(Press-News.org) A curiously yellow star has caused astrophysicists to reevaluate what's possible within our universe.
Led by Northwestern University, the international team used NASA's Hubble Space Telescope to examine the massive star two-and-a-half years before it exploded into a supernova. At the end of their lives, cool, yellow stars are typically shrouded in hydrogen, which conceals the star's hot, blue interior. But this yellow star, located 35 million lightyears from Earth in the Virgo galaxy cluster, was mysteriously lacking this crucial hydrogen layer at the time of its explosion.
"We haven't seen this scenario before," said Northwestern's Charles Kilpatrick, who led the study. "If a star explodes without hydrogen, it should be extremely blue -- really, really hot. It's almost impossible for a star to be this cool without having hydrogen in its outer layer. We looked at every single stellar model that could explain a star like this, and every single model requires that the star had hydrogen, which, from its supernova, we know it did not. It stretches what's physically possible."
The team describes the peculiar star and its resulting supernova in a new study, which was published today (May 5) in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. In the paper, the researchers hypothesize that, in the years preceding its death, the star might have shed its hydrogen layer or lost it to a nearby companion star.
Kilpatrick is a postdoctoral fellow at Northwestern's Center for Interdisciplinary Exploration and Research in Astrophysics (CIERA) and member of the Young Supernova Experiment, which uses the Pan-STARSS telescope at Haleakalā, Hawaii, to catch supernovae right after they explode.
Catching a star before it explodes
After the Young Supernova Experiment spotted supernova 2019yvr in the relatively nearby spiral galaxy NGC 4666, the team used deep space images captured by NASA's Hubble Space Telescope, which fortunately already observed this section of the sky.
"What massive stars do right before they explode is a big unsolved mystery," Kilpatrick said. "It's rare to see this kind of star right before it explodes into a supernova."
The Hubble images showed the source of the supernova, a massive star imaged just a couple years before the explosion. Although the supernova itself appeared completely normal, its source -- or progenitor star -- was anything but.
"When it exploded, it seemed like a very normal hydrogen-free supernova," Kilpatrick said. "There was nothing outstanding about this. But the progenitor star didn't match what we know about this type of supernova."
Direct evidence of violent death
Several months after the explosion, however, Kilpatrick and his team discovered a clue. As ejecta from the star's final explosion traveled through its environment, it collided with a large mass of hydrogen. This led the team to hypothesize that the progenitor star might have expelled the hydrogen within a few years before its death.
"Astronomers have suspected that stars undergo violent eruptions or death throes in the years before we see supernovae," Kilpatrick said. "This star's discovery provides some of the most direct evidence ever found that stars experience catastrophic eruptions, which cause them to lose mass before an explosion. If the star was having these eruptions, then it likely expelled its hydrogen several decades before it exploded."
In the new study, Kilpatrick's team also presents another possibility: A less massive companion star might have stripped away hydrogen from the supernova's progenitor star. The team, however, will not be able to search for the companion star until after the supernova's brightness fades, which could take up to 10 years.
"Unlike it's normal behavior right after it exploded, the hydrogen interaction revealed it's kind of this oddball supernova," Kilpatrick said. "But it's exceptional that we were able to find its progenitor star in Hubble data. In four or five years, I think we will be able to learn more about what happened."
INFORMATION:
The study, "A cool and inflated progenitor candidate for the type Ib supernova 2019 yvr at 2.6 years before explosion," was supported by NASA (award numbers GO-15691 and AR-16136), the National Science Foundation (award numbers AST-1909796, AST-1944985), the Canadian Institute for Advanced Research, the VILLUM Foundation and the Australian Research Council Centre of Excellence. In addition to the Hubble Space Telescope, the researchers used instruments at the Gemini Observatory, Keck Observatory, Las Cumbres Observatory, Spitzer Space Telescope and the Swope Telescope.
CATONSVILLE, MD, May 4, 2021 - Paid video streaming services on your television, smart phone or other devices are increasingly replacing traditional video entertainment platforms of cable, satellite and broadcast TV. The growth of these services, known in the industry as over-the-top (OTT) media services, may be accompanied by a rise in pirated content, particularly where access to those services may be restricted, a group of researchers has found.
The researchers studied the effects of the Netflix - one of the leading global companies in paid video streaming - and its growth in 40 Asian countries. They also studied one country where access to Netflix was restricted, which is where ...
Carnegie Mellon University's He Lab is focusing on noninvasive neuroengineering solutions that not only provide diagnostic techniques, but also innovative treatment options. Their latest research has demonstrated that noninvasive neuromodulation via low-intensity ultrasound can have cell-type selectivity in manipulating neurons.
Parkinson's Disease, epilepsy and insomnia are just a few of the neurological disorders that use neuromodulation treatment techniques today. Neuromodulation delivers controlled physical energy to the nervous system to treat and improve patients' quality of life. Current neuromodulation approaches, while effective, bring both drawbacks and limitations.
"Deep ...
When light hits certain molecules, it dislodges electrons that then move from one location to another, creating areas of positive and negative charge. This "charge transfer" is highly important in many areas of chemistry, in biological processes like photosynthesis and in technologies like semiconductor devices and solar cells.
Even though theories have been developed to explain and predict how charge transfer works, they have been validated only indirectly because of the difficulty of observing how a molecule's structure responds to charge movements with the ...
Researchers from the UCLA School of Dentistry have discovered a key molecule that allows cancer stem cells to bypass the body's natural immune defenses, spurring the growth and spread of head and neck squamous cell cancers. Their study, conducted in mice, also demonstrates that inhibiting this molecule derails cancer progression and helps eliminate these stem cells.
Published in the journal Cell Stem Cell, the findings could help pave the way for more effective targeted treatments for this highly invasive type of cancer, which is characterized by frequent resistance to therapies, rapid metastasis and a ...
A hot topic symposia session during thePediatric Academic Societies (PAS) 2021 Virtual Meeting will provide a forum for policy and physician experts to predict major child health legislative and policy changes which will occur over the next four years.
The outcome of the presidential election has significant impact on the child health policy agenda. The goal of the session is to prepare academic pediatricians so they can be ideally positioned to promote or impede specific policies which are not evidenced-based to improve child health.
"The subject matter ...
The emergence and spread of new forms of resistance remains a concern that urgently demand new antibiotics. Transcription is a vital process in bacterial cell, where genetic information in DNA is transcribed to RNA for the translation of proteins that perform cellular function. Hence, transcription serves as a promising target to develop new antibiotics because inhibition the transcription process should effectively kill the bacteria. Bacterial RNA Polymerase, the core enzyme for transcription, must load the DNA and separate the double-stranded DNA to single stranded DNA to read the genetic information to initiate transcription. This process is also called DNA melting and is facilitated ...
ORLANDO, May 5, 2021 - New research indicates that the legendary Sargasso Sea, which includes part of the Bermuda Triangle and has long featured in fiction as a place where ships go derelict, may actually be an important nursery habitat for young sea turtles.
In a study led by a University of Central Florida researcher and published today in the journal Proceedings of the Royal Society B, researchers presented evidence of baby green sea turtles arriving at the Sargasso Sea after entering the ocean off the east coast of Florida.
The study was the first time that green sea turtles have been tracked during their early "lost years," which is defined ...
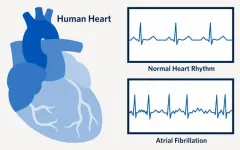
A UBC Okanagan researcher is urging people to learn and then heed the symptoms of Atrial Fibrillation (AF). Especially women.
Dr. Ryan Wilson, a post-doctoral fellow in the School of Nursing, says AF is the most commonly diagnosed arrhythmia (irregular heartbeat) in the world. Despite that, he says many people do not understand the pre-diagnosis symptoms and tend to ignore them. In fact, 77 per cent of the women in his most recent study had experienced symptoms for more than a year before receiving a diagnosis.
While working in a hospital emergency department (ED), Dr. Wilson noted that many patients came in with AF symptoms that included, but were not limited to, shortness of breath, feeling of butterflies (fluttering) in the chest, dizziness or general fatigue. Many women ...
Seeing through smog and fog. Mapping out a person's blood vessels while monitoring heart rate at the same time--without touching the person's skin. Seeing through silicon wafers to inspect the quality and composition of electronic boards. These are just some of the capabilities of a new infrared imager developed by a team of researchers led by electrical engineers at the University of California San Diego.
The imager detects a part of the infrared spectrum called shortwave infrared light (wavelengths from 1000 to 1400 nanometers), which is right outside of the visible spectrum (400 to 700 nanometers). Shortwave infrared imaging is not to be confused with thermal imaging, which detects much longer infrared wavelengths ...
A new Tel Aviv University study has revealed, for the first time, that bats know the speed of sound from birth. In order to prove this, the researchers raised bats from the time of their birth in a helium-enriched environment in which the speed of sound is higher than normal. They found that unlike humans, who map the world in units of distance, bats map the world in units of time. What this means is that the bat perceives an insect as being at a distance of nine milliseconds, and not one and a half meters, as was thought until now.
The Study was published in PNAS.
In order to determine ...