New study explores functionality in aquatic ecosystems
The functions of water-dominated ecosystems can be considerably influenced and changed by hydrological fluctuation; the varying states of redox-active substances are of crucial importance here
2021-05-07
(Press-News.org) The functions of water-dominated ecosystems can be considerably influenced and changed by hydrological fluctuation. The varying states of redox-active substances are of crucial importance here. Researchers at the University of Bayreuth have discovered this, in cooperation with partners from the Universities of Tübingen and Bristol and the Helmholtz Centre for Environmental Research, Halle-Leipzig. They present their discovery in the journal Nature Geoscience. The new study enables a more precise understanding of the biogeochemical processes that contribute to the degradation of pollutants and the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions.
Reducing the generation of greenhouse gases, storing carbon, removing environmental pollutants such as nitrate, and providing high-quality drinking water - these are important services provided by aquatic ecosystems, such as lakes, streams, marshes, and bogs. The functions of such aquatic ecosystems are closely linked to the cycles of oxygen, nitrogen, carbon, and other elements in nature. It has long been known that elemental cycles are interconnected biogeochemical processes that can be significantly influenced by hydrological fluctuation. Examples of this are fluctuations in the water level of wetlands, peatlands, and groundwater, or even changing flow directions in groundwater.
The research team led by Prof. Dr. Stefan Peiffer at the University of Bayreuth has now succeeded in understanding the dependence of element cycles on hydrological fluctuation more precisely. As numerous laboratory studies have shown, redox-active substances have a key function in this. "Anyone who has ever trudged through a swamp or rummaged in the sand of a swimming lake will have noticed these substances because of their variety of colour. In a very confined space, colour shades alternate from deep black to grey and brown to light red. What is behind this, is an interplay of microbiological and chemical processes in which electrons are being transferred. In research, we call them redox reactions," says Peiffer.
A comparatively simple form of redox reaction is respiration in humans and animals. Carbon is oxidised by oxygen to form carbon dioxide. In the microbially driven redox reactions that take place in a swamp, for example, the role of oxygen is taken over by a variety of redox-active substances - iron, sulphur, and manganese compounds or humic substances. The life span of these substances is very short, but they show a very strong tendency to engage in redox reactions. They are therefore called "redox-active metastable phases" (RAMPs). Due to their high reactivity, RAMPs play a major role in elemental cycles in ecosystems. For example, they are able to degrade pollutants such as nitrates or various other organic chemicals.
One reason for the short lifespan of RAMPs is the constant change between electron-donating and electron-accepting conditions. The study, published in Nature Geoscience, comes to a conclusion decisive for ecological and environmental research. The dynamics of the redox reactivity of RAMPs is triggered by hydrological fluctuations that occur in shore zones, in wetlands, in waterlogged soils, in rice-growing soils or at the surface of sediments in lakes and rivers. These small-scale biogeochemical reactions, in turn, influence the large-scale reactions of the ecosystem, for example, the amount of greenhouse gases released into the atmosphere. This makes it understandable for the first time how hydrological fluctuations, for example fluctuating water levels, affect elemental cycles in nature, and thus the functioning of ecosystems.
"Our study shows that biogeochemical reactions on a scale of only a few micrometres form an important crux between two large-scale processes: between hydrological fluctuations on the one hand, and ecosystem functions on the other. Our new findings will therefore help to better predict pollutant degradation in aquatic ecosystems in future. The consequences of climate change for carbon and nitrogen conversion in these ecosystems may also be more accurately assessed in future," says Peiffer.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-07
More than ever, patients are using telehealth to ask doctors and nurses about worrying blood-pressure readings, nauseating migraines and stubborn foot ulcers. But for patients with chronic conditions, how frequent should telehealth appointments be? Can that frequency change? Under what conditions?
West Virginia University researcher Jennifer Mallow is trying to answer these questions. In a new project, she and her colleagues completed a systematic review of studies that dealt with telehealth and chronic conditions. They found that--in general--telehealth services benefitted patients more if they ...
2021-05-07
A comprehensive review into what we know about COVID-19 and the way it functions suggests the virus has a unique infectious profile, which explains why it can be so hard to treat and why some people experience so-called "long-COVID", struggling with significant health issues months after infection.
There is growing evidence that the virus infects both the upper and lower respiratory tracts - unlike "low pathogenic" human coronavirus sub-species, which typically settle in the upper respiratory tract and cause cold-like symptoms, or "high pathogenic" viruses such as those that cause SARS and ARDS, which typically settle in the lower respiratory tract.
Additionally, more frequent multi-organ impacts, and blood clots, and ...
2021-05-07
Which wound cuts deeper: the loss of an only child or loss of a spouse? A new study led by researchers at NYU Rory Meyers College of Nursing and Fudan University suggests that Chinese parents find the loss of an only child to be approximately 1.3 times as psychologically distressing than the loss of a spouse. The findings are published in the journal Aging & Mental Health.
Older adults in China rely heavily on family support, particularly from their adult children. Filial piety--the Confucian idea describing a respect for one's parents and responsibility for adult children to care for ...
2021-05-07
Observing how cells stick to surfaces and their motility is vitally important in the study of tissue maintenance, wound healing and even understanding how cancers progress. A new paper published in EPJ Plus, by Raj Kumar Sadhu, Weizmann Institute of Science, Rehovot, Israel, takes a step towards a deeper understanding of these processes.
"Cell adhesion is the ability of a cell to stick to another cell or an extracellular matrix. This process is important in order to understand how cells interact and coordinate their behaviour in multicellular organisms," says sadhu. "We theoretically model the adhesion of a cell-like vesicle by describing the cell as a three-dimensional vesicle adhering on a flat substrate with a constant adhesion interaction."
Alongside ...
2021-05-07
Neuroblastoma is a childhood cancer, most commonly affecting children aged between 2 -3 and can be fatal. Since the tumour cells resemble certain cells in the adrenal glands, a joint research group from MedUni Vienna's Center for Brain Research and the Swedish Karolinska Institute investigated the cellular origin of these cells and sympathetic neurons during the embryonic development of human adrenal glands. During the course of their investigations, they discovered a previously unknown cell type that might potentially be the origin of the tumour cells.
Treatments for this disease are extremely aggressive and challenging ...
2021-05-07
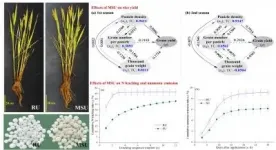
The applied nitrogen in crop production is easily lost through ammonia emission and nitrogen leaching. Therefore, many attempts have been made on the development of novel slow-release fertilizers to reduce nitrogen loss and improve crop production.
A research team led by Prof. WU Yuejin from the Institute of Intelligent Machines of the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science developed a novel matrix-based slow-release urea (MSU) recently to improve nitrogen use efficiency in rice production, and they assessed the performances of it.
"MSU is a promising fertilizer for rice production," said WU, "as less nitrogen loss and greater soil nitrogen ...
2021-05-07
Physicists at Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg (FAU) have for the first time been able to prove a long-predicted but as yet unconfirmed fundamental effect. In Faraday chiral anisotropy, the propagation characteristics of light waves are changed simultaneously by the natural and magnetic-field induced material properties of the medium through which the light travels. The researchers obtained proof that this is the case by conducting experiments using nickel helices at the nanometre scale. Their findings have now been published in the academic journal 'Physical Review Letters'.
Light is transmitted as sine waves consisting of crossed electric and magnetic fields and interacts with matter. This ...
2021-05-07
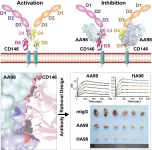
Recently, Prof. XIE Can from the High Magnetic Field Laboratory of the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS), in a collaboration with Prof. YAN Xiyun's lab from the Institute of Biophysics, reported the structural basis of mAb AA98's inhibition on CD146-mediated endothelial cells (EC) activation and designed higher affinity monoclonal antibody HA98 for cancer treatment.
CD146 is an adhesion molecule that plays important roles in angiogenesis, cancer metastasis, and immune response. Prof. YAN Xiyun's lab has been focused on the function of CD146 and the mechanism ...
2021-05-07
Australia, the driest inhabited continent, is prone to natural disasters and wild swings in weather conditions - from floods to droughts, heatwaves and bushfires.
Now two new Flinders University studies of long-term hydro-climatic patterns provide fresh insights into the causes of the island continent's strong climate variability which affect extreme wet or dry weather and other conditions vital to water supply, agriculture, the environment and the nation's future.
For the first time, researchers from the National Centre for Groundwater Research and Training (NCGRT) at Flinders have revealed a vegetation-mediated seesaw wetting-drying phenomenon between eastern and western Australia. ...
2021-05-07
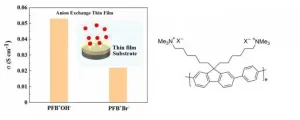
Ishikawa, Japan - As decarbonization progresses rapidly in the world, fuel cells offer potentially higher electrical efficiency than conventional power-generating systems. Anion exchange membrane fuel cells offer advantages of using non-precious metal catalysts than proton exchange membrane fuel cells. One of the challenges of this next-generation fuel cell is to clarify the hydroxide ion conductivity in the ion conductive polymer around the electrode catalyst. The difficulty of studying the hydroxide ion conductivity at the electrode interface is that the hydroxide ion, which is a carrier, easily reacts with carbon dioxide in the air. To solve this problem, all evaluation devices were improved so that the sample did not come into contacting with air.
In a new study published ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New study explores functionality in aquatic ecosystems
The functions of water-dominated ecosystems can be considerably influenced and changed by hydrological fluctuation; the varying states of redox-active substances are of crucial importance here