Microalgae biofuels: Changing carbohydrates into lipids
2021-05-06
(Press-News.org) A cross-institutional collaboration has developed a technique to repartition carbon resources from carbohydrates to lipids in microalgae. It is hoped that this method can be applied to biofuel production. This discovery was the result of a collaboration between a research group at Kobe University's Engineering Biology Research Center consisting of Project Assistant Professor KATO Yuichi and Professor HASUNUMA Tomohisa et al., and Senior Researcher SATOH Katsuya et al. at the Takasaki Advanced Radiation Research Institute of the Quantum Beam Science Research Directorate (National institutes for Quantum and Radiological Science and Technology).
These research results were published on April 9, 2021 in the international academic journal Communications Biology.
Main Points
Microalgae are highly capable of producing lipids by fixing atmospheric CO2 via photosynthesis, making them promising candidates for biofuel production.
In light/dark conditions (i.e. day and night), the majority of microalgae's carbon resources obtained from CO2 are accumulated as carbohydrates (starch). This makes it difficult to get microalgae to produce lipids.
The researchers used ion beam mutagenesis to develop a strain of microalgae that can produce large amounts of lipids even under light/dark conditions.
In this microalgae mutant, the starch debranching enzyme gene was disrupted, causing it to produce phytoglycogen, which is easily broken down. The carbon resources were then repartitioned from carbohydrate production to lipid production.
Research Background
Biofuels are renewable resources that have received much attention in the move towards creating more sustainable societies. Microalgae are photosynthetic organisms that are highly capable of producing lipids from carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, making them promising candidates for biofuel production. However, a Kobe University research group consisting of Project Assistant Professor Kato Yuichi and Professor Hasunuma Tomohisa et al. discovered that the majority of carbon resources were diverted to starch production instead of lipid production under light/dark conditions (i.e. day and night). This is a problem when cultivating microalgae species outside.
Research Methodology
For this research study, Project Assistant Professor Kato and Professor Hasunuma's Kobe University research group collaborated with Senior Researcher Satoh et al. at the National institutes for Quantum and Radiological Science and Technology (QST). The researchers used the ion beam at QST's Takasaki Advanced Radiation Research Institute to induce mutation in the microalgae. This enabled them to cultivate a new mutant strain called Chlamydomonas sp. KOR1 (*1), which can produce large quantities of lipids even in light/dark conditions.
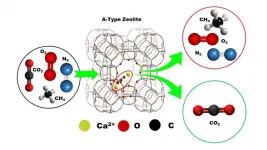
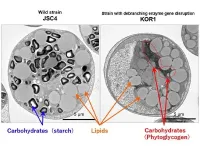
The researchers discovered that this KOR1 strain has disruptions in the starch debranching enzyme (*2) gene ISA1, causing it to produce a different carbohydrate: phytoglycogen (*3) instead of starch (Figure 1).
Normally, microalgae synthesize and accumulate carbohydrates (starch) during light periods and break them down when it is dark. However, many carbohydrates accumulate that cannot be completely broken down. Contrary to this, the carbohydrate synthesized by KOR1 (phytoglycogen) was completely broken down during the dark period. The results of the KOR1 metabolome analysis (*4) revealed a total increase in intermediate metabolites in both the starch and lipid synthesis pathways (intermediate metabolites included fructose-6-phosphate, glucose-6-phosphate, acetyl-CoA and glycerol 3-phosphate). From this analysis, the researchers illuminated the metabolic mechanism underlying the increased lipid production that resulted from ISA1 gene disruption. In the KOR1 strain, the carbohydrate (phytoglycogen) was quickly broken down and intermediate metabolites subsequently induced the carbon resource to be repartitioned to lipid production (Figure 2).
Further Developments
In order to produce biofuels using microalgae, it is necessary to cultivate these organisms outside in the sunlight. However, there is an unavoidable decrease in lipid production under these light/dark conditions. The technique of 'repartitioning carbon resources by disrupting the starch debranching enzyme gene' developed through this research is one answer to this problem. It is hoped that this new method can contribute towards the large-scale implementation of biofuel production using microalgae.
Glossary
1. Chlamydomonas sp. KOR1: Using the microalgae Chlamydomonas sp. JSC4 (isolated from brackish waters in Taiwan) as the parental strain, KOR1 is a mutant obtained via ion beam mutagenesis (*5). It can be cultivated in either freshwater or saltwater. With its ability to break down carbohydrates and convert them into lipids, it has both a high proliferation rate and a high lipid accumulation rate, demonstrating highly efficient lipid production.
2. Starch debranching enzyme: Protein that slices through starch's branch structure. It not only breaks down starch but also creates appropriate structures for synthesis.
3. Phytoglycogen: Phytoglycogen has a highly branched structure compared to starch. It is also highly soluble in water, which means that it is easily broken down and is easy for intercellular enzymes to use.
4. Metabolome analysis: A method of comprehensively analyzing ionic small molecules in a sample using CE-TOFMS (Capillary electrophoresis-time of flight mass spectrometry) apparatus.
5. Ion beam mutagenesis: This involves hitting cells in a plant or microorganism with the accelerated ion molecules of various atoms (such as carbon) at tenths of the speed of light using a particle accelerator. This irradiation technique alters DNA, thus making it possible to create a breed with useful characteristics.
Acknowledgements
This research received financial support from the following:
The Impulsing Paradigm Change through Disruptive Technologies (ImPACT) program (of the Cabinet Office of the Government of Japan).
The Japan Science and Technology Agency (JST)'s Adaptable and Seamless Technology transfer Program (A-STEP).
Journal Information
Title:
"Enhancing carbohydrate repartitioning into lipid and carotenoid by disruption of microalgae starch debranching enzyme"
DOI: 10.1038/s42003-021-01976-8
Authors:
Yuichi Kato, Tomoki Oyama, Kentaro Inokuma, Christopher J. Vavricka, Mami Matsuda, Ryota Hidese, Katsuya Satoh, Yutaka Oono, Jo-Shu Chang, Tomohisa Hasunuma*, and Akihiko Kondo
* Corresponding author
Journal:
Communications Biology
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-06
Scientists are calling for more stringent pesticide bans to lower deaths caused by deliberately ingesting toxic agricultural chemicals, which account for one fifth of global suicides.
A NHMRC funded study, in which the University of South Australia analysed the patient plasma pesticide concentrations, has identified discrepancies in World Health Organization (WHO) classifications of pesticide hazards that are based on animal doses rather than human data.
As a result, up to five potentially lethal pesticides are still being used in developing countries in the Asia Pacific, where self-poisonings account for up to two thirds of suicides.
In ...
2021-05-06
New research from the University of Virginia School of Medicine reveals why sleep can put people with epilepsy at increased risk of sudden death.
Both sleep and seizures work together to slow the heart rate, the researchers found. Seizures also disrupt the body's natural regulation of sleep-related changes. Together, in some instances, this can prove deadly, causing Sudden Unexpected Death in Epilepsy, or SUDEP.
"We have been trying to better understand the cardiac changes around the time of a seizure in patients with epilepsy. When we looked ...
2021-05-06
Proteins are the workhorses of cells, responsible for almost all biological functions that make life possible.
Understanding how specific proteins work is key to disease prevention and treatment, allowing us to lead longer, healthier lives.
Yet scientists still know nothing or very little about thousands of proteins that exist in our bodies and their role in keeping us alive.
Now researchers from Xi'an Jiaotong-Liverpool University have uncovered a new protein analysis tool - coined the Bacterial Growth Inhibition Screen (BGIS) - that could fast-track the process of assessing proteins. The tool allows for quick and efficient basic characterisation of protein function with no special equipment or cost involved.
Dr Ferdinand Kappes of XJTLU's ...
2021-05-06
It is now well known that carbon dioxide is the biggest contributor to climate change and originates primarily from burning of fossil fuels. While there are ongoing efforts around the world to end our dependence on fossil fuels as energy sources, the promise of green energy still lies in the future. Can something be done in the meantime to reduce the concentrations of CO2 in the atmosphere?
It would, in fact, be great if the CO2 in the atmosphere could simply be adsorbed! Turns out, this is exactly what direct air capture (DAC), or the capture of CO2 under ambient conditions, aims to do. However, no such material with the ability to adsorb CO2 efficiently under DAC ...
2021-05-06
In Alzheimer's disease, neurons in the brain die. Largely responsible for the death of neurons are certain protein deposits in the brains of affected individuals: So-called beta-amyloid proteins, which form clumps (plaques) between neurons, and tau proteins, which stick together the inside of neurons. The causes of these deposits are as yet unclear. In addition, a rapidly progressive atrophy, i.e. a shrinking of the brain volume, can be observed in affected persons. Alzheimer's symptoms such as memory loss, disorientation, agitation and challenging behavior are the consequences.
Scientists at the DZNE led by Prof. Michael Wagner, head of a research group at the DZNE and senior ...
2021-05-06
Determining safe yet effective drug dosages for children is an ongoing challenge for pharmaceutical companies and medical doctors alike. A new drug is usually first tested on adults, and results from these trials are used to select doses for pediatric trials. The underlying assumption is typically that children are like adults, just smaller, which often holds true, but may also overlook differences that arise from the fact that children's organs are still developing.
Compounding the problem, pediatric trials don't always shed light on other differences that can affect recommendations for drug doses. There are many factors that limit children's participation in drug trials - for instance, some diseases simply ...
2021-05-06
AURORA, Colo. (May 6, 2021) - Scientists examining the remains of 36 bubonic plague victims from a 16th century mass grave in Germany have found the first evidence that evolutionary adaptive processes, driven by the disease, may have conferred immunity on later generations of people from the region.
"We found that innate immune markers increased in frequency in modern people from the town compared to plague victims," said the study's joint-senior author Paul Norman, PhD, associate professor in the Division of Personalized Medicine at the University of Colorado School of Medicine. "This suggests these markers might have evolved to resist the plague."
The study, done in conjunction with the Max Planck Institute in Germany, was published online Thursday in the journal Molecular ...
2021-05-06
Ultrasound is an indispensable tool for the life sciences and various industrial applications due to its non-destructive, high contrast, and high resolution qualities. A persistent challenge over the years has been how to increase the resolution of an acoustic endoscope without drastically increasing the footprint of the probe, or risking the robustness of the ultrasonic transducer. In recent years, a host of all-optical ultrasonic imaging techniques have emerged - which generally utilise pulsed lasers and optical cavities to excite and detect ultrasound waves - without sacrificing device footprint, sensitivity, or the integrity of the transducer. Thus far these powerful techniques have achieved imaging resolutions on microscopic-mesoscopic length ...
2021-05-06
Researchers at the University of Eastern Finland have discovered previously unknown non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) involved in regulating the gene expression of vascular endothelial growth factors (VEGF), the master regulators of angiogenesis. The study, conducted by the research groups of Associate Professor Minna Kaikkonen-Määttä and Academy Professor Seppo Ylä-Herttuala, provides a better understanding of the complex interplay of ncRNAs with gene regulation, which might open up novel therapeutic approaches in the future. The results were published in the Molecular and Cellular Biology Journal.
Over the past years, the development of next generation ...
2021-05-06
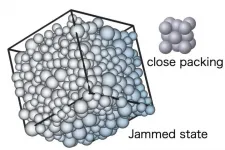
Researchers at Chinese Academy of Science and Osaka University show that, unlike the crystalline close packing of spheres, random close packing or jamming of spheres in a container can take place in a broad range of densities and anisotropies. Furthermore, they show that such diverse jammed states are all just marginally stable and exhibit common universal critical properties.
Osaka, Japan - Scientists at the theoretical institutes, Chinese Academy of Science and Cybermedia Center at Osaka University performed extensive computer simulations to generate and examine random packing of spheres. They show that the "jamming" ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Microalgae biofuels: Changing carbohydrates into lipids