Realization of the highest laser intensity ever reached
The record-breaking laser intensity over 1023 W/cm2 enables us to explore novel physical phenomena occurring under extreme physical conditions
2021-05-06
(Press-News.org) Recently, laser scientists at the Center for Relativistic Laser Science (CoReLS) within the Institute for Basic Science (IBS) in South Korea realized the unprecedented laser intensity of 1023 W/cm2. This has been a milestone that has been pursued for almost two decades by many laser institutes around the world.
An ultrahigh intensity laser is an important research tool in several fields of science, including those which explore novel physical phenomena occurring under extreme physical conditions. Since the demonstration of the 1022 W/cm2 intensity laser by a team at the University of Michigan in 2004, the realization of laser intensity over 1023 W/cm2 has been pursued for nearly 20 years.
In general, achieving such a level of ultra-high laser intensity requires two things: laser with extremely high power output, and focusing that laser to the smallest spot as possible. While continuous-wave lasers are limited to megawatt-scale intensity, far higher peak power output (on the order of petawatt) is possible in pulsed laser systems by delivering the energy in the time scale as short as femtoseconds. In order to reach the goal of developing the world's most powerful laser, several ultrahigh power laser facilities with outputs of 10 PW and beyond, such as ELI (EU), Apollon (France), EP-OPAL (USA), and SEL (China), have been built or are being planned. A recent study from Osaka University even proposed a concept prototype for an exawatt class laser.
Meanwhile, the CoReLS laser team has been operating a 4-PW laser system since 2016. This year in April 2021, they have finally achieved the record-breaking milestone of 1023 W/cm2 by tightly focusing the multi-PW laser beam.
Several special techniques have been employed to achieve this feat. The power intensity was maximized by using a focusing optics called an off-axis parabolic mirror, which was used to focus a 28 cm laser beam down to a spot only 1.1 micrometers wide. Such a diffraction-limited tight focusing can be obtained only with a clean laser beam without wavefront distortion. The CoReLS laser team, thus, made its PW laser beam as clean as possible using a set of deformable mirrors to correct the wavefront distortion of the PW laser.
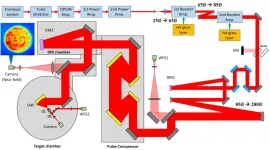
The CoReLS 4-PW laser is a femtosecond, ultrahigh power Ti:sapphire laser, based on the chirped pulse amplification (CPA) technique. The layout of the CoReLS 4-PW laser, including the experimental setup to control the wavefront and to measure the intensity, is given in Fig. 1. A low-energy femtosecond laser pulse from the front-end was stretched to a nanosecond pulse by the pulse stretcher. The initial laser pulse was then amplified to 4.5 J by the two power amplifiers and then up to 112 J by the two booster amplifiers. The size of the laser beam increased along the beam path by a series of beam expanders; 25 mm right after the power amplifiers, 65 mm at the entrance of the 1st booster amplifier, 85 mm at the entrance of the 2nd booster amplifier, and 280 mm at the entrance of the pulse compressor. In the pulse compressor, the laser pulse was recompressed to 20 fs (FWHM), which caused its peak power to become 4 PW after the compression.
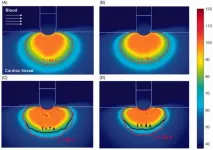
In order to compensate for the wavefront distortion of the PW laser beam, two deformable mirrors were employed in the PW laser beamline. The first deformable mirror (DM1) with a diameter of 100 mm was installed after the final booster amplifier, with its role being to correct the wavefront distortion accumulated from the front end to the final beam expander. The second deformable mirror (DM2) with a diameter of 310 mm was installed after the pulse compressor, which corrects the additional aberrations induced from large aperture optics in the pulse compressor, the beam delivery line, and the target area. In the target chamber, the PW laser beam was tightly focused with an f /1.1 off-axis parabolic mirror, which possessed an effective focal length of 300 mm. For imaging and characterization of the focused spot, the focused beam was collimated by an objective lens. It was then divided into two beams with a beam splitter for the focal spot and wavefront characterization. A camera was used for the focal spot monitoring of the transmitted laser beam, and a wavefront sensor was used to measure the wavefront of the reflected laser beam. Figure 3 shows the 3-D focal spot image measured by the camera in the target chamber.
Prof. NAM Chang Hee, the Director of CoReLS, notes, "This work has shown that the CoReLS PW laser is the most powerful laser in the world. With the highest laser intensity achieved ever, we can tackle new challenging areas of experimental science, especially strong field quantum electrodynamics (QED) that has been dealt with mainly by theoreticians. We can explore new physical problems of electron-photon scattering (Compton scattering) and photon-photon scattering (Breit-Wheeler process) in the nonlinear regime. This kind of research is directly related to various astrophysical phenomena occurring in the universe and can help us to further expand our knowledge horizon."
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-06
The health benefits of sardines and oily fish are widely known: their high levels of unsaturated fats help to regulate cholesterol levels and prevent the onset of cardiovascular diseases. However, the benefits don't end there. A study led by Diana Diaz Rizzolo, lecturer and researcher of the Universitat Oberta de Catalunya's (UOC) Faculty of Health Sciences and the August Pi i Sunyer Biomedical Research Institute (IDIBAPS), has discovered that the regular consumption of sardines helps to prevent the onset of type 2 diabetes. Nutrients found in high quantities in sardines - such as taurine, omega 3, calcium and vitamin D - help to protect against this disease which, according to CIBERDEM's Di@betes study, affects around 14% of the Spanish population over the ...
2021-05-06
The published data provide additional detail of an initial analysis conducted in January, while more robust data from a complete analysis of the study was subsequently shared in March 2021.
Publication of initial primary analysis highlights cross-protection by the Novavax Covid-19 vaccine against the B.1.351 variant prevalent in South Africa during the study.
This is the first published study to show protection against mild Covid-19 caused by the B.1.351 variant circulating in South Africa.
An updated analysis of the study indicated 100% protection against severe Covid-19 due to the B.1.351 variant.
"An efficacy of 50% is sufficient to meet the World ...
2021-05-06
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- Social media has become a platform for new mothers to openly share their experiences of the joys and challenges of parenthood. Researchers at Penn State and Dalhousie University have unraveled the sentiments in nursing mothers' tweets to better understand the factors influencing breastfeeding behaviors. They hope the findings can inform policies and interventions to support and improve resources for nursing mothers, such as breastfeeding support, workplace accommodations and technological aids such as apps.
"We are getting the raw sentiment of nursing mothers without putting them in a controlled experiment environment ...
2021-05-06
The world's first-ever 'academic paper which is not a paper' is due to be presented by a Lancaster University research team at the premier international conference on human-computer interaction.
Dr Joseph Lindley, a researcher at Lancaster University's ImaginationLancaster design-led research laboratory, Dr Miriam Sturdee, from the University's School of Computing and Communications, Senior Research Associate Dr David Green and Research Associate Hayley Alter have been invited to take part in the 2021 ACM CHI Virtual Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems in May.
Using the innovative 'Gather Town' online video-calling and conferencing platform, they have experimented in setting up a conference paper as an interactive but virtual ...
2021-05-06
Clinical practice guidelines for dealing with the physical and mental health of transgender people highlight the current lack of a solid research base which must be improved, according to a new study published in the journal BMJ Open.
A team of researchers from Anglia Ruskin University (ARU) and King's College London searched world literature for all international clinical practice guidelines on the healthcare needs of gender minority and trans people.
Results showed that higher quality guidelines tended to focus mainly on HIV, and most others were on transition-related interventions. There were noticeable gaps in the topics of guidelines, with none addressing ...
2021-05-06
An article published in International Journal of Hyperthermia proposes a more effective protocol for the treatment of cardiac arrhythmias when applying radiofrequency energy at the site of the arrhythmia by catheterization. The research results from the final year project (TFG) on the bachelor's degree in Biomedical Engineering by Sergi Coderch Navarro, supervised by Ana González Suárez and Oscar Camara, researchers with the PhySense group of the BCN MedTech Research Unit at the UPF Department of Information and Communication Technologies (DTIC). Sergi Coderch Navarro defended his TFG in July 2019 and was a runner-up in the 2019 Gemma Rossell i Romero Awards. Currently, Ana González Suárez is a postdoctoral ...
2021-05-06
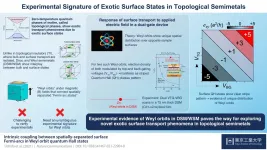
Scientists at Tokyo Institute of Technology experimentally verify the existence of exotic surface conduction states in topological semimetals (TSMs), materials that lie at the boundary between conductors and insulators, by performing voltage scans of these surface states on a thin film sample of a TSM. The findings can pave the way for future study and exploitation of such conduction states in realizing novel, quantum transport phenomena.
All of us are probably familiar with the idea of conductors and insulators. But what would you call a material that can conduct on the surface but insulate on the inside? Physicists call it a "topological insulator" (TI), a term that highlights the geometric aspect of its strange conduction behavior. Even stranger ...
2021-05-06
ITHACA, N.Y. - Solar-power developers need to explore using lower-quality agricultural land for solar energy, incentivize dual-use (combined agriculture and solar) options, avoid concentrated solar development and engage communities early to achieve New York's green energy goals, according to forthcoming Cornell University research.
"As farmland is generally flat and cleared, agricultural land will be the prime target for future solar energy development," said Max Zhang, professor in the Sibley School of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering. "Good farmland, however, is not ideal."
Zhang is senior author of "Strategic Land Use Analysis for Solar Energy Development in New York State," which will publish in August 2021 in Renewable Energy.
Under New York state's 2019 Climate ...
2021-05-06
A recent study analyses data collect4d at 44 of the darkest places in the world, including the Canary Island Observatories, to develop the first complete reference method to measure the natural brightness of the night sky using low-cost photometers.
Of the 44 photometers in the survey, the Roque de los Muchachos Observatory (Garafía, La Palma, Canary Islands) stands out at the darkest of all the skies analysed.
The night sky is not completely dark; even in the remotest places there is a glow in the sky produced by natural components, both terrestrial and extraterrestrial, ...
2021-05-06
They are 50,000 times thinner than a human hair, and just a few atoms thick: two-dimensional materials are the thinnest substances it is possible to make today. They have completely new properties and are regarded as the next major step in modern semiconductor technology. In the future they could be used instead of silicon in computer chips, light-emitting diodes and solar cells. Until now, the development of new two-dimensional materials has been limited to structures with layers of rigid chemical bonds in two spatial directions - like a sheet of paper in a stack. Now for the first time, a research team from the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Realization of the highest laser intensity ever reached
The record-breaking laser intensity over 1023 W/cm2 enables us to explore novel physical phenomena occurring under extreme physical conditions