Losing an only child is more devastating than losing a spouse, according to study of Chinese parents
With millions of one-child families in China, study highlights distress experienced after loss
2021-05-07
(Press-News.org) Which wound cuts deeper: the loss of an only child or loss of a spouse? A new study led by researchers at NYU Rory Meyers College of Nursing and Fudan University suggests that Chinese parents find the loss of an only child to be approximately 1.3 times as psychologically distressing than the loss of a spouse. The findings are published in the journal Aging & Mental Health.
Older adults in China rely heavily on family support, particularly from their adult children. Filial piety--the Confucian idea describing a respect for one's parents and responsibility for adult children to care for their parents as they age--is a central value in traditional Chinese culture.
In the 1970s, China introduced a one-child policy to slow the population growth, resulting in hundreds of millions of families with only children. While the policy ended in 2016, its consequences will be felt for decades, particularly for families who experience the loss of a child.
"The death of a child has been recognized as one of the most challenging and traumatic events for a parent," said Bei Wu, PhD, Dean's Professor in Global Health at NYU Rory Meyers College of Nursing and co-director of the NYU Aging Incubator, as well as the study's senior author. "Within the cultural context of China, the death of an only child is devastating not only due to the emotional loss, but also the loss of financial and instrumental support that is critical to older adults."
The death of a spouse is also recognized as a distressing life event, forcing older adults to navigate both the emotional loss and the shattering of a married couple's social and economic circumstances. In this study, Wu and her colleagues wanted to examine whether the loss of a spouse had a similar impact on psychological well-being as the loss of an only child, and whether the presence of one mitigated the absence of the other.
The researchers analyzed data from a 2013 survey conducted in Shanghai involving more than 1,100 adults, including 128 parents who lost their only child. The survey evaluated the impact of the loss of a spouse or child on participants' psychological well-being, including depression, loneliness, and life satisfaction.
They found that adults who lost their only child but have a living spouse had more psychological distress than those who lost their spouse but have a living child. This effect appeared to be stronger in women than in men.
Losing an only child resulted in 1.37 times the level of loneliness and 1.51 times the level depression as losing a spouse, and life satisfaction was 1.14 times worse for those who lost an only child vs. their spouse. Adults whose children and spouse were both alive had better psychological well-being than those who experienced loss.
"Our findings demonstrate that the loss of an only child carries more psychological weight than the loss of a spouse in Chinese culture," said Wu.
Wu and her colleagues recommend increasing access to professional mental health services for adults who experience loss, as well as developing culturally relevant interventions to address social isolation and loneliness among older Chinese adults.
INFORMATION:
Wu collaborated on this study with Yan Liang and Hong Liang of Fudan University, Hanzhang Xu of Duke University, and Feinian Chen of the University of Maryland.
About NYU Rory Meyers College of Nursing (@NYUNursing)
NYU Rory Meyers College of Nursing is a global leader in nursing and health. Founded in 1932, the College offers B.S., M.S., DNP and Ph.D. degree programs providing the educational foundation to prepare the next generation of nursing leaders and researchers. NYU Meyers has several programs that are highly ranked by U.S. News & World Report and is among the top 10 nursing schools receiving NIH funding, thanks to its research mission and commitment to innovative approaches to health care worldwide.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-07
Observing how cells stick to surfaces and their motility is vitally important in the study of tissue maintenance, wound healing and even understanding how cancers progress. A new paper published in EPJ Plus, by Raj Kumar Sadhu, Weizmann Institute of Science, Rehovot, Israel, takes a step towards a deeper understanding of these processes.
"Cell adhesion is the ability of a cell to stick to another cell or an extracellular matrix. This process is important in order to understand how cells interact and coordinate their behaviour in multicellular organisms," says sadhu. "We theoretically model the adhesion of a cell-like vesicle by describing the cell as a three-dimensional vesicle adhering on a flat substrate with a constant adhesion interaction."
Alongside ...
2021-05-07
Neuroblastoma is a childhood cancer, most commonly affecting children aged between 2 -3 and can be fatal. Since the tumour cells resemble certain cells in the adrenal glands, a joint research group from MedUni Vienna's Center for Brain Research and the Swedish Karolinska Institute investigated the cellular origin of these cells and sympathetic neurons during the embryonic development of human adrenal glands. During the course of their investigations, they discovered a previously unknown cell type that might potentially be the origin of the tumour cells.
Treatments for this disease are extremely aggressive and challenging ...
2021-05-07
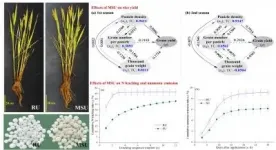
The applied nitrogen in crop production is easily lost through ammonia emission and nitrogen leaching. Therefore, many attempts have been made on the development of novel slow-release fertilizers to reduce nitrogen loss and improve crop production.
A research team led by Prof. WU Yuejin from the Institute of Intelligent Machines of the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science developed a novel matrix-based slow-release urea (MSU) recently to improve nitrogen use efficiency in rice production, and they assessed the performances of it.
"MSU is a promising fertilizer for rice production," said WU, "as less nitrogen loss and greater soil nitrogen ...
2021-05-07
Physicists at Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg (FAU) have for the first time been able to prove a long-predicted but as yet unconfirmed fundamental effect. In Faraday chiral anisotropy, the propagation characteristics of light waves are changed simultaneously by the natural and magnetic-field induced material properties of the medium through which the light travels. The researchers obtained proof that this is the case by conducting experiments using nickel helices at the nanometre scale. Their findings have now been published in the academic journal 'Physical Review Letters'.
Light is transmitted as sine waves consisting of crossed electric and magnetic fields and interacts with matter. This ...
2021-05-07
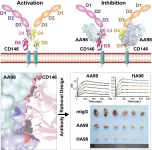
Recently, Prof. XIE Can from the High Magnetic Field Laboratory of the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS), in a collaboration with Prof. YAN Xiyun's lab from the Institute of Biophysics, reported the structural basis of mAb AA98's inhibition on CD146-mediated endothelial cells (EC) activation and designed higher affinity monoclonal antibody HA98 for cancer treatment.
CD146 is an adhesion molecule that plays important roles in angiogenesis, cancer metastasis, and immune response. Prof. YAN Xiyun's lab has been focused on the function of CD146 and the mechanism ...
2021-05-07
Australia, the driest inhabited continent, is prone to natural disasters and wild swings in weather conditions - from floods to droughts, heatwaves and bushfires.
Now two new Flinders University studies of long-term hydro-climatic patterns provide fresh insights into the causes of the island continent's strong climate variability which affect extreme wet or dry weather and other conditions vital to water supply, agriculture, the environment and the nation's future.
For the first time, researchers from the National Centre for Groundwater Research and Training (NCGRT) at Flinders have revealed a vegetation-mediated seesaw wetting-drying phenomenon between eastern and western Australia. ...
2021-05-07
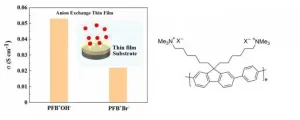
Ishikawa, Japan - As decarbonization progresses rapidly in the world, fuel cells offer potentially higher electrical efficiency than conventional power-generating systems. Anion exchange membrane fuel cells offer advantages of using non-precious metal catalysts than proton exchange membrane fuel cells. One of the challenges of this next-generation fuel cell is to clarify the hydroxide ion conductivity in the ion conductive polymer around the electrode catalyst. The difficulty of studying the hydroxide ion conductivity at the electrode interface is that the hydroxide ion, which is a carrier, easily reacts with carbon dioxide in the air. To solve this problem, all evaluation devices were improved so that the sample did not come into contacting with air.
In a new study published ...
2021-05-07
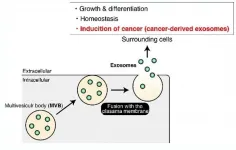
Cells talk to each other to coordinate nutrition, waste removal, energy use, and, in some cases, disease progression. The cells that line the surfaces of organs or specific tissues, called epithelial cells, appear to speak two different languages - one for either side of the cell, according to a new study by researchers based in Japan.
The discovery, published on March 16 in EMBO Reports, could have implications for understanding how cancer spreads and, potentially, for advanced treatments, the team says.
The team, led by Mitsunori Fukuda, professor in the Laboratory of Membrane Trafficking Mechanisms, Department of Integrative ...
2021-05-07
Patients with lasting symptoms of COVID-19 who completed a six week, supervised rehabilitation programme demonstrated significant improvements in exercise capacity, respiratory symptoms, fatigue and cognition, according to researchers at the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) Leicester Biomedical Research Centre - a partnership between Leicester's Hospitals, the University of Leicester and Loughborough University.
The study, which is published in the journal Chronic Respiratory Disease today (Friday 7 May 2021), followed thirty patients who took part in face-to-face ...
2021-05-07
Dispersal is an important process governing the persistence of wild animal populations. Upon reaching sexual maturity, individuals usually disperse from their natal home range to search for suitable habitat and mates for reproduction. As such, dispersal promotes gene flow among populations, allows rescuing small and isolated populations, and enables the colonization of unoccupied habitats. In human-dominated landscapes, however, dispersing animals find it increasingly difficult to cross densely populated areas that separate suitable habitats. For this reason, the identification and preservation of wildlife corridors has become of utmost importance for conservation authorities worldwide.
In southern Africa, the governments ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Losing an only child is more devastating than losing a spouse, according to study of Chinese parents
With millions of one-child families in China, study highlights distress experienced after loss