INFORMATION:
Lancaster University team's 'eggstraordinary' paper revealed at major conference
The world's first-ever 'academic paper which is not a paper' is due to be presented by a Lancaster University research team at the premier international conference on human-computer interaction.
2021-05-06
(Press-News.org) The world's first-ever 'academic paper which is not a paper' is due to be presented by a Lancaster University research team at the premier international conference on human-computer interaction.
Dr Joseph Lindley, a researcher at Lancaster University's ImaginationLancaster design-led research laboratory, Dr Miriam Sturdee, from the University's School of Computing and Communications, Senior Research Associate Dr David Green and Research Associate Hayley Alter have been invited to take part in the 2021 ACM CHI Virtual Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems in May.
Using the innovative 'Gather Town' online video-calling and conferencing platform, they have experimented in setting up a conference paper as an interactive but virtual space.
The unique part of this type of video-calling is the ability for multiple people to hold separate conversations in parallel, and to walk in and out of those conversations just as easily as they would in a real room.
"So, with this, you can actually walk 'in' to the paper. Each 'room' is a page or section within the paper where you can read the text, but also talk to other conference delegates about it," explains Dr Lindley, a lecturer in design research.
Quirky egg-themed graphics (eggs are used as they are a symbol of new life) give the 'page-spaces' character as different destinations, while the menu page is inspired by Piet Mondrian's map-like painting, 'Broadway Boogie Woogie'.
"The beauty with this approach is that you don't have to read from start to finish, you can experience it in any order you like," Dr Lindley explains.
Instead of hearing a formal presentation, participants will be asked to don their choice of avatar before being invited into the two-dimensional spaces to meet, chat and 'explore' the egg.
"This is the world's first paper that is not an actual paper," says Dr Lindley. "It's a video conferencing platform that hosts 20 interconnected 'rooms' with a 'poster' in each one. People can mill about and discuss each poster and, by leaving additional comments they can effectively help to keep 'writing' the paper as they go.
"This prototype is about collapsing barriers between video conferencing, research conferences, and publication traditions. It's about exploring creative ways of using technology and bringing them together."
"It's looking at how the research landscape will evolve. The pandemic is making people look at that again."
"We are now in a state of comprehensive flux as 'new normals' emerge, begin to solidify, and may evolve into an--as yet undetermined--futures.
"This 'not paper' is a facet and exploration of that flux as it relates to publication and conference culture, video conferencing systems, and how we both conduct, and share, research."
Step inside the paper if you dare...
https://gather.town/app/EpkqTfKctHPjRS0m/the_egg (NOTE: Please use a Chrome or Firefox based browser).
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Better healthcare guidance needed for trans people
2021-05-06
Clinical practice guidelines for dealing with the physical and mental health of transgender people highlight the current lack of a solid research base which must be improved, according to a new study published in the journal BMJ Open.
A team of researchers from Anglia Ruskin University (ARU) and King's College London searched world literature for all international clinical practice guidelines on the healthcare needs of gender minority and trans people.
Results showed that higher quality guidelines tended to focus mainly on HIV, and most others were on transition-related interventions. There were noticeable gaps in the topics of guidelines, with none addressing ...
Greater effectiveness in the treatment of arrhythmia with radio frequency energy and catheterization
2021-05-06
An article published in International Journal of Hyperthermia proposes a more effective protocol for the treatment of cardiac arrhythmias when applying radiofrequency energy at the site of the arrhythmia by catheterization. The research results from the final year project (TFG) on the bachelor's degree in Biomedical Engineering by Sergi Coderch Navarro, supervised by Ana González Suárez and Oscar Camara, researchers with the PhySense group of the BCN MedTech Research Unit at the UPF Department of Information and Communication Technologies (DTIC). Sergi Coderch Navarro defended his TFG in July 2019 and was a runner-up in the 2019 Gemma Rossell i Romero Awards. Currently, Ana González Suárez is a postdoctoral ...
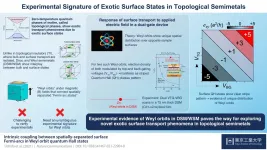
Unusual semimetal shows evidence of unique surface conduction states
2021-05-06
Scientists at Tokyo Institute of Technology experimentally verify the existence of exotic surface conduction states in topological semimetals (TSMs), materials that lie at the boundary between conductors and insulators, by performing voltage scans of these surface states on a thin film sample of a TSM. The findings can pave the way for future study and exploitation of such conduction states in realizing novel, quantum transport phenomena.
All of us are probably familiar with the idea of conductors and insulators. But what would you call a material that can conduct on the surface but insulate on the inside? Physicists call it a "topological insulator" (TI), a term that highlights the geometric aspect of its strange conduction behavior. Even stranger ...
Researchers unveil roadmap to expand NY solar energy, meet green goals
2021-05-06
ITHACA, N.Y. - Solar-power developers need to explore using lower-quality agricultural land for solar energy, incentivize dual-use (combined agriculture and solar) options, avoid concentrated solar development and engage communities early to achieve New York's green energy goals, according to forthcoming Cornell University research.
"As farmland is generally flat and cleared, agricultural land will be the prime target for future solar energy development," said Max Zhang, professor in the Sibley School of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering. "Good farmland, however, is not ideal."
Zhang is senior author of "Strategic Land Use Analysis for Solar Energy Development in New York State," which will publish in August 2021 in Renewable Energy.
Under New York state's 2019 Climate ...
The natural brightness of the night sky
2021-05-06
A recent study analyses data collect4d at 44 of the darkest places in the world, including the Canary Island Observatories, to develop the first complete reference method to measure the natural brightness of the night sky using low-cost photometers.
Of the 44 photometers in the survey, the Roque de los Muchachos Observatory (Garafía, La Palma, Canary Islands) stands out at the darkest of all the skies analysed.
The night sky is not completely dark; even in the remotest places there is a glow in the sky produced by natural components, both terrestrial and extraterrestrial, ...
Just a few atoms thick: New functional materials developed
2021-05-06
They are 50,000 times thinner than a human hair, and just a few atoms thick: two-dimensional materials are the thinnest substances it is possible to make today. They have completely new properties and are regarded as the next major step in modern semiconductor technology. In the future they could be used instead of silicon in computer chips, light-emitting diodes and solar cells. Until now, the development of new two-dimensional materials has been limited to structures with layers of rigid chemical bonds in two spatial directions - like a sheet of paper in a stack. Now for the first time, a research team from the ...
Researchers find association between financial strain due to COVID-19 and depression
2021-05-06
Philadelphia, May 6, 2021--Researchers have found an independent association between COVID-19-related income loss and financial strain and depression, according to the latest study from the COVID-19 Resilience Project, run by the Lifespan Brain Institute (LiBI) of Children's Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) and Penn Medicine. This association was found in two separate cohorts - one primarily in the United States and one in Israel - and the depressive symptoms worsened over time in participants who were hit financially, above and beyond pandemic-related anxiety. The findings were published today in the Journal of Affective Disorders.
"This study is an important first step in understanding the unique ...
ATTR amyloidosis during the COVID-19 Pandemic: Insights from a global medical roundtablp
2021-05-06
(Boston)-- The global spread of COVID-19 has raised serious concern for patients with chronic disease. A correlation has been identified between the severity of COVID-19 and a patient's preexisting comorbidities. Although COVID-19 primarily involves the respiratory system, dysfunction in multiple organ systems is common, particularly in the cardiovascular, gastrointestinal, immune, renal, and nervous systems. Patients with transthyretin amyloidosis (ATTR) (a disease caused by an abnormal misfolded protein that causes buildup of amyloid deposits in the heart, peripheral nervous system including the autonomic nervous system, or other organs) represent a population particularly vulnerable to COVID-19 morbidity due to the multisystem nature of ATTR amyloidosis.
Early ...
Cell cytoskeleton as target for new active agents
2021-05-06
Through a unique combination of computer simulations and laboratory experiments, researchers at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI have discovered new binding sites for active agents - against cancer, for example - on a vital protein of the cell cytoskeleton. Eleven of the sites hadn't been known before. The study appears today in the journal Angewandte Chemie International Edition.
The protein tubulin is an essential building block of the so-called cell cytoskeleton. In cells, tubulin molecules arrange themselves into tube-like structures, the microtubule filaments. These give cells their shape, aid in transporting proteins and larger cellular components, and play a crucial role in cell division.
Thus tubulin performs diverse functions in the ...
2D materials offer unique stretching properties
2021-05-06
Like most materials, an elastic band gets thinner when it is stretched. But some materials behave in the opposite way -- they grow thicker when stretched and thinner when compressed. These counterintuitive substances, known as auxetic materials, tend to have a high resistance to shear or fracture and are used in applications such as medical implants and sensors. But typically, this auxetic effect is only seen when the material is distorted in one particular direction.
Now, Minglei Sun and Udo Schwingenschlo?gl have predicted that a group of carbon-based materials, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Study finds more parents saying ‘No’ to vitamin K, putting babies’ brains at risk
Scientists develop new gut health measure that tracks disease
Rice gene discovery could cut fertiliser use while protecting yields
Jumping ‘DNA parasites’ linked to early stages of tumour formation
Ultra-sensitive CAR T cells provide potential strategy to treat solid tumors
Early Neanderthal-Human interbreeding was strongly sex biased
North American bird declines are widespread and accelerating in agricultural hotspots
Researchers recommend strategies for improved genetic privacy legislation
How birds achieve sweet success
More sensitive cell therapy may be a HIT against solid cancers
Scientists map how aging reshapes cells across the entire mammalian body
Hotspots of accelerated bird decline linked to agricultural activity
How ancient attraction shaped the human genome
NJIT faculty named Senior Members of the National Academy of Inventors
App aids substance use recovery in vulnerable populations
College students nationwide received lifesaving education on sudden cardiac death
Oak Ridge National Laboratory launches the Next-Generation Data Centers Institute
Improved short-term sea level change predictions with better AI training
UAlbany researchers develop new laser technique to test mRNA-based therapeutics
New water-treatment system removes nitrogen, phosphorus from farm tile drainage
Major Canadian study finds strong link between cannabis, anxiety and depression
New discovery of younger Ediacaran biota
Lymphovenous bypass: Potential surgical treatment for Alzheimer's disease?
When safety starts with a text message
CSIC develops an antibody that protects immune system cells in vitro from a dangerous hospital-acquired bacterium
New study challenges assumptions behind Africa’s Green Revolution efforts and calls for farmer-centered development models
Immune cells link lactation to long-lasting health
Evolution: Ancient mosquitoes developed a taste for early hominins
Pickleball players’ reported use of protective eyewear
Changes in organ donation after circulatory death in the US
[Press-News.org] Lancaster University team's 'eggstraordinary' paper revealed at major conferenceThe world's first-ever 'academic paper which is not a paper' is due to be presented by a Lancaster University research team at the premier international conference on human-computer interaction.