An uncrackable combination of invisible ink and artificial intelligence
2021-05-05
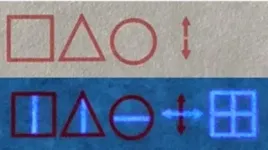
(Press-News.org) Coded messages in invisible ink sound like something only found in espionage books, but in real life, they can have important security purposes. Yet, they can be cracked if their encryption is predictable. Now, researchers reporting in ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces have printed complexly encoded data with normal ink and a carbon nanoparticle-based invisible ink, requiring both UV light and a computer that has been taught the code to reveal the correct messages.
Even as electronic records advance, paper is still a common way to preserve data. Invisible ink can hide classified economic, commercial or military information from prying eyes, but many popular inks contain toxic compounds or can be seen with predictable methods, such as light, heat or chemicals. Carbon nanoparticles, which have low toxicity, can be essentially invisible under ambient lighting but can create vibrant images when exposed to ultraviolet (UV) light - a modern take on invisible ink. In addition, advances in artificial intelligence (AI) models -- made by networks of processing algorithms that learn how to handle complex information -- can ensure that messages are only decipherable on properly trained computers. So, Weiwei Zhao, Kang Li, Jie Xu and colleagues wanted to train an AI model to identify and decrypt symbols printed in a fluorescent carbon nanoparticle ink, revealing hidden messages when exposed to UV light.
The researchers made carbon nanoparticles from citric acid and cysteine, which they diluted with water to create an invisible ink that appeared blue when exposed to UV light. The team loaded the solution into an ink cartridge and printed a series of simple symbols onto paper with an inkjet printer. Then, they taught an AI model, composed of multiple algorithms, to recognize symbols illuminated by UV light and decode them using a special codebook. Finally, they tested the AI model's ability to decode messages printed using a combination of both regular red ink and the UV fluorescent ink. With 100% accuracy, the AI model read the regular ink symbols as "STOP", but when a UV light was shown on the writing, the invisible ink illustrated the desired message "BEGIN". Because these algorithms can notice minute modifications in symbols, this approach has the potential to encrypt messages securely using hundreds of different unpredictable symbols, the researchers say.
INFORMATION:
The authors acknowledge funding from the Shenzhen Peacock Team Plan and the Bureau of Industry and Information Technology of Shenzhen through the Graphene Manufacturing Innovation Center (201901161514).
The abstract that accompanies this paper can be viewed here.
The American Chemical Society (ACS) is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. ACS' mission is to advance the broader chemistry enterprise and its practitioners for the benefit of Earth and all its people. The Society is a global leader in promoting excellence in science education and providing access to chemistry-related information and research through its multiple research solutions, peer-reviewed journals, scientific conferences, eBooks and weekly news periodical Chemical & Engineering News. ACS journals are among the most cited, most trusted and most read within the scientific literature; however, ACS itself does not conduct chemical research. As a leader in scientific information solutions, its CAS division partners with global innovators to accelerate breakthroughs by curating, connecting and analyzing the world's scientific knowledge. ACS' main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
To automatically receive news releases from the American Chemical Society, contact newsroom@acs.org.
Follow us: Twitter | Facebook
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-05
Marine scientists are calling on the EU to adopt a comprehensive plan to protect dolphins and porpoises from fisheries bycatch in European waters.
A team of conservation experts, including Newcastle University's Professor Per Berggren, highlight limitations in EU's efforts to address and mitigate bycatch. The scientists argue this infective response is a result of scattered and complicated management responsibility for the conservation of dolphins and porpoises in Europe, and from a lack of quantitative conservation objectives, including biological reference points ...
2021-05-05
Reflexes protect our bodies - for example when we pull our hand back from a hot stove. These protective mechanisms could also be useful for robots. In this interview, Prof. Sami Haddadin and Johannes Kühn of the Munich School of Robotics and Machine Intelligence (MSRM) of the Technical University of Munich (TUM) explain why giving test subjects a "slap on the hand" could lay the foundations for the robots of the future.
In your paper, published in Scientific Reports, you describe an experimental setup where people were actually slapped on the hand - to study their reflexes....
Kühn: Yes, you can put it that way. For our study, in cooperation with Imperial College London, the test ...
2021-05-05
Clothing, from tank tops to parkas, helps people adapt to temperatures outdoors. But you can only put on or take off so much of it, and fluctuations in weather can render what you are wearing entirely inadequate. In a new study in ACS' Nano Letters, researchers describe a high-tech alternative: a reversible textile they designed to trap warmth in the cold and reflect it during hot weather, all while generating small amounts of electricity.
Previous attempts to develop such sophisticated textiles for outdoor use have generally focused on either capturing thermal radiation or dispersing it. To integrate the two, Qiang Li, Min Qiu and colleagues made a ...
2021-05-05
More research is urgently needed into the impact that attending suicide events is having on paramedics and other first responders, a researcher at the University of Otago, New Zealand, says.
PhD student Renan Lyra, a psychologist by training, says a significant proportion of police officers, firefighters and paramedics will attend at least one suicide event in their careers, but there has been little research into the impact this has on their personal and professional lives and on their own suicide risk.
Mr Lyra has reviewed 25 research papers on the impact attending a suicide event has on those ...
2021-05-05
A curiously yellow star has caused astrophysicists to reevaluate what's possible within our universe.
Led by Northwestern University, the international team used NASA's Hubble Space Telescope to examine the massive star two-and-a-half years before it exploded into a supernova. At the end of their lives, cool, yellow stars are typically shrouded in hydrogen, which conceals the star's hot, blue interior. But this yellow star, located 35 million lightyears from Earth in the Virgo galaxy cluster, was mysteriously lacking this crucial hydrogen layer at the time of its explosion.
"We haven't seen this scenario before," said Northwestern's ...
2021-05-05
CATONSVILLE, MD, May 4, 2021 - Paid video streaming services on your television, smart phone or other devices are increasingly replacing traditional video entertainment platforms of cable, satellite and broadcast TV. The growth of these services, known in the industry as over-the-top (OTT) media services, may be accompanied by a rise in pirated content, particularly where access to those services may be restricted, a group of researchers has found.
The researchers studied the effects of the Netflix - one of the leading global companies in paid video streaming - and its growth in 40 Asian countries. They also studied one country where access to Netflix was restricted, which is where ...
2021-05-05
Carnegie Mellon University's He Lab is focusing on noninvasive neuroengineering solutions that not only provide diagnostic techniques, but also innovative treatment options. Their latest research has demonstrated that noninvasive neuromodulation via low-intensity ultrasound can have cell-type selectivity in manipulating neurons.
Parkinson's Disease, epilepsy and insomnia are just a few of the neurological disorders that use neuromodulation treatment techniques today. Neuromodulation delivers controlled physical energy to the nervous system to treat and improve patients' quality of life. Current neuromodulation approaches, while effective, bring both drawbacks and limitations.
"Deep ...
2021-05-05
When light hits certain molecules, it dislodges electrons that then move from one location to another, creating areas of positive and negative charge. This "charge transfer" is highly important in many areas of chemistry, in biological processes like photosynthesis and in technologies like semiconductor devices and solar cells.
Even though theories have been developed to explain and predict how charge transfer works, they have been validated only indirectly because of the difficulty of observing how a molecule's structure responds to charge movements with the ...
2021-05-05
Researchers from the UCLA School of Dentistry have discovered a key molecule that allows cancer stem cells to bypass the body's natural immune defenses, spurring the growth and spread of head and neck squamous cell cancers. Their study, conducted in mice, also demonstrates that inhibiting this molecule derails cancer progression and helps eliminate these stem cells.
Published in the journal Cell Stem Cell, the findings could help pave the way for more effective targeted treatments for this highly invasive type of cancer, which is characterized by frequent resistance to therapies, rapid metastasis and a ...
2021-05-05
A hot topic symposia session during thePediatric Academic Societies (PAS) 2021 Virtual Meeting will provide a forum for policy and physician experts to predict major child health legislative and policy changes which will occur over the next four years.
The outcome of the presidential election has significant impact on the child health policy agenda. The goal of the session is to prepare academic pediatricians so they can be ideally positioned to promote or impede specific policies which are not evidenced-based to improve child health.
"The subject matter ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] An uncrackable combination of invisible ink and artificial intelligence






