INFORMATION:
Katie Hall's work was funded by the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council - South West Biosciences Doctoral Training Partnership.
The study was carried out as part of a wider collaboration with the South Devon Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty.
The paper, published in the journal Ecology and Evolution, is entitled: "Onset of morning activity in bumblebee foragers under natural low light conditions."
Large bumblebees start work earlier
2021-05-05
(Press-News.org) Larger bumblebees are more likely to go out foraging in the low light of dawn, new research shows.
University of Exeter scientists used RFID - similar technology to contactless card payments - to monitor when bumblebees of different sizes left and returned to their nest.
The biggest bees, and some of the most experienced foragers (measured by number of trips out), were the most likely to leave in low light.
Bumblebee vision is poor in low light, so flying at dawn or dusk raises the risk of getting lost or being eaten by a predator.
However, the bees benefit from extra foraging time and fewer competitors for pollen in the early morning.
"Larger bumblebees have bigger eyes than their smaller-sized nest mates and many other bees, and can therefore see better in dim light," said lead author Katie Hall, of the University of Exeter.
"We might expect all bumblebee foragers to leave the colony to forage as soon as there is enough light to allow them to fly.
"In fact, colonies seem to regulate the start of foraging.
"There is a balance of risks and rewards in low light - and most bees wait for higher light levels when they can see better and fly faster, with less risk from predators or getting lost and running out of energy.
"Our finding that more experienced bees are more likely to fly in lower light suggests that knowledge of food locations helps them navigate safely."
The study tracked the bees' behaviour over five days during warm periods of the flowering season.
Only a small proportion of foragers left the colony at dawn when light levels were below 10 lux.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
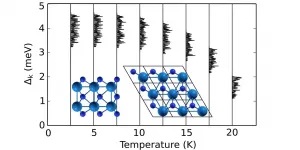
Superconductivity, high critical temperature found in 2D semimetal W2N3
2021-05-05
Superconductivity in two-dimensional (2D) systems has attracted much attention in recent years, both because of its relevance to our understanding of fundamental physics and because of potential technological applications in nanoscale devices such as quantum interferometers, superconducting transistors and superconducting qubits.
The critical temperature (Tc), or the temperature under which a material acts as a superconductor, is an essential concern. For most materials, it is between absolute zero and 10 Kelvin, that is, between -273 Celsius and -263 Celsius, too cold to be of any practical use. Focus has then been on finding materials with a higher Tc.
While researchers have discovered materials ...
Mysterious hydrogen-free supernova sheds light on stars' violent death throes
2021-05-05
A curiously yellow pre-supernova star has caused astrophysicists to re-evaluate what's possible at the deaths of our Universe's most massive stars. The team describe the peculiar star and its resulting supernova in a new study published today in Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.
At the end of their lives, cool, yellow stars are typically shrouded in hydrogen, which conceals the star's hot, blue interior. But this yellow star, located 35 million light years from Earth in the Virgo galaxy cluster, was mysteriously lacking this crucial hydrogen layer at the time of its explosion.
"We haven't seen this scenario before," said Charles Kilpatrick, postdoctoral fellow at Northwestern ...
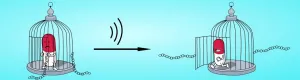
Release of drugs from a supramolecular cage
2021-05-05
How can a highly effective drug be transported to the precise location in the body where it is needed? In the journal Angewandte Chemie, chemists at Heinrich Heine University Düsseldorf (HHU) together with colleagues in Aachen present a solution using a molecular cage that opens through ultrasonification.
Supramolecular chemistry involves the organization of molecules into larger, higher-order structures. When suitable building blocks are chosen, these systems 'self-assemble' from their individual components.
Certain supramolecular compounds are well suited for 'host-guest chemistry'. In such cases, a host structure encloses a guest molecule and can shield, protect and transport it away from its environment. This is a specialist field of Dr. Bernd M. Schmidt and ...
Bees thrive where it's hot and dry: A unique biodiversity hotspot located in North America
2021-05-05
The United States-Mexico border traverses through large expanses of unspoiled land in North America, including a newly discovered worldwide hotspot of bee diversity. Concentrated in 16 km2 of protected Chihuahuan Desert are more than 470 bee species, a remarkable 14% of the known United States bee fauna.
This globally unmatched concentration of bee species is reported by Dr. Robert Minckley of the University of Rochester and William Radke of the United States Fish and Wildlife Service in the open-access, peer-reviewed Journal of Hymenoptera Research.
Scientists studying native U.S. bees have long recognized that the Sonoran and Chihuahuan deserts of North America, home to species with interesting life histories, have high bee biodiversity. Exactly how many species ...
Tübingen study raises hope for effective malaria vaccine
2021-05-05
Sanaria® PfSPZ-CVac" is a live vaccine consisting of infectious Plasmodium falciparum (Pf) malaria parasites that are injected into the subject at the same time as they receive an antimalarial drug. The parasites quickly enter the liver where they develop and multiply for 6 days, and then emerge into the blood As soon as the parasites leave the liver, the drug kills them immediately. Thus, the immune system of the vaccinated subject is primed against many parasite proteins and becomes highly effective at killing malaria parasites in the liver to block infection and prevent disease.
"With this study, we have reached a new important milestone in the development of an effective malaria vaccine. With only three immunizations over four weeks, we achieved very good protection ...
Coalitions and conflict among men
2021-05-05
Daniel Redhead, from the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology, and Chris von Rueden, from the University of Richmond, published a new study that describes coalition formation among men in Tsimané Amerindians living in Amazonian Bolivia, over a period of eight years. In two Tsimané communities, the authors describe the inter-personal conflicts that tend to arise between men, and the individual attributes and existing relationships that predict the coalitional support men receive in the event of conflicts.
Conflicts that arise between men concern disputes over access to forest for slash-and-burn horticulture, as well as accusations of theft, laziness, negligence, ...
Examination of an Estonian patient helped discover a new form of muscular dystrophy
2021-05-05
In about a quarter of patients with hereditary diseases, the cause of the disease remains unclear even after extensive genetic testing. One reason is that we still do not know enough about the function of many genes. Of the 30,000 known genes, just a little more than 4,000 have been found to be associated with hereditary diseases.
At the Department of Clinical Genetics of the University of Tartu Institute of Clinical Medicine, under the leadership of Professor Katrin Õunap, patients with hereditary diseases of unclear cause have been studied in various research projects since 2016. In collaboration with the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard, these patients have undergone extensive genome-wide sequencing analyses at the level of the exome (the sequence of all genes), ...
The ants, bees and wasps of Canada, Alaska and Greenland - a checklist of 9250 species
2021-05-05
Knowing what species live in which parts of the world is critical to many fields of study, such as conservation biology and environmental monitoring. This is also how we can identify present or potential invasive and non-native pest species. Furthermore, summarizing what species are known to inhabit a given area is essential for the discovery of new species that have not yet been known to science.
For less well-studied groups and regions, distributional species checklists are often not available. Therefore, a series of such checklists is being published in the open-access, peer-reviewed Journal of Hymenoptera Research, in order ...
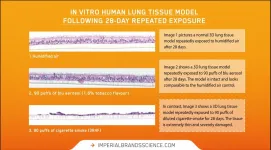
Repeat vape aerosol exposure causes minimal damage to lung tissue compared to cigarettes
2021-05-05
5 May 2021, Bristol - In one of the most advanced applications of in-vitro 3D human lung models in vape research to date, a new peer-reviewed Imperial Brands study shows that, unlike combustible cigarette smoke, blu aerosol had little to no impact on numerous toxicological endpoints under the conditions of test using laboratory models.
Published in the journal Current Research in Toxicology, the experiments compared the toxicological responses of an in vitro 3D lung model (MucilAir™ from Epithelix) after repeated exposure to undiluted whole blu aerosol (1.6% tobacco flavour) or diluted whole cigarette smoke (3R4F Kentucky Reference) over a 28-day period.
After repeatedly exposing the model to ...
Biophotonics in photomedicine
2021-05-05
Announcing a new article publication for BIO Integration journal. In this editorial the authors Hui Liu and Juan Chen from Shanxi Eye Hospital, Taiyuan, China discuss biophotonics in photomedicine.
As a cross-disciplinary field, biophotonics is a natural platform for innovation, e.g. researchers have taken advantages of the recently developed nanostructures in Photomedicine to optimize imaging signals and improve drug delivery efficiency. Active investment in healthcare also contributes to the quick clinical transitions of biophotonic innovations.
However, to genuinely and successfully improve people's lives, many gaps have to be bridged. Horizontally, ...