Unusual semimetal shows evidence of unique surface conduction states
2021-05-06
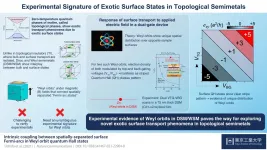
(Press-News.org) Scientists at Tokyo Institute of Technology experimentally verify the existence of exotic surface conduction states in topological semimetals (TSMs), materials that lie at the boundary between conductors and insulators, by performing voltage scans of these surface states on a thin film sample of a TSM. The findings can pave the way for future study and exploitation of such conduction states in realizing novel, quantum transport phenomena.
All of us are probably familiar with the idea of conductors and insulators. But what would you call a material that can conduct on the surface but insulate on the inside? Physicists call it a "topological insulator" (TI), a term that highlights the geometric aspect of its strange conduction behavior. Even stranger than TIs are "topological semimetals" (TSMs)-- bizarre materials that straddle the boundary between metals (conductors) and insulators.
While TIs have found practical applications thanks to their unusual properties, notably in advanced optoelectronic devices, TSMs are still largely a curiosity among material scientists. "In TIs, the surface conduction states can be isolated from the bulk insulating states, whereas in typical TSMs, such as Dirac and Weyl semimetals, the bulk and surface states touch at points called 'Weyl nodes,' leading to an interplay between them," explains Associate Professor Masaki Uchida from Tokyo Institute of Technology, Japan, whose research is focused on topological materials.
According to theoretical predictions, an interesting consequence of such an interplay is the formation of a coupled pair of electronic "Weyl orbits" under a magnetic field on opposite surfaces of a TSM that can lead to a novel 2D quantum transport. However, the experimental verification of Weyl orbits has, so far, remained challenging due to the seeming lack of a unique signature. Now, a new study by a team of scientists from Japan, led by Dr. Uchida, might change all that.
Published in Nature Communications, the study focuses on the unique spatial distribution of the Weyl orbits. Specifically, scientists carried out a mapping of Weyl orbit "Quantum Hall" (QH) states under the influence of electric voltages applied on the top and bottom surface of a TSM sample comprising a 75-nm-thick film of (Cd1-xZnx) 3 As2. "The key observation to distinguish the Weyl orbit from a TI-like orbit is the response of the surface transport to electric fields applied in a dual-gate device configuration," says Dr. Uchida.
Scientists began by studying the magnetic field dependence of film resistance at zero gating voltages at a temperature of 3K (?270°C) and ensured that the film was thick enough to let the Weyl orbits form. Initially, bulk transport dominated the conduction due to a high electron density. However, as scientists depleted the electrons by applying gating voltages, surface transport and its evolution into QH states became more prominent.
Next, the scientists studied the influence of gating voltage scans on these QH states in presence of a strong magnetic field and observed a peculiar striped pattern in the mapped states due to a modulation in their electron density, suggesting the presence of a coupled Weyl orbit pair!
The research team is thrilled by this finding. An excited Dr. Uchida concludes, "Our work revealing the role of unique distribution of Weyl orbits in quantum transport can open doors to finding various exotic surface transport phenomena in TSMs and controlling them via external fields and interface engineering."
The hunt for these novel quantum phenomena is on, with new and exciting discoveries just be around the corner!
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-06
ITHACA, N.Y. - Solar-power developers need to explore using lower-quality agricultural land for solar energy, incentivize dual-use (combined agriculture and solar) options, avoid concentrated solar development and engage communities early to achieve New York's green energy goals, according to forthcoming Cornell University research.
"As farmland is generally flat and cleared, agricultural land will be the prime target for future solar energy development," said Max Zhang, professor in the Sibley School of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering. "Good farmland, however, is not ideal."
Zhang is senior author of "Strategic Land Use Analysis for Solar Energy Development in New York State," which will publish in August 2021 in Renewable Energy.
Under New York state's 2019 Climate ...
2021-05-06
A recent study analyses data collect4d at 44 of the darkest places in the world, including the Canary Island Observatories, to develop the first complete reference method to measure the natural brightness of the night sky using low-cost photometers.
Of the 44 photometers in the survey, the Roque de los Muchachos Observatory (Garafía, La Palma, Canary Islands) stands out at the darkest of all the skies analysed.
The night sky is not completely dark; even in the remotest places there is a glow in the sky produced by natural components, both terrestrial and extraterrestrial, ...
2021-05-06
They are 50,000 times thinner than a human hair, and just a few atoms thick: two-dimensional materials are the thinnest substances it is possible to make today. They have completely new properties and are regarded as the next major step in modern semiconductor technology. In the future they could be used instead of silicon in computer chips, light-emitting diodes and solar cells. Until now, the development of new two-dimensional materials has been limited to structures with layers of rigid chemical bonds in two spatial directions - like a sheet of paper in a stack. Now for the first time, a research team from the ...
2021-05-06
Philadelphia, May 6, 2021--Researchers have found an independent association between COVID-19-related income loss and financial strain and depression, according to the latest study from the COVID-19 Resilience Project, run by the Lifespan Brain Institute (LiBI) of Children's Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) and Penn Medicine. This association was found in two separate cohorts - one primarily in the United States and one in Israel - and the depressive symptoms worsened over time in participants who were hit financially, above and beyond pandemic-related anxiety. The findings were published today in the Journal of Affective Disorders.
"This study is an important first step in understanding the unique ...
2021-05-06
(Boston)-- The global spread of COVID-19 has raised serious concern for patients with chronic disease. A correlation has been identified between the severity of COVID-19 and a patient's preexisting comorbidities. Although COVID-19 primarily involves the respiratory system, dysfunction in multiple organ systems is common, particularly in the cardiovascular, gastrointestinal, immune, renal, and nervous systems. Patients with transthyretin amyloidosis (ATTR) (a disease caused by an abnormal misfolded protein that causes buildup of amyloid deposits in the heart, peripheral nervous system including the autonomic nervous system, or other organs) represent a population particularly vulnerable to COVID-19 morbidity due to the multisystem nature of ATTR amyloidosis.
Early ...
2021-05-06
Through a unique combination of computer simulations and laboratory experiments, researchers at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI have discovered new binding sites for active agents - against cancer, for example - on a vital protein of the cell cytoskeleton. Eleven of the sites hadn't been known before. The study appears today in the journal Angewandte Chemie International Edition.
The protein tubulin is an essential building block of the so-called cell cytoskeleton. In cells, tubulin molecules arrange themselves into tube-like structures, the microtubule filaments. These give cells their shape, aid in transporting proteins and larger cellular components, and play a crucial role in cell division.
Thus tubulin performs diverse functions in the ...
2021-05-06
Like most materials, an elastic band gets thinner when it is stretched. But some materials behave in the opposite way -- they grow thicker when stretched and thinner when compressed. These counterintuitive substances, known as auxetic materials, tend to have a high resistance to shear or fracture and are used in applications such as medical implants and sensors. But typically, this auxetic effect is only seen when the material is distorted in one particular direction.
Now, Minglei Sun and Udo Schwingenschlo?gl have predicted that a group of carbon-based materials, ...
2021-05-06
Epithelial cells form the covering of most internal and external surfaces of the human body. This protective layer acts as a defense against invaders - including bacteria, viruses, environmental toxins, pollutants and allergens. If the skin and mucosal barriers are damaged or leaky, foreign agents such as bacteria can enter into the tissue and cause local, often chronic inflammation. This has both direct and indirect consequences.
Chronic diseases due to defective epithelial barriers
Cezmi Akdis, Director of the Swiss Institute of Allergy and Asthma Research ...
2021-05-06
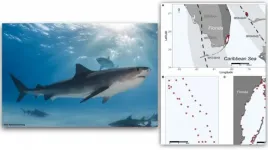
MIAMI--A new study led by scientists at the University of Miami (UM) Rosenstiel School of Marine and Atmospheric Science tracked large sharks in Miami and The Bahamas to understand how these migratory animals respond to major storms, like hurricanes.
The researchers analyzed acoustic tag data from tiger sharks (Galeocerdo cuvier), bull sharks (Carcharhinus leucas), nurse sharks (Ginglymostoma cirratum), and great hammerheads (Sphyrna mokarran) before, during, and after Hurricane Matthew in 2016 and Hurricane Irma in 2017. They found that they behaved differently by species and location.
For example, in response to ...
2021-05-06
May 6, 2021 - With mass shootings and other seemingly meaningless acts of violence in the headlines all too frequently, strategies to assess the risk and reduce the potential for violent acts are sorely needed. The fourth in a series of five columns devoted to therapeutic risk management of violence - focusing on a method called chain analysis to identify and target pathways leading to violent thoughts and behaviors - appears in the May issue of the Journal of Psychiatric Practice. The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
An innovative model for therapeutic risk management of the potentially violent patient has been developed by Hal Wortzel, MD, and colleagues of ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Unusual semimetal shows evidence of unique surface conduction states