The ants, bees and wasps of Canada, Alaska and Greenland - a checklist of 9250 species
2021-05-05
(Press-News.org) Knowing what species live in which parts of the world is critical to many fields of study, such as conservation biology and environmental monitoring. This is also how we can identify present or potential invasive and non-native pest species. Furthermore, summarizing what species are known to inhabit a given area is essential for the discovery of new species that have not yet been known to science.
For less well-studied groups and regions, distributional species checklists are often not available. Therefore, a series of such checklists is being published in the open-access, peer-reviewed Journal of Hymenoptera Research, in order to address the issue for a group of organisms that, despite its size and diversity, is still poorly known: the insect order Hymenoptera, which includes ants, bees and wasps. The surveyed area spreads across northern North America, which comprises Canada, Alaska (U.S.) and Greenland (Denmark), and occupies about 9.3% of the world's total land mass.
The last distributional survey of Hymenoptera in North America was published in 1979, where about 6000 described species were recorded from Canada and 600 from Alaska. The current survey lists 8933 species in Canada and 1513 in Alaska, marking an increase of 49% and 152%, respectively. A total of 9250 described species are recorded from northern North America. Considering that there are approximately 154,000 described species of Hymenoptera, northern North America has about 6% of the current world total.
Highlights of the series will include updated distributions of over 900 species of bees, which will provide valuable insight into native pollinators at a time when honey bees are in decline. Nearly 230 species of ants and over 100 species of vespid wasps (hornets and yellow jackets) are recorded, including pest species such as the widespread pharaoh ant and the newly invasive Asian giant hornet in British Columbia.
By far, the majority of species of Hymenoptera found in northern North America and the world are parasitoids, which develop on or in other invertebrate hosts and are therefore of great interest to the biological control of pests. Of the 9250 species recorded, more than three-quarters (over 7150 species) are parasitoids. These distributional lists provide essential baseline information required prior to undertaking studies to introduce biological control agents of invasive pests that may have escaped their native, natural enemies when they arrived in North America.
The topical collection "Checklists of the Hymenoptera of Canada, Alaska and Greenland" is to contain a total of eleven papers, where the introduction and the first two checklists: of sawflies (758 species) and one of the groups of "microhymenoptera" (the chalcidoid parasitic wasps) (1246 species) have just been published.The other checklists are to follow over the next several years. The associated data are also being uploaded to the Global Biodiversity Information Facility (GBIF), allowing for periodic updates over time.
When complete, this will be the largest species checklist for any group of organisms in northern North America. Considering that it is estimated that we currently have documented less than half of the species of Hymenoptera present in northern North America, there is still a great amount of work to do on this fascinating group of insects.
INFORMATION:
Original sources:
Bennett AMR (2021a) Checklists of the Hymenoptera of Canada, Alaska and Greenland - Introduction. Journal of Hymenoptera Research 82: 1-19. https://doi.org/10.3897/jhr.82.60054
Bennett AMR (2021b) Checklist of the Hymenoptera of Canada, Alaska and Greenland. Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada. Checklist dataset https://doi.org/10.5886/4piso5 [accessed via GBIF.org: 12 March 2021].
Goulet H, Bennett AMR (2021) Checklist of the sawflies (Hymenoptera) of Canada, Alaska and Greenland. Journal of Hymenoptera Research 82: 21-67. https://doi.org/10.3897/jhr.82.60057
Huber JT, Bennett AMR, Gibson GAP, Zhang YM, Darling DC (2021) Checklist of Chalcidoidea and Mymarommatoidea (Hymenoptera) of Canada, Alaska and Greenland. Journal of Hymenoptera Research 82: 69-138. https://doi.org/10.3897/jhr.82.60058
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-05
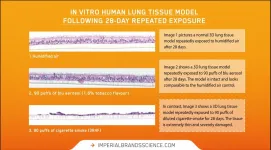
5 May 2021, Bristol - In one of the most advanced applications of in-vitro 3D human lung models in vape research to date, a new peer-reviewed Imperial Brands study shows that, unlike combustible cigarette smoke, blu aerosol had little to no impact on numerous toxicological endpoints under the conditions of test using laboratory models.
Published in the journal Current Research in Toxicology, the experiments compared the toxicological responses of an in vitro 3D lung model (MucilAir™ from Epithelix) after repeated exposure to undiluted whole blu aerosol (1.6% tobacco flavour) or diluted whole cigarette smoke (3R4F Kentucky Reference) over a 28-day period.
After repeatedly exposing the model to ...
2021-05-05
Announcing a new article publication for BIO Integration journal. In this editorial the authors Hui Liu and Juan Chen from Shanxi Eye Hospital, Taiyuan, China discuss biophotonics in photomedicine.
As a cross-disciplinary field, biophotonics is a natural platform for innovation, e.g. researchers have taken advantages of the recently developed nanostructures in Photomedicine to optimize imaging signals and improve drug delivery efficiency. Active investment in healthcare also contributes to the quick clinical transitions of biophotonic innovations.
However, to genuinely and successfully improve people's lives, many gaps have to be bridged. Horizontally, ...
2021-05-05
After reviewing a database of gene mutations in children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD), a team of Medical University of South Carolina (MUSC) researchers decided to study a specific gene mutation that likely caused ASD in a girl. They demonstrated that the mutation was damaging to the gene, and that female, but not male, mice lacking a working copy of the gene also showed ASD-associated symptoms. Better understanding the interplay between genetics and sex in ASD could set the stage for developing sex-specific treatments for autism.
The MUSC team was led by Christopher Cowan, Ph.D., the William E. Murray SmartState Endowed Chair in Neuroscience and chair of the Department of Neuroscience, and Ahlem Assali, Ph.D., research assistant ...
2021-05-05
A recent study from the University of Helsinki monitors the breakthrough progresses in the development of microneedles for immunotherapy and discusses the challenges regarding their production. Researchers suggest using microneedles for immunotherapy due to the high abundance of immune cells under the skin. The aim is to vaccinate or treat different diseases, such as cancer and autoimmune disorders, with minimal invasiveness and side effects.
"Our study addresses the recent achievements in the development of microneedles for immunotherapy of hard-to-treat and chronic diseases to achieve the highest efficiency with minimal side effects," says ...
2021-05-05
There is currently no consensus on what quality end-of-life care for children with cancer looks like, or how to measure and deliver it; however, investigators recently assembled an expert panel to help fill this void. In a study published early online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society, the panel endorsed 16 measures that cover different aspects of care that are important for children with cancer and their families.
"Measuring the quality of the care delivered is an essential part of ensuring high quality end-of-life care ...
2021-05-05
Coded messages in invisible ink sound like something only found in espionage books, but in real life, they can have important security purposes. Yet, they can be cracked if their encryption is predictable. Now, researchers reporting in ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces have printed complexly encoded data with normal ink and a carbon nanoparticle-based invisible ink, requiring both UV light and a computer that has been taught the code to reveal the correct messages.
Even as electronic records advance, paper is still a common way to preserve data. Invisible ink can hide classified economic, commercial or military ...
2021-05-05
Marine scientists are calling on the EU to adopt a comprehensive plan to protect dolphins and porpoises from fisheries bycatch in European waters.
A team of conservation experts, including Newcastle University's Professor Per Berggren, highlight limitations in EU's efforts to address and mitigate bycatch. The scientists argue this infective response is a result of scattered and complicated management responsibility for the conservation of dolphins and porpoises in Europe, and from a lack of quantitative conservation objectives, including biological reference points ...
2021-05-05
Reflexes protect our bodies - for example when we pull our hand back from a hot stove. These protective mechanisms could also be useful for robots. In this interview, Prof. Sami Haddadin and Johannes Kühn of the Munich School of Robotics and Machine Intelligence (MSRM) of the Technical University of Munich (TUM) explain why giving test subjects a "slap on the hand" could lay the foundations for the robots of the future.
In your paper, published in Scientific Reports, you describe an experimental setup where people were actually slapped on the hand - to study their reflexes....
Kühn: Yes, you can put it that way. For our study, in cooperation with Imperial College London, the test ...
2021-05-05
Clothing, from tank tops to parkas, helps people adapt to temperatures outdoors. But you can only put on or take off so much of it, and fluctuations in weather can render what you are wearing entirely inadequate. In a new study in ACS' Nano Letters, researchers describe a high-tech alternative: a reversible textile they designed to trap warmth in the cold and reflect it during hot weather, all while generating small amounts of electricity.
Previous attempts to develop such sophisticated textiles for outdoor use have generally focused on either capturing thermal radiation or dispersing it. To integrate the two, Qiang Li, Min Qiu and colleagues made a ...
2021-05-05
More research is urgently needed into the impact that attending suicide events is having on paramedics and other first responders, a researcher at the University of Otago, New Zealand, says.
PhD student Renan Lyra, a psychologist by training, says a significant proportion of police officers, firefighters and paramedics will attend at least one suicide event in their careers, but there has been little research into the impact this has on their personal and professional lives and on their own suicide risk.
Mr Lyra has reviewed 25 research papers on the impact attending a suicide event has on those ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] The ants, bees and wasps of Canada, Alaska and Greenland - a checklist of 9250 species