(Press-News.org) Narrow-gap semiconductors with the ability to use visible light have garnered significant interest thanks to their versatility. Now, scientists in Japan have developed and characterized a new semiconductor material for application in process components stimulated by light. The findings have, for the first time, suggested a new way to reduce the band gap in cheaper and non-toxic tin-based oxide semiconductors for efficient light-based applications.
Semiconductors that can exploit the omnipresent visible spectrum of light for different technological applications would serve as a boon to the material world. However, such semiconductors often do not come cheap and can often be toxic. Now, a group of material scientists from Tokyo Institute of Technology and Kyushu University have collaborated to develop a cheaper and non-toxic narrow-gap semiconductor material with potential 'light-based' or photofunctional applications, according to a recent study published in Chemistry of Materials.
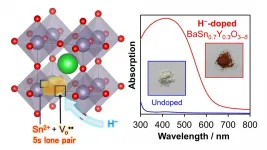
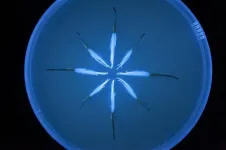
Tin-containing oxide semiconductors are cheaper than most semiconductor materials, but their photofunctional applications are constrained by a wide optical band gap. The aforementioned team of scientists, led by Dr. Kazuhiko Maeda, Associate Professor at the Department of Chemistry, Tokyo Institute of Technology, developed a perovskite-based semiconductor material that is free of toxic lead and can absorb a wide range of visible light (Figure 1). The team "doped," or intentionally introduced, hydride ions into the tin-containing semiconductor material. In doing so, they successfully reduced the band gap from 4 eV to 2 eV, due to the chemical reduction of the tin component that accompanied the hydride ion doping.
The scientists were also able to pinpoint a crucial tin reduction reaction in the semiconductor material through physicochemical measurements. This reduction leads to the generation of a "tin lone electron pair," whose different electronic states notably contribute to the visible light absorption of the material. They also attribute this desired property to the prior introduction of oxygen defects into the material. Highlighting the importance of the oxygen defects, Dr. Maeda, who is also a corresponding author of the study, explains, "The prior introduction of oxygen defects into BaSnO3 by Y3+ substitution for Sn4+ is also indispensable to realize a significant reduction of the band gap."
To confirm that the developed semiconductor material is indeed photofunctional, the scientists tested the applicability of the semiconductor material in a photoelectrode. They observed that the developed material gave a clear anodic photoresponse up to the expected 600 nm.
Speaking about the impact of the study, Dr. Katsuro Hayashi, Professor of the Faculty of Engineering, Kyushu University, and the other corresponding author of the study, says, "Overall, the study has enabled a giant leap in the development of a cheaper, non-toxic, narrow optical band gap, tin-containing semiconductor material for practical applications in solar cells, photocatalysis and pigments."
Thanks to the efforts of the researchers, we can expect significant advancements in the development of several more novel lead-free visible-light absorbing materials with myriad applications.
INFORMATION:
About Tokyo Institute of Technology
Tokyo Tech stands at the forefront of research and higher education as the leading university for science and technology in Japan. Tokyo Tech researchers excel in fields ranging from materials science to biology, computer science, and physics. Founded in 1881, Tokyo Tech hosts over 10,000 undergraduate and graduate students per year, who develop into scientific leaders and some of the most sought-after engineers in industry. Embodying the Japanese philosophy of "monotsukuri," meaning "technical ingenuity and innovation," the Tokyo Tech community strives to contribute to society through high-impact research.
https://www.titech.ac.jp/english/
About Kyushu University
Kyushu U is one of Japan's leading research-oriented institutes of higher education since its foundation in 1911. Home to around 19,000 students and 8,000 faculty and staff, Kyushu U is making advances in medicine, sustainable energy technologies, materials, and more from its highly accessible location on the southwestern Japanese island of Kyushu in Fukuoka City, a coastal metropolis frequently ranked among the world's most livable cities and historically known as a gateway to Asia.
https://www.kyushu-u.ac.jp/en/
About Dr. Kazuhiko Maeda
Dr. Kazuhiko Maeda is an Associate Professor at Associate Professor at Department of Chemistry, School of Science, Tokyo Institute of Technology. Dr. Maeda's focus areas of research include heterogeneous photocatalysis, solar energy conversion, photoelectrode, layered compounds, water splitting, hydrogen production, and CO2 reduction. He is a member of esteemed academic institutions like The Chemical Society of Japan, Catalysis Society of Japan, and The Japanese Photochemistry Association. He has over 250 publication as journal and conference papers, and books, among others. He is the recipient of several prestigious awards and prizes, like Highly Cited Researchers 2018-2020, from Clarivate Analytics.
May 7, 2021 - Among collegiate football players and other athletes, Black athletes recognize fewer concussion-related symptoms than their White counterparts, reports a study in the May/June issue of the Journal of Head Trauma Rehabilitation (JHTR). The official journal of the Brain Injury Association of America, JHTR is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
"Despite NCAA concussion education requirements for athletes, Black collegiate-athletes were found to have lower concussion symptom knowledge than White collegiate-athletes," according to the new research by Jessica Wallace, PhD, MPH, LAT, ATC, of University of Alabama, Tuscaloosa, and colleagues. The ...
RNA-based drugs have the potential to change the standard of care for many diseases, making personalized medicine a reality. This rapidly expanding class of therapeutics are cost-effective, fairly easy to manufacture, and able to go where no drug has gone before, reaching previously undruggable pathways.
Mostly.
So far, these promising drugs haven't been very useful in getting through to the well-protected brain to treat tumors or other maladies.
Now a multi-institutional team of researchers, led by Costas Arvanitis at the Georgia Institute of Technology and Emory University, has figured out a way: using ultrasound and RNA-loaded nanoparticles to get through the protective blood-brain barrier and deliver potent medicine to brain tumors.
"We're able to make this drug more available ...
Some meat eaters feel disgusted by meat, according to a new study.
University of Exeter scientists showed food pictures to more than 700 people, including omnivores (who eat meat and other foods), flexitarians (who try to eat less meat) and vegetarians.
About 7% of meat eaters (15% of flexitarians and 3% of omnivores) had a "fairly strong disgust response" to images of meat dishes commonly eaten in the UK, like roast chicken or bacon.
As a group, omnivores rated meat images about twice as disgusting on average as pictures of carbohydrate-rich foods like bread, chips and rice.
Based on the findings, the researchers say harnessing the "yuk factor" may ...
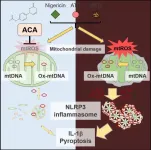
Ikoma, Japan - Many natural compounds have various anti-inflammatory and other beneficial properties that humans have been utilizing for medicinal purposes for hundreds of years. However, the specific molecular mechanisms behind these health-promoting effects are not always clear. One such compound is 1'-acetoxychavicol acetate, or ACA, which comes from the tropical ginger Alpinia plant. Now, researchers from Nara Institute of Science and Technology (NAIST) have identified how ACA can help in the treatment of inflammatory diseases.
In a report published in International Immunology, they found that ACA attenuates mitochondrial damage through decreasing mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS), blocking ...
Scientists from Nanjing University and University of Macau have discovered nano-scaled apoptotic bodies (ABs) as a new brain-targeting drug carrier, bringing new promise for the Parkinson's Disease as well as other brain diseases.
The blood-brain barrier (BBB) is the most restrictive barrier that keeps most biomolecules and drugs from the brain, setting "barriers" for the treatment of cerebrovascular diseases. With the increasingly serious ageing problem, the treatment of brain diseases now faces tough challenges, and therefore efficient brain drug delivery ...
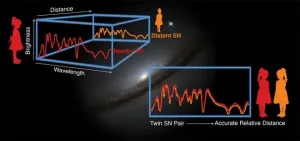
Cosmologists have found a way to double the accuracy of measuring distances to supernova explosions - one of their tried-and-true tools for studying the mysterious dark energy that is making the universe expand faster and faster. The results from the Nearby Supernova Factory (SNfactory) collaboration, led by Greg Aldering of the Department of Energy's Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab), will enable scientists to study dark energy with greatly improved precision and accuracy, and provide a powerful crosscheck of the technique across vast distances ...
Computer science researchers at the University of Central Florida have developed a sarcasm detector.
Social media has become a dominant form of communication for individuals, and for companies looking to market and sell their products and services. Properly understanding and responding to customer feedback on Twitter, Facebook and other social media platforms is critical for success, but it is incredibly labor intensive.
That's where sentiment analysis comes in. The term refers to the automated process of identifying the emotion -- either positive, negative or neutral -- associated with text. While ...
Tsukuba, Japan - Scientists from the Faculty of Health and Sports Sciences at the University of Tsukuba used aerodynamics experiments to empirically test the flight properties of a new four-panel soccer ball adopted by the English Premier League this year. Based on projectile and wind-tunnel data, they computed the drag and side forces and found that the new ball was marginally more stable than previous versions but may not fly as far. This work may help improve the design of future sports equipment.
Sports players know that millions of dollars in salary and potential endorsement deals can be at stake during each match. Soccer players often complain about the aerodynamic ...
Researchers have traced the remaining last steps of the biological pathway that gives oats resistance to the deadly crop disease take-all.
The discovery creates opportunities for new ways of defending wheat and other cereals against the soil-borne root disease.
The research team have already taken the first step in this aim by successfully reconstituting the self-defence system in the model plant Nicotiana benthamiana.
Further experiments to establish the avenacin biosynthetic pathway in wheat's more complex genome, to test if it will provide the same resistance ...
They may be tiny weapons, but Brigham Young University's holography research group has figured out how to create lightsabers -- green for Yoda and red for Darth Vader, naturally -- with actual luminous beams rising from them.
Inspired by the displays of science fiction, the researchers have also engineered battles between equally small versions of the Starship Enterprise and a Klingon Battle Cruiser that incorporate photon torpedoes launching and striking the enemy vessel that you can see with the naked eye.
"What you're seeing in the scenes we create is real; there is nothing computer generated about them," said lead researcher Dan Smalley, a professor of electrical engineering at BYU. "This is not like the movies, where the lightsabers ...