(Press-News.org) May 6, 2021 - With mass shootings and other seemingly meaningless acts of violence in the headlines all too frequently, strategies to assess the risk and reduce the potential for violent acts are sorely needed. The fourth in a series of five columns devoted to therapeutic risk management of violence - focusing on a method called chain analysis to identify and target pathways leading to violent thoughts and behaviors - appears in the May issue of the Journal of Psychiatric Practice. The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
An innovative model for therapeutic risk management of the potentially violent patient has been developed by Hal Wortzel, MD, and colleagues of the Rocky Mountain Mental Illness Research, Education and Clinical Center (MIRECC) at the VA Rocky Mountain Regional Medical Center (RMRMC), Aurora, Colo. The authors note that "Adding chain analysis builds on the structural assessment of violence risk discussed in our previous columns, and can be crucial to guiding effective, individually focused interventions to prevent future other-directed violence."
Chain analysis targets pathways leading to violence
In a previous series, Dr. Wortzel and colleagues shared their approach to assessing the risk of self-directed violence (SDV) in potentially suicidal patients. The authors emphasized the benefits of a patient-centered model that supports the patient's overall treatment and the therapeutic alliance with mental health professionals.
In a new series, the therapeutic risk management approach is applied to patients at risk for other-directed violence (ODV) - borrowing from the SDV risk assessment skills that many clinicians already have. For the next two months, the series can be freely accessed on the journal website. The three previously published articles have focused on:
Clinical risk assessment starts with a clinical interview to assess the risk of ODV, including the circumstances in which clinicians have a legal duty to warn and protect. Assessing violence risk can form an integral part of providing competent and compassionate mental health care: a trusting therapeutic relationship facilitates the ability to elicit details pertaining to violence risk, as well as to institute therapies that might mitigate risk for future violent behaviors.
Structured screening or assessment tools to augment clinical assessment of ODV. Tools include the Violence Risk Screening-10 (V-RISK-10), appropriate for use in psychiatric inpatient and community care; and the Violence Screening and Assessment of Needs (VIO-SCAN), specifically designed for use with military Veterans.
Risk stratification, illustrated by the case scenario of a Veteran with posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and polysubstance use disorder who has made angry and violent threats. Risk of ODV can be assessed in terms of both the severity and temporality (acute versus chronic) of the risk - helping to guide critical decisions as to patient management and the duty to warn.
Published yesterday, the fourth column in the series describes chain analysis as a key tool in therapeutic management of ODV. Using the same case scenario involving a Veteran with PTSD, the authors demonstrate how to apply chain analysis to identify pathways of reinforcement that can cause violent ideas and behaviors to persist. In this case, the Veteran was able to recognize that experiencing sadness and hurt caused him to feel vulnerable and out of control in a difficult personal situation - while aggressive behavior and violent threats led to a sense of feeling in control. The use of chain analysis led to identification of interventional strategies to disrupt the chain - and ultimately reduce the risk for violence.
The fifth and final part of the series, scheduled for publication in July 2021, will discuss safety planning as a critical component of therapeutic risk management of violence. The authors will provide recommendations for using this innovative strategy to therapeutically mitigate the risk of ODV.
Dr. Wortzel and colleagues hope their series will provide mental health professionals with a "cogent process" for conducting violence risk assessments in a way that fulfills legal and ethical responsibilities, protects the safety of patients and potential victims, and supports the patient's overall mental health care.
Click here to read "Therapeutic Risk Management for Violence: Chain Analysis of Other-Directed Violent Ideation and Behavior."
DOI: 10.1097/PRA.0000000000000552
INFORMATION:
About Journal of Psychiatric Practice
Journal of Psychiatric Practice®, a peer reviewed journal, publishes reports on new research, clinically applicable reviews, articles on treatment advances, and case studies, with the goal of providing practical and informative guidance for clinicians. Mental health professionals will want access to this journal¬--for sharpening their clinical skills, discovering the best in treatment, and navigating this rapidly changing field. John M. Oldham, MD, is the editor in chief and past president of the American Psychiatric Association.
About Wolters Kluwer
Wolters Kluwer (WKL) is a global leader in professional information, software solutions, and services for the clinicians, nurses, accountants, lawyers, and tax, finance, audit, risk, compliance, and regulatory sectors. We help our customers make critical decisions every day by providing expert solutions that combine deep domain knowledge with advanced technology and services.
Wolters Kluwer reported 2020 annual revenues of €4.6 billion. The group serves customers in over 180 countries, maintains operations in over 40 countries, and employs approximately 19,200 people worldwide. The company is headquartered in Alphen aan den Rijn, the Netherlands.
Wolters Kluwer provides trusted clinical technology and evidence-based solutions that engage clinicians, patients, researchers and students in effective decision-making and outcomes across healthcare. We support clinical effectiveness, learning and research, clinical surveillance and compliance, as well as data solutions. For more information about our solutions, visit https://www.wolterskluwer.com/en/health and follow us on LinkedIn and Twitter @WKHealth.
For more information, visit http://www.wolterskluwer.com, follow us on Twitter, Facebook, LinkedIn, and YouTube.
A program that provides ongoing support to patients with painful conditions and complex medication regimens may also help them avoid using potentially risky opioid pain medications, or reduce the amount they use, a new study finds.
The study looked at people with a wide range of autoimmune disorders, including arthritis and psoriasis, who were taking an injected biologic medication to treat their symptoms and prevent painful flare-ups. Such treatment involves frequent self-injections on a strict schedule, special disposal of used supplies and often high out-of-pocket costs - which ...
DURHAM, N.C. - A study designed to enroll an equal number of Black and white men with advanced prostate cancer confirms key findings that have been evident in retrospective analyses and suggest potential new avenues for treating Black patients who disproportionately die of the disease.
Researchers at Duke Cancer Institute enrolled 50 Black and 50 white men with advanced prostate cancer to test whether there were outcome differences on treatment with the hormone therapy abiraterone acetate plus the steroid prednisone. In retrospective data reviews, the Duke researchers had previously found racial differences in PSA responses among advanced prostate cancer patients.
Publishing online in the journal Cancer, the researchers ...
"The overarching idea of this research project is to influence different biological processes at the cellular level (i.e., wound healing, brain synapses or nervous system responses) by developing timely engineering applications", explains 4D-BIOMAP's lead researcher, Daniel García González from the UC3M's Department of Continuum Mechanics and Structural Analysis.
The so-called magneto-active polymers are revolutionising the fields of solid mechanics and materials science. These composites consist of a polymeric matrix (i.e., an elastomer) that contains magnetic particles (i.e., iron) that react mechanically ...
The study says differences in children's brains, which affect their sensitivity to pressure and rewards, and differences in the way they process information, make it more likely they will admit to crimes they didn't commit when incentivized to do so.
These developmental vulnerabilities mean solicitors and barristers should get extra support to help them better support young people deciding whether to admit guilt.
Dr Rebecca Helm, from the University of Exeter, who led the research, published in the Journal of Law and Society, said: "The criminal justice system relies almost exclusively on the autonomy of defendants, rather than accuracy, when justifying convictions ...
DURHAM, N.H.-- As climate change continues to trigger the rise in temperature, increase drier conditions and shift precipitation patterns, adapting to new conditions will be critical for the long-term survival of most species. Researchers at the University of New Hampshire found that to live in hotter more desert-like surroundings, and exist without water, there is more than one genetic mechanism allowing animals to adapt. This is important not only for their survival but may also provide important biomedical groundwork to develop gene therapies to treat human dehydration related illnesses, like kidney disease.
"To reference a familiar phrase, it tells us that there is more than one way to bake a ...
Reducing net greenhouse gas emissions to zero as soon as possible and achieving "carbon neutrality" is the key to addressing global warming and climate change. The ocean is the largest active carbon pool on the planet, with huge potential to help achieve negative emissions by serving as a carbon sink.
Recently, researchers found that adding a small amount of aluminum to achieve concentrations in the 10x nanomolar (nM) range can increase the net fixation of CO2 by marine diatoms and decrease their decomposition, thus improving the ocean's ability to absorb CO2 and sequester ...
Students struggling academically benefited most when schools around the world transitioned from classroom teaching to online learning in response to the COVID-19 pandemic, and the switch also didn't negatively impact higher achievers.
A new study has analysed the impact of online learning during the pandemic by crunching data at three middle schools in China, which administered different educational practices for about 7 weeks during the country's Covid-19 lockdown.
Online learning was shown to have a positive impact on overall student performance when compared to not receiving any support from school during lockdown, and the best results were achieved by ...
Australia's 'black summer' of bushfires was depicted on the front pages of the world's media with images of wildlife and habitat destruction, caused by climate change, while in Australia the toll on ordinary people remained the visual front-page focus.
QUT visual communication researcher Dr TJ Thomson compared the front-page bushfire imagery of the Sydney Morning Herald over three months from November 10, 2019 to January 31 2020 with 119 front pages from international media from the start of January, when the world sat up and took notice, to January 31.
"The international sample of front pages included the Americas and Europe (about 90 per cent) representing Australia's 'black summer'. Asia represented around 7 per cent of the international ...
Transitioning from fossil fuels to a clean hydrogen economy will require cheaper and more efficient ways to use renewable sources of electricity to break water into hydrogen and oxygen.
But a key step in that process, known as the oxygen evolution reaction or OER, has proven to be a bottleneck. Today it's only about 75% efficient, and the precious metal catalysts used to accelerate the reaction, like platinum and iridium, are rare and expensive.
Now an international team led by scientists at Stanford University and the Department of Energy's SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory has developed a ...
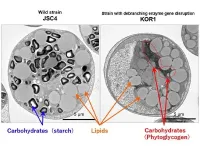
A cross-institutional collaboration has developed a technique to repartition carbon resources from carbohydrates to lipids in microalgae. It is hoped that this method can be applied to biofuel production. This discovery was the result of a collaboration between a research group at Kobe University's Engineering Biology Research Center consisting of Project Assistant Professor KATO Yuichi and Professor HASUNUMA Tomohisa et al., and Senior Researcher SATOH Katsuya et al. at the Takasaki Advanced Radiation Research Institute of the Quantum Beam Science Research Directorate ...