Research breakthrough in the fight against cancer
Team of UMass Amherst researchers unveils the latest advance in targeted delivery of therapeutic proteins
2021-05-06
(Press-News.org) AMHERST, Mass. - A team of researchers at the Center for Bioactive Delivery at the University of Massachusetts Amherst's Institute for Applied Life Sciences has engineered a nanoparticle that has the potential to revolutionize disease treatment, including for cancer. This new research, which appears today in Angewandte Chemie, combines two different approaches to more precisely and effectively deliver treatment to the specific cells affected by cancer.
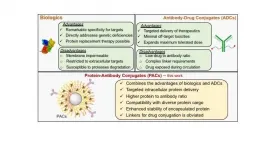
Two of the most promising new treatments involve delivery of cancer-fighting drugs via biologics or antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs). Each has its own advantages and limitations. Biologics, such as protein-based drugs, can directly substitute for a malfunctioning protein in cells. As a result, they have less serious side effects than those associated with traditional chemotherapy. But, because of their large size, they are unable to get into specific cells. ADCs, on the other hand, are able to target specific malignant cells with microdoses of therapeutic drugs, but the antibodies can only carry a limited drug cargo. Since the drugs are more toxic than biologics, increasing the dose of ADCs increases the risk of harmful side effects.
"What our team has done," explains Khushboo Singh, a graduate student in the chemistry department and one of the study's lead authors, "is to combine the advantages of biologics and ADCs and address their weaknesses. It is a new platform for cancer therapy."
The team's approach depends on a nanoparticle the team engineered called a "protein-antibody conjugate," or PAC. "Imagine that the antibodies in PACs are the address on an envelope," adds Sankaran "Thai" Thayumanavan, distinguished professor in chemistry and interim head of biomedical engineering at UMass, "and that the cancer-fighting protein is the contents of that envelope. The PAC allows us to deliver the envelope with its protected treatment to the correct address. So, safer drugs are delivered to the right cell--the result would be a treatment with fewer side effects"
At the heart of the PAC is a "polymer brush," a nanoparticle that the team engineered. This brush does two things. First, it is studded with antibodies that are capable of locating individual cancerous cells. Next, the brush has to both hold a sizable cargo of biologics but also keep that dose intact. The team found that their nanoparticle could carry four times the therapeutic dose of a typical ADC, and, through a variety of techniques, could be increased many times over.
While the UMass team's research represents a major milestone in cancer research, their findings are also widely applicable, and "open many new opportunities in biomedicine, extending far beyond cancer to all sorts of genetic diseases, or really any abnormality that occurs inside a human cell," says Bin Liu, one of the papers lead authors and a graduate student in the UMass chemistry department at the time of the research.
"Among the implications," says Thayumanavan, "perhaps the most exciting part is that this opens the door to develop cures for certain cancers that have been long considered undruggable or incurable" The team's research is currently being tested in models beyond a petri-dish.
INFORMATION:
Contacts: S. "Thai" Thayumanavan, thai@umass.edu
Daegan Miller, drmiller@umass.edu
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-06
May 6, 2021 -- A significant level of symptoms of depression, anxiety and post-traumatic stress may follow COVID-19 independent of any previous psychiatric diagnoses, according to new research by Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health with colleagues at Universidade Municipal de São Caetano do Sul in Brazil. Exposure to increased symptomatic levels of COVID-19 may be associated with psychiatric symptoms after the acute phase of the disease. This is the largest study to evaluate depressive, anxiety, and post-traumatic stress symptoms in tandem among patients who had mild COVID-19 ...
2021-05-06
Quantum computers or quantum sensors consist of materials that are completely different to their classic predecessors. These materials are faced with the challenge of combining contradicting properties that quantum technologies entail, as for example good accessibility of quantum bits with maximum shielding from environmental influences. In this regard, so-called two-dimensional materials, which only consist of a single layer of atoms, are particularly promising.
Researchers at the new Center for Applied Quantum Technologies and the 3rd Institute of Physics at the University of Stuttgart have now succeeded in identifying promising quantum bits in these materials. They were able to show that the quantum bits can be generated, read out and coherently controlled in a very ...
2021-05-06
The Marburg virus, a relative of the Ebola virus, causes a serious, often-fatal hemorrhagic fever. Transmitted by the African fruit bat and by direct human-to-human contact, Marburg virus disease currently has no approved vaccine or antivirals to prevent or treat it.
A team of researchers is working to change that. In a new paper in the journal Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, investigators from Penn's School of Veterinary Medicine, working together with scientists from the Fox Chase Chemical Diversity Center and the Texas Biomedical Research Institute, report encouraging results from tests of an experimental ...
2021-05-06
WASHINGTON -- Researchers have demonstrated a record-high laser pulse intensity of over 1023 W/cm2 using the petawatt laser at the Center for Relativistic Laser Science (CoReLS), Institute for Basic Science in the Republic of Korea. It took more than a decade to reach this laser intensity, which is ten times that reported by a team at the University of Michigan in 2004. These ultrahigh intensity light pulses will enable exploration of complex interactions between light and matter in ways not possible before.
The powerful laser can be used to examine phenomena believed to be responsible for ...
2021-05-06
Recently, laser scientists at the Center for Relativistic Laser Science (CoReLS) within the Institute for Basic Science (IBS) in South Korea realized the unprecedented laser intensity of 1023 W/cm2. This has been a milestone that has been pursued for almost two decades by many laser institutes around the world.
An ultrahigh intensity laser is an important research tool in several fields of science, including those which explore novel physical phenomena occurring under extreme physical conditions. Since the demonstration of the 1022 W/cm2 intensity laser by a team at the ...
2021-05-06
The health benefits of sardines and oily fish are widely known: their high levels of unsaturated fats help to regulate cholesterol levels and prevent the onset of cardiovascular diseases. However, the benefits don't end there. A study led by Diana Diaz Rizzolo, lecturer and researcher of the Universitat Oberta de Catalunya's (UOC) Faculty of Health Sciences and the August Pi i Sunyer Biomedical Research Institute (IDIBAPS), has discovered that the regular consumption of sardines helps to prevent the onset of type 2 diabetes. Nutrients found in high quantities in sardines - such as taurine, omega 3, calcium and vitamin D - help to protect against this disease which, according to CIBERDEM's Di@betes study, affects around 14% of the Spanish population over the ...
2021-05-06
The published data provide additional detail of an initial analysis conducted in January, while more robust data from a complete analysis of the study was subsequently shared in March 2021.
Publication of initial primary analysis highlights cross-protection by the Novavax Covid-19 vaccine against the B.1.351 variant prevalent in South Africa during the study.
This is the first published study to show protection against mild Covid-19 caused by the B.1.351 variant circulating in South Africa.
An updated analysis of the study indicated 100% protection against severe Covid-19 due to the B.1.351 variant.
"An efficacy of 50% is sufficient to meet the World ...
2021-05-06
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- Social media has become a platform for new mothers to openly share their experiences of the joys and challenges of parenthood. Researchers at Penn State and Dalhousie University have unraveled the sentiments in nursing mothers' tweets to better understand the factors influencing breastfeeding behaviors. They hope the findings can inform policies and interventions to support and improve resources for nursing mothers, such as breastfeeding support, workplace accommodations and technological aids such as apps.
"We are getting the raw sentiment of nursing mothers without putting them in a controlled experiment environment ...
2021-05-06
The world's first-ever 'academic paper which is not a paper' is due to be presented by a Lancaster University research team at the premier international conference on human-computer interaction.
Dr Joseph Lindley, a researcher at Lancaster University's ImaginationLancaster design-led research laboratory, Dr Miriam Sturdee, from the University's School of Computing and Communications, Senior Research Associate Dr David Green and Research Associate Hayley Alter have been invited to take part in the 2021 ACM CHI Virtual Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems in May.
Using the innovative 'Gather Town' online video-calling and conferencing platform, they have experimented in setting up a conference paper as an interactive but virtual ...
2021-05-06
Clinical practice guidelines for dealing with the physical and mental health of transgender people highlight the current lack of a solid research base which must be improved, according to a new study published in the journal BMJ Open.
A team of researchers from Anglia Ruskin University (ARU) and King's College London searched world literature for all international clinical practice guidelines on the healthcare needs of gender minority and trans people.
Results showed that higher quality guidelines tended to focus mainly on HIV, and most others were on transition-related interventions. There were noticeable gaps in the topics of guidelines, with none addressing ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Research breakthrough in the fight against cancer
Team of UMass Amherst researchers unveils the latest advance in targeted delivery of therapeutic proteins