Study helps to better understand the link between indoor and outdoor air quality
2021-05-07
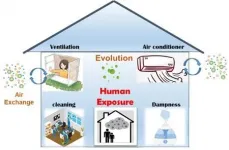
(Press-News.org) People spend about 80-90% of their time indoors. Compared to outdoor air quality, the indoor air quality is more relevant to people's health. Therefore, understanding the levels, sources and evolution of particulate matter (PM) indoors is important for the accurate evaluation of people's health risks to aerosol exposure.
A research team led by Prof. Yele Sun from the Institute of Atmospheric Physics (IAP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences deployed a time-of-flight aerosol chemical speciation monitor (ToF-ACSM) to measure time series and mass spectra of non-refractory species in a typical academic office in IAP. The study was published in Indoor Air.
The researchers measured the concentration and chemical composition of indoor PM2.5 for one month along with simultaneous measurements outdoors. They also performed the open-close window and the dampness experiments in order to figure out the mechanism of indoor/outdoor air exchange, and the influence of increased humidity on the indoor PM2.5.
They found that the indoor aerosol species were primarily from outdoor air exchange. "The indoor and outdoor variation trends are similar for most of aerosol species," said Prof. Sun, "However, the chemical compositions of PM2.5 are different. The concentration of organic aerosol from fossil fuel combustion and ammonium nitrate decreases because they evaporate or turn from particle to gas upon indoor transport when the indoor temperature is much higher than the outside in winter."
It is often believed that opening windows to ventilate can improve the indoor air quality. However, according to this newly published study, the PM mass concentration outdoors is significantly higher than that in the office. Elevated natural ventilation will increase PM exposure indoors instead, and this increased exposure might be prolonged when outdoor PM got cleared up. "So it's not a good idea to open windows when the air quality is not good outdoors." Said Prof. Sun.
The team also investigated the effect of air humidifiers, which are widely used to increase the indoor humidity. Prof. Sun said, "The increase of indoor relative humidity could lead to a significant increase in PM2.5 mass concentration, especially for organic aerosol. The increase is likely due to the partitioning of hygroscopic organic species from gas phase to particle phase in indoor air."
"Better understanding of the links between indoor and outdoor air quality will be needed in the future, as well as a more quantitative assessment of human exposure risks indoors," said Sun.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-07
To understand the world, we arrange individual objects, people, and events into different categories or concepts. Concepts such as 'the telephone' consist primarily of visible features, i.e. shape and color, and sounds, such as ringing. In addition, there are actions, i.e. how we use a telephone.
However, the concept of telephone does not only arise in the brain when we have a telephone in front of us. It also appears when the term is merely mentioned. If we read the word "telephone", our brain also calls up the concept of telephone. The same regions in the brain are activated that would be activated ...
2021-05-07
To infect its host plant maize, the fungal parasite Ustilago maydis uses a complex of seven proteins. Numerous findings reveal an essential role of the complex in causing disease and suggest a widespread occurence in fungal plant pathogens.
Each year, fungal plant pathogens such as rusts, rice blast and mildews destroy huge amounts of cereal crops that could feed millions of people. Many of these fungi are biotrophic pathogens: Instead of killing their host plants, they manipulate host cells to assure that these sustain fungal growth. Among these pathogens, the corn smut fungus Ustilago maydis has emerged as a model for basic research on biotrophic fungi.
During the infection, U. maydis releases an entire cocktail of so-called ...
2021-05-07
7 May 2021/Kiel. Corals are the backbone of marine ecosystems in the tropics. They are threatened by rising water temperatures caused by global warming and they are among the first ecosystems worldwide that are on the verge of ecological collapse. Coral bleaching, which is becoming stronger and more frequent due to heat stress, has already wiped out corals at many locations globally. With the help of a microbiome-targeting strategy developed by an international team led by GEOMAR Helmholtz Centre for Ocean Research Kiel, it could become feasible to help protect corals from heat stress. The work has now been published in the international journal Microbiome.
Corals are the backbone of marine ecosystems in the tropics. They are threatened by rising water temperatures caused by global warming ...
2021-05-07
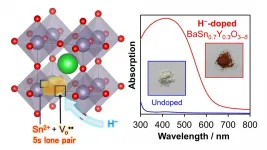
Narrow-gap semiconductors with the ability to use visible light have garnered significant interest thanks to their versatility. Now, scientists in Japan have developed and characterized a new semiconductor material for application in process components stimulated by light. The findings have, for the first time, suggested a new way to reduce the band gap in cheaper and non-toxic tin-based oxide semiconductors for efficient light-based applications.
Semiconductors that can exploit the omnipresent visible spectrum of light for different technological applications would serve as a boon to the material world. However, such semiconductors often do not come cheap and can often be toxic. Now, a group of material scientists ...
2021-05-07
May 7, 2021 - Among collegiate football players and other athletes, Black athletes recognize fewer concussion-related symptoms than their White counterparts, reports a study in the May/June issue of the Journal of Head Trauma Rehabilitation (JHTR). The official journal of the Brain Injury Association of America, JHTR is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
"Despite NCAA concussion education requirements for athletes, Black collegiate-athletes were found to have lower concussion symptom knowledge than White collegiate-athletes," according to the new research by Jessica Wallace, PhD, MPH, LAT, ATC, of University of Alabama, Tuscaloosa, and colleagues. The ...
2021-05-07
RNA-based drugs have the potential to change the standard of care for many diseases, making personalized medicine a reality. This rapidly expanding class of therapeutics are cost-effective, fairly easy to manufacture, and able to go where no drug has gone before, reaching previously undruggable pathways.
Mostly.
So far, these promising drugs haven't been very useful in getting through to the well-protected brain to treat tumors or other maladies.
Now a multi-institutional team of researchers, led by Costas Arvanitis at the Georgia Institute of Technology and Emory University, has figured out a way: using ultrasound and RNA-loaded nanoparticles to get through the protective blood-brain barrier and deliver potent medicine to brain tumors.
"We're able to make this drug more available ...
2021-05-07
Some meat eaters feel disgusted by meat, according to a new study.
University of Exeter scientists showed food pictures to more than 700 people, including omnivores (who eat meat and other foods), flexitarians (who try to eat less meat) and vegetarians.
About 7% of meat eaters (15% of flexitarians and 3% of omnivores) had a "fairly strong disgust response" to images of meat dishes commonly eaten in the UK, like roast chicken or bacon.
As a group, omnivores rated meat images about twice as disgusting on average as pictures of carbohydrate-rich foods like bread, chips and rice.
Based on the findings, the researchers say harnessing the "yuk factor" may ...
2021-05-07
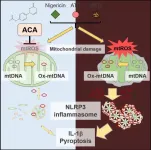
Ikoma, Japan - Many natural compounds have various anti-inflammatory and other beneficial properties that humans have been utilizing for medicinal purposes for hundreds of years. However, the specific molecular mechanisms behind these health-promoting effects are not always clear. One such compound is 1'-acetoxychavicol acetate, or ACA, which comes from the tropical ginger Alpinia plant. Now, researchers from Nara Institute of Science and Technology (NAIST) have identified how ACA can help in the treatment of inflammatory diseases.
In a report published in International Immunology, they found that ACA attenuates mitochondrial damage through decreasing mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS), blocking ...
2021-05-07
Scientists from Nanjing University and University of Macau have discovered nano-scaled apoptotic bodies (ABs) as a new brain-targeting drug carrier, bringing new promise for the Parkinson's Disease as well as other brain diseases.
The blood-brain barrier (BBB) is the most restrictive barrier that keeps most biomolecules and drugs from the brain, setting "barriers" for the treatment of cerebrovascular diseases. With the increasingly serious ageing problem, the treatment of brain diseases now faces tough challenges, and therefore efficient brain drug delivery ...
2021-05-07
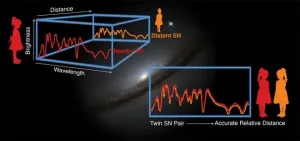
Cosmologists have found a way to double the accuracy of measuring distances to supernova explosions - one of their tried-and-true tools for studying the mysterious dark energy that is making the universe expand faster and faster. The results from the Nearby Supernova Factory (SNfactory) collaboration, led by Greg Aldering of the Department of Energy's Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab), will enable scientists to study dark energy with greatly improved precision and accuracy, and provide a powerful crosscheck of the technique across vast distances ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Study helps to better understand the link between indoor and outdoor air quality