WHO 'needs to act' on suicides caused by pesticides
Researchers call for stricter regulation
2021-05-06
(Press-News.org) Scientists are calling for more stringent pesticide bans to lower deaths caused by deliberately ingesting toxic agricultural chemicals, which account for one fifth of global suicides.
A NHMRC funded study, in which the University of South Australia analysed the patient plasma pesticide concentrations, has identified discrepancies in World Health Organization (WHO) classifications of pesticide hazards that are based on animal doses rather than human data.
As a result, up to five potentially lethal pesticides are still being used in developing countries in the Asia Pacific, where self-poisonings account for up to two thirds of suicides.
In a paper published in Lancet Global Health, UniSA Research Chair of Therapeutics and Pharmaceutical Science, Professor Michael Roberts, says while deaths from pesticide poisonings have fallen dramatically in recent years, it is still a common cause of global suicides.
Each year, more than 150,000 people die from deliberately ingesting pesticides, although this number was much higher - averaging 260,000 a year - before specific chemicals were banned.
Prof Roberts was a member of a team of international researchers who used Sri Lanka as a case study, in which they compared the number of deaths from pesticides in a rural area between 2002 and 2019.
Of 35,000 people (mainly men aged in their late 20s) hospitalised for pesticide self-poisoning, 6.6 per cent died.
The three most toxic agents were paraquat, dimethoate and fenthion, which were all banned by 2011, reflected in much lower fatalities after that date. Since then, five other common pesticides still allowed by the WHO were disproportionately responsible for 24 per cent of fatalities, the team found.
"If human data for acute toxicity of pesticides was used for hazard classification and regulation worldwide, it would prevent many deaths and have a substantial impact on global suicide rates," Prof Roberts says. "Australia is fortunate in that its regulations properly balance good pesticide use versus public health concern."
He predicts that fatal poisonings across Asia could fall by more than 50 per cent, and total suicides in the region could fall by at least a third.
"Instead, the WHO classifications are largely based on animal median lethal doses. This method ignores the differences between species and how they respond to treatment, and the formulations used."
Fatalities from pesticide poisonings also differed greatly from that predicted by the WHO classification.
The researchers have called for the WHO to eliminate all pesticides with fatality rates above five per cent.
"Setting a global benchmark and relying on human data is critical to reducing suicides, particularly in countries such as Sri Lanka, South Korea, Bangladesh and China, where agriculture is still a dominant industry."
"We also found evidence that some banned agents were still in circulation due to illegal importation, so there is still a need to tighten existing regulations," Prof Roberts says.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-06
New research from the University of Virginia School of Medicine reveals why sleep can put people with epilepsy at increased risk of sudden death.
Both sleep and seizures work together to slow the heart rate, the researchers found. Seizures also disrupt the body's natural regulation of sleep-related changes. Together, in some instances, this can prove deadly, causing Sudden Unexpected Death in Epilepsy, or SUDEP.
"We have been trying to better understand the cardiac changes around the time of a seizure in patients with epilepsy. When we looked ...
2021-05-06
Proteins are the workhorses of cells, responsible for almost all biological functions that make life possible.
Understanding how specific proteins work is key to disease prevention and treatment, allowing us to lead longer, healthier lives.
Yet scientists still know nothing or very little about thousands of proteins that exist in our bodies and their role in keeping us alive.
Now researchers from Xi'an Jiaotong-Liverpool University have uncovered a new protein analysis tool - coined the Bacterial Growth Inhibition Screen (BGIS) - that could fast-track the process of assessing proteins. The tool allows for quick and efficient basic characterisation of protein function with no special equipment or cost involved.
Dr Ferdinand Kappes of XJTLU's ...
2021-05-06
It is now well known that carbon dioxide is the biggest contributor to climate change and originates primarily from burning of fossil fuels. While there are ongoing efforts around the world to end our dependence on fossil fuels as energy sources, the promise of green energy still lies in the future. Can something be done in the meantime to reduce the concentrations of CO2 in the atmosphere?
It would, in fact, be great if the CO2 in the atmosphere could simply be adsorbed! Turns out, this is exactly what direct air capture (DAC), or the capture of CO2 under ambient conditions, aims to do. However, no such material with the ability to adsorb CO2 efficiently under DAC ...
2021-05-06
In Alzheimer's disease, neurons in the brain die. Largely responsible for the death of neurons are certain protein deposits in the brains of affected individuals: So-called beta-amyloid proteins, which form clumps (plaques) between neurons, and tau proteins, which stick together the inside of neurons. The causes of these deposits are as yet unclear. In addition, a rapidly progressive atrophy, i.e. a shrinking of the brain volume, can be observed in affected persons. Alzheimer's symptoms such as memory loss, disorientation, agitation and challenging behavior are the consequences.
Scientists at the DZNE led by Prof. Michael Wagner, head of a research group at the DZNE and senior ...
2021-05-06
Determining safe yet effective drug dosages for children is an ongoing challenge for pharmaceutical companies and medical doctors alike. A new drug is usually first tested on adults, and results from these trials are used to select doses for pediatric trials. The underlying assumption is typically that children are like adults, just smaller, which often holds true, but may also overlook differences that arise from the fact that children's organs are still developing.
Compounding the problem, pediatric trials don't always shed light on other differences that can affect recommendations for drug doses. There are many factors that limit children's participation in drug trials - for instance, some diseases simply ...
2021-05-06
AURORA, Colo. (May 6, 2021) - Scientists examining the remains of 36 bubonic plague victims from a 16th century mass grave in Germany have found the first evidence that evolutionary adaptive processes, driven by the disease, may have conferred immunity on later generations of people from the region.
"We found that innate immune markers increased in frequency in modern people from the town compared to plague victims," said the study's joint-senior author Paul Norman, PhD, associate professor in the Division of Personalized Medicine at the University of Colorado School of Medicine. "This suggests these markers might have evolved to resist the plague."
The study, done in conjunction with the Max Planck Institute in Germany, was published online Thursday in the journal Molecular ...
2021-05-06
Ultrasound is an indispensable tool for the life sciences and various industrial applications due to its non-destructive, high contrast, and high resolution qualities. A persistent challenge over the years has been how to increase the resolution of an acoustic endoscope without drastically increasing the footprint of the probe, or risking the robustness of the ultrasonic transducer. In recent years, a host of all-optical ultrasonic imaging techniques have emerged - which generally utilise pulsed lasers and optical cavities to excite and detect ultrasound waves - without sacrificing device footprint, sensitivity, or the integrity of the transducer. Thus far these powerful techniques have achieved imaging resolutions on microscopic-mesoscopic length ...
2021-05-06
Researchers at the University of Eastern Finland have discovered previously unknown non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) involved in regulating the gene expression of vascular endothelial growth factors (VEGF), the master regulators of angiogenesis. The study, conducted by the research groups of Associate Professor Minna Kaikkonen-Määttä and Academy Professor Seppo Ylä-Herttuala, provides a better understanding of the complex interplay of ncRNAs with gene regulation, which might open up novel therapeutic approaches in the future. The results were published in the Molecular and Cellular Biology Journal.
Over the past years, the development of next generation ...
2021-05-06
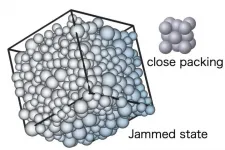
Researchers at Chinese Academy of Science and Osaka University show that, unlike the crystalline close packing of spheres, random close packing or jamming of spheres in a container can take place in a broad range of densities and anisotropies. Furthermore, they show that such diverse jammed states are all just marginally stable and exhibit common universal critical properties.
Osaka, Japan - Scientists at the theoretical institutes, Chinese Academy of Science and Cybermedia Center at Osaka University performed extensive computer simulations to generate and examine random packing of spheres. They show that the "jamming" ...
2021-05-06
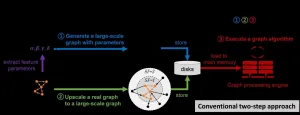
A KAIST research team has developed a new technology that enables to process a large-scale graph algorithm without storing the graph in the main memory or on disks. Named as T-GPS (Trillion-scale Graph Processing Simulation) by the developer Professor Min-Soo Kim from the School of Computing at KAIST, it can process a graph with one trillion edges using a single computer.
Graphs are widely used to represent and analyze real-world objects in many domains such as social networks, business intelligence, biology, and neuroscience. As the number of graph applications increases rapidly, developing and testing new graph algorithms is becoming more important than ever before. Nowadays, many industrial ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] WHO 'needs to act' on suicides caused by pesticides
Researchers call for stricter regulation