Distinct cell-to-cell communication processes controlled differently
2021-05-07
(Press-News.org) Cells talk to each other to coordinate nutrition, waste removal, energy use, and, in some cases, disease progression. The cells that line the surfaces of organs or specific tissues, called epithelial cells, appear to speak two different languages - one for either side of the cell, according to a new study by researchers based in Japan.
The discovery, published on March 16 in EMBO Reports, could have implications for understanding how cancer spreads and, potentially, for advanced treatments, the team says.
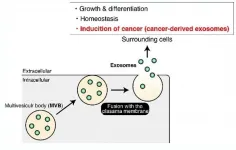
The team, led by Mitsunori Fukuda, professor in the Laboratory of Membrane Trafficking Mechanisms, Department of Integrative Life Sciences, Graduate School of Life Sciences at Tohoku University, examined epithelial cells from a kidney model. The cells release particles called exosomes that carry bits of the cells themselves or information about the cells. The proteins and other genetic information in the exosomes can then influence how other cells behave or function. In health, such an information exchange could help the immune system mount a more tailored approach to an invading pathogen. Some diseased cells, such as cancer, can release exosomes that make healthy cells less resistant to invasion.
"Single cells are known to release various kinds of exosomes, but very little is known about the mechanisms by which they are produced and released," Fukuda said. "In this paper, we found that epithelial cells asymmetrically release two distinct types of exosomes with distinct protein compositions."
The researchers developed a purification method to separate out exosomes based on their protein makeup.
"In this paper, we found that epithelial cells asymmetrically release two distinct types of exosomes - apical and basolateral - with distinct protein compositions," said first author Takahide Matsui, assistant professor, Laboratory of Membrane Trafficking Mechanisms, Department of Integrative Life Sciences, Graduate School of Life Sciences at Tohoku University.
They found that exosomes released from the apical side of the cell, which faces an external space or lumen, were modulated by ALIX, a protein related to the particle formation inside the cells. Exosomes released from the basolateral side of the cell closest to other tissues and neighboring cells were triggered by ceramide, a fatty molecule. They also found that depleting ALIX and ceramide reduced the number of apical exosomes and basolateral exosomes released, respectively.
Fukuda said that the results could help elucidate the cell-to-cell communication that allows cancer to migrate - and put a stop to it.
"It will be interesting to investigate how cancer cells use two distinct mechanisms of exosome production during cancer progression," Fukuda said. "Since exosomes from cancer cells are involved in their progression, our findings could lead to the discovery of new drugs for treatments for cancers in the future."
Matsui agreed, noting that their research could expand to other realms in health and in disease.
"Our discovery provides an important clue to understanding the generation of different exosomes in many cell types in addition to epithelial cells," Matsui said.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-07
Patients with lasting symptoms of COVID-19 who completed a six week, supervised rehabilitation programme demonstrated significant improvements in exercise capacity, respiratory symptoms, fatigue and cognition, according to researchers at the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) Leicester Biomedical Research Centre - a partnership between Leicester's Hospitals, the University of Leicester and Loughborough University.
The study, which is published in the journal Chronic Respiratory Disease today (Friday 7 May 2021), followed thirty patients who took part in face-to-face ...
2021-05-07
Dispersal is an important process governing the persistence of wild animal populations. Upon reaching sexual maturity, individuals usually disperse from their natal home range to search for suitable habitat and mates for reproduction. As such, dispersal promotes gene flow among populations, allows rescuing small and isolated populations, and enables the colonization of unoccupied habitats. In human-dominated landscapes, however, dispersing animals find it increasingly difficult to cross densely populated areas that separate suitable habitats. For this reason, the identification and preservation of wildlife corridors has become of utmost importance for conservation authorities worldwide.
In southern Africa, the governments ...
2021-05-07
Inclusion of soybean and linseed oils in the diet of dairy cows made the fatty acid content of their milk even healthier for human nutrition. It also increased the proportions of omega-6 and omega-3, which in the right balance play a key role in preventing cardiovascular diseases, for example, as well as chronic inflammation and some kinds of cancer.
Cardiovascular diseases are one of the world’s main public health problems. In Brazil, they are among the foremost causes of death. Each year some 300,000 Brazilians have heart attacks, dying in 30% of cases, according to the Health Ministry.
Research led by Arlindo Saran Netto, a professor at the University of São Paulo’s School of Animal Science and Food Engineering (FZEA-USP) in Pirassununga, São Paulo ...
2021-05-07
People spend about 80-90% of their time indoors. Compared to outdoor air quality, the indoor air quality is more relevant to people's health. Therefore, understanding the levels, sources and evolution of particulate matter (PM) indoors is important for the accurate evaluation of people's health risks to aerosol exposure.
A research team led by Prof. Yele Sun from the Institute of Atmospheric Physics (IAP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences deployed a time-of-flight aerosol chemical speciation monitor (ToF-ACSM) to measure time series and mass spectra of non-refractory species in a typical academic office in IAP. The study was published in Indoor Air.
The researchers measured the concentration and chemical composition of indoor PM2.5 ...
2021-05-07
To understand the world, we arrange individual objects, people, and events into different categories or concepts. Concepts such as 'the telephone' consist primarily of visible features, i.e. shape and color, and sounds, such as ringing. In addition, there are actions, i.e. how we use a telephone.
However, the concept of telephone does not only arise in the brain when we have a telephone in front of us. It also appears when the term is merely mentioned. If we read the word "telephone", our brain also calls up the concept of telephone. The same regions in the brain are activated that would be activated ...
2021-05-07
To infect its host plant maize, the fungal parasite Ustilago maydis uses a complex of seven proteins. Numerous findings reveal an essential role of the complex in causing disease and suggest a widespread occurence in fungal plant pathogens.
Each year, fungal plant pathogens such as rusts, rice blast and mildews destroy huge amounts of cereal crops that could feed millions of people. Many of these fungi are biotrophic pathogens: Instead of killing their host plants, they manipulate host cells to assure that these sustain fungal growth. Among these pathogens, the corn smut fungus Ustilago maydis has emerged as a model for basic research on biotrophic fungi.
During the infection, U. maydis releases an entire cocktail of so-called ...
2021-05-07
7 May 2021/Kiel. Corals are the backbone of marine ecosystems in the tropics. They are threatened by rising water temperatures caused by global warming and they are among the first ecosystems worldwide that are on the verge of ecological collapse. Coral bleaching, which is becoming stronger and more frequent due to heat stress, has already wiped out corals at many locations globally. With the help of a microbiome-targeting strategy developed by an international team led by GEOMAR Helmholtz Centre for Ocean Research Kiel, it could become feasible to help protect corals from heat stress. The work has now been published in the international journal Microbiome.
Corals are the backbone of marine ecosystems in the tropics. They are threatened by rising water temperatures caused by global warming ...
2021-05-07
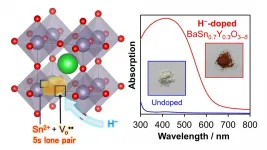
Narrow-gap semiconductors with the ability to use visible light have garnered significant interest thanks to their versatility. Now, scientists in Japan have developed and characterized a new semiconductor material for application in process components stimulated by light. The findings have, for the first time, suggested a new way to reduce the band gap in cheaper and non-toxic tin-based oxide semiconductors for efficient light-based applications.
Semiconductors that can exploit the omnipresent visible spectrum of light for different technological applications would serve as a boon to the material world. However, such semiconductors often do not come cheap and can often be toxic. Now, a group of material scientists ...
2021-05-07
May 7, 2021 - Among collegiate football players and other athletes, Black athletes recognize fewer concussion-related symptoms than their White counterparts, reports a study in the May/June issue of the Journal of Head Trauma Rehabilitation (JHTR). The official journal of the Brain Injury Association of America, JHTR is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
"Despite NCAA concussion education requirements for athletes, Black collegiate-athletes were found to have lower concussion symptom knowledge than White collegiate-athletes," according to the new research by Jessica Wallace, PhD, MPH, LAT, ATC, of University of Alabama, Tuscaloosa, and colleagues. The ...
2021-05-07
RNA-based drugs have the potential to change the standard of care for many diseases, making personalized medicine a reality. This rapidly expanding class of therapeutics are cost-effective, fairly easy to manufacture, and able to go where no drug has gone before, reaching previously undruggable pathways.
Mostly.
So far, these promising drugs haven't been very useful in getting through to the well-protected brain to treat tumors or other maladies.
Now a multi-institutional team of researchers, led by Costas Arvanitis at the Georgia Institute of Technology and Emory University, has figured out a way: using ultrasound and RNA-loaded nanoparticles to get through the protective blood-brain barrier and deliver potent medicine to brain tumors.
"We're able to make this drug more available ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Distinct cell-to-cell communication processes controlled differently