include large conjugated systems and are inherently photo-physically active, thus endowing the resulting SCCs with light-emitting properties," they added. "To date, researchers have employed luminophores as donor or acceptor building blocks, or encapsulated guest molecules inside the cavity of the metallacages."
"The almost limitless structural versatility of metallacages provides modularity over the photophysical profiles of the incorporated luminophore. These benefits are exemplified by studies on metallacages comprising luminophores with aggregation-induced emission (AIE) character," the researchers stated.
The first attempt to explore the AIE behavior of self-assembled metallacages in 2015 has resulted in a new class of AIE-active metallacages with high luminescence efficiency in both dilute solutions and in the aggregated states, thereby bridging the gap between AIE and ACQ. These two photophysical phenomena are often considered to be diametrically opposed.
"Initial studies in this area focused on examining their "turn-on" luminescence in both solutions and aggregated states and their levels of responsiveness towards different solvents," they stated. Advances of AIE-active metallacages based on tetraphenylethylene (TPE) and its derivatives (Table 1) have promoted investigations of factors that influence their emission properties and inspired applications utilizing this unique photophysical behavior. "Notably, combining metallacage chemistry with AIE has led to the development of AIE-active metallacages displaying favorable photophysical properties such as high luminescence efficiency and good modularity and having impressive relevance to a wide variety of areas such as sensing, energy conversion, and the development of theranostic agents," they stated.
"The use of AIEgens with properties such as multiphoton absorption, red/near-infrared emission, enhanced solubility, and biocompatibility -- that is, properties more desirable than those of the extensively studied based on TPE -- is expected to result in the development of supramolecular luminophores with broader potentials," the authors predicted. "Overall, with the rapid advances of both coordination-driven self-assembly and luminophores with favorable photophysical properties such as AIE, it is expected that research on light-emitting self-assembled metallacages will continue to flourish."
INFORMATION:
This research received funding from the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai.
See the article:
Jun Zhao†, Zhixuan Zhou†, Guangfeng Li, Peter J Stang*, Xuzhou Yan*
Light-emitting self-assembled metallacages
Natl Sci Rev: nwab045.
https://doi.org/10.1093/nsr/nwab045
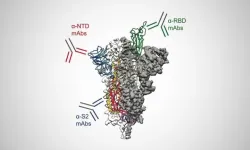
The most complete picture yet is coming into focus of how antibodies produced in people who effectively fight off SARS-CoV-2 work to neutralize the part of the virus responsible for causing infection. In the journal Science, researchers at The University of Texas at Austin describe the finding, which represents good news for designing the next generation of vaccines to protect against variants of the virus or future emerging coronaviruses.
Previous research focused on one group of antibodies that target the most obvious part of the coronavirus's spike protein, called the receptor-binding domain (RBD). Because the RBD is the part of the spike that attaches directly to human cells and enables the virus to infect them, ...
New York, NY (May 4, 2021) - A powerful, long-term study from WCS adds scientific backing for global calls for conserving 30 percent of the world's ocean. The studied no-take marine protected areas (MPAs) increased the growth of fish populations by 42 percent when fishing was unsustainable in surrounding areas, achieving the benefits of stable and high production of fish populations for fishers, while protecting threatened ecosystems.
The study recorded fish catches for 24-years across a dozen fish landing sites within two counties in Kenya, which allowed scientists to evaluate the long-term impacts of two different fisheries management methods. While one county ...
Harsh prison sentences for juvenile crimes do not reduce the probability of conviction for violent crimes as an adult, and actually increase the propensity for conviction of drug-related crimes, finds a new study by economists at UC Riverside and the University of Louisiana. Harsh juvenile sentences do reduce the likelihood of conviction for property crimes as an adult. But the increase in drug-related crimes cancels out any benefit harsh sentences might offer, researchers found.
"Juvenile incarceration is a double-edged sword which deters future property crimes but makes drug convictions more likely in adulthood. Thus, it's hard to make firm policy recommendations ...
Scientists believe a stomach-specific protein plays a major role in the progression of obesity, according to new research in Scientific Reports. The study co-authored by an Indiana University School of Medicine researcher, could help with development of therapeutics that would help individuals struggling with achieving and maintaining weight loss.
Researchers focused on Gastrokine-1 (GKN1) -- a protein produced exclusively and abundantly in the stomach. Previous research has suggested GKN1 is resistant to digestion, allowing it to pass into the intestine and interact with microbes in the gut.
In the Scientific Reports study, researchers show that inhibiting GKN1 produced significant differences in weight and levels of body fat in comparison to when the protein was expressed.
"While ...
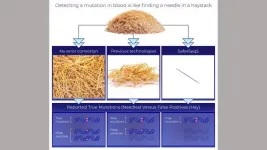
Next-generation gene sequencing (NGS) technologies --in which millions of DNA molecules are simultaneously but individually analyzed-- theoretically provides researchers and clinicians the ability to noninvasively identify mutations in the blood stream. Identifying such mutations enables earlier diagnosis of cancer and can inform treatment decisions. Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center researchers developed a new technology to overcome the inefficiencies and high error rates common among next-generation sequencing techniques that have previously limited their clinical application.
To correct for these sequencing errors, the research team from the Ludwig Center and Lustgarten Laboratory at the Johns Hopkins ...
ROCHESTER, Minn. -- A pair of Mayo Clinic studies shed light on something that is typically difficult to see with the eye: respiratory aerosols. Such aerosol particles of varying sizes are a common component of breath, and they are a typical mode of transmission for respiratory viruses like COVID-19 to spread to other people and surfaces.
Researchers who conduct exercise stress tests for heart patients at Mayo Clinic found that exercising at increasing levels of exertion increased the aerosol concentration in the surrounding room. Then also found that a high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) device effectively filtered out the aerosols and decreased the time needed to ...
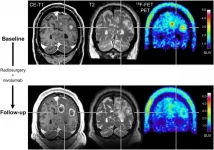
Reston, VA--For patients with brain metastases, amino acid positron emission tomography (PET) can provide valuable information about the effectiveness of state-of-the-art treatments. When treatment monitoring with contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is unclear, adding 18F-FET PET can help to accurately diagnose recurring brain metastases and reliably assess patient response. This research was published in The Journal of Nuclear Medicine.
Newer treatment options for patients with brain metastases--such as immune checkpoint inhibitors and targeted therapies--are effective, but can cause a variety of side effects. ...
The human immune system doesn't just protect our health, it reflects it. Each encounter with a potential disease-causing agent causes the body to produce specific immune agents -- proteins known as antibodies and T-cell receptors -- tailor-made to recognize and destroy the invader. Tasked with preventing re-infection, antibodies and T-cell receptors (TCR) from your previous encounters circulate throughout the body indefinitely, like a record of your personal medical history that you carry inside of you.
Clinical pathologist Ramy Arnaout, MD, DPhil, ...
WASHINGTON, DC -- A new case report, detailed in Annals of Emergency Medicine, is the first known case of a patient with VITT (vaccine-induced thrombotic thrombocytopenia) treated with a heparin alternative following the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) guidance.
An otherwise healthy female patient in her 40s came to the emergency department at UCHealth University of Colorado Hospital twelve days after receiving the Johnson & Johnson vaccine with a headache, dizziness, and vision changes. The patient was treated on April 13, 2021, the same day that the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) announced a pause in the administration of the Johnson & Johnson vaccine. CDC guidance recommended ...
You know that raw overwhelm people have been reporting after months of a pandemic, compounded by economic issues and social unrest? Does fatigue and compulsive social media scrolling strike a familiar chord?
Those brittle feelings offer us a glimpse into what regular life can be like for individuals with sensory processing sensitivity (SPS), a biological trait possessed by roughly a third of the population. In a world of constant information overload and stress, it's a characteristic that can result in a variety of behaviors, from emotional outbursts to withdrawal, overwhelm and procrastination.
"Behaviorally, we observe it as being more careful and cautious when approaching new things," said Bianca Acevedo, a researcher ...