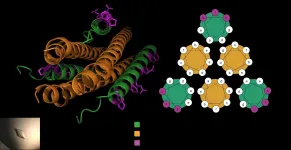
How Legionella makes itself at home
Protein remodels intracellular membrane to help bacteria survive in host cells
2021-05-10
(Press-News.org) DALLAS - May 10, 2021 - Scientists at UT Southwestern have discovered a key protein that helps the bacteria that causes Legionnaires' disease to set up house in the cells of humans and other hosts. The findings, published in Science, could offer insights into how other bacteria are able to survive inside cells, knowledge that could lead to new treatments for a wide variety of infections.
"Many infectious bacteria, from listeria to chlamydia to salmonella, use systems that allow them to dwell within their host's cells," says study leader Vincent Tagliabracci, Ph.D., assistant professor of molecular biology at UTSW and member of the Harold C. Simmons Comprehensive Cancer Center. "Better understanding the tools they use to make this happen is teaching us some interesting biochemistry and could eventually lead to new targets for therapy."
Tagliabracci's lab studies atypical kinases, unusual forms of enzymes that transfer chemical groups called phosphates onto proteins or lipids, changing their function. Research here and elsewhere has shown that Legionella, the genus of bacteria that cause Legionnaires' disease, is a particularly rich source of these noncanonical kinases. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, nearly 10,000 cases of Legionnaires' disease were reported in the U.S. in 2018, though the true incidence is believed to be higher.
After identifying a new Legionella atypical kinase named MavQ, Tagliabracci and his colleagues used a live-cell imaging technique combined with a relatively new molecular tagging method to see where MavQ is found in infected human cells, a clue to its function. Rather than residing in a specific location, the researchers were surprised to see that the protein oscillated back and forth between the endoplasmic reticulum - a network of membranes important for protein and lipid synthesis - and bubble- or tube-shaped structures within the cell.
Further research suggests that MavQ, along with a partner molecule called SidP, remodels the endoplasmic reticulum so that Legionella can steal parts of the membrane to help create and sustain the vacuole, a structure that houses the parasite inside cells and protects it from immune attack.
Tagliabracci, a Michael L. Rosenberg Scholar in Medical Research and a Cancer Prevention & Research Institute of Texas (CPRIT) Scholar, says that he suspects other bacterial pathogens may use similar mechanisms to co-opt existing host cell structures to create their own protective dwellings.
INFORMATION:
UTSW scientists who contributed to this study include Ting-Sung Hsieh, Victor A. Lopez, Miles H. Black, Adam Osinski, Krzysztof Pawlowski, Diana R. Tomchick, and Jen Liou, a Sowell Family Scholar in Medical Research.
This work was funded by NIH grants DP2GM137419, R01GM113079, T32GM008203-29, F30HL143859-01, Welch Foundation grants I-1911, I-1789, CPRIT grant RP170674, and Polish National Agency for Scientific Exchange scholarship PPN/BEK/2018/1/00431.
About UT Southwestern Medical Center
UT Southwestern, one of the premier academic medical centers in the nation, integrates pioneering biomedical research with exceptional clinical care and education. The institution's faculty has received six Nobel Prizes, and includes 25 members of the National Academy of Sciences, 17 members of the National Academy of Medicine, and 13 Howard Hughes Medical Institute Investigators. The full-time faculty of more than 2,800 is responsible for groundbreaking medical advances and is committed to translating science-driven research quickly to new clinical treatments. UT Southwestern physicians provide care in about 80 specialties to more than 117,000 hospitalized patients, more than 360,000 emergency room cases, and oversee nearly 3 million outpatient visits a year.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-10
Many have assumed that the rates of major abdominal surgeries in adults over 65 is increasing over time as the U.S. population ages and as new technology renders surgical procedures safer for older adults. Contrary to this popular belief, a new study from the University of Chicago Medicine found the frequency of abdominal surgery in older adults is decreasing, especially among adults over the age of 85. The study, which examined data from 2002 to 2014, was published May 10 in the Journal of the American Geriatric Society.
While the research was not able to determine the exact reasons for this shift, the results indicate that improvements ...
2021-05-10
The relationship a dog has with its owner is related to its stress level. This is the conclusion of a newly published study from Linköping University, Sweden. The results, published in the journal Scientific Reports, also suggest that the link between stress and the owner's personality traits differs between dog breeds.
Researchers at Linköping University have investigated whether the stress levels of dogs are affected by the people they live with. Stress levels for the past several months can be determined in both dogs and humans by measuring the levels of stress hormone stored in hairs as they grow.
The researchers have collected hair from both dogs and owners, and measured levels of cortisol, the most important stress hormone, in them. They were interested in whether there ...
2021-05-10
For organizations to reach their potential, they must leverage the expertise of their employees. However, research demonstrates that lower-status employees may not be heard because their "voices" are more likely to be ignored.
New research from the University of Notre Dame is the first to show that peers can help boost marginalized voices, and at the same time benefit their own status, all while helping their organization realize the potential of its employees' diverse perspectives.
Publicly endorsing -- or amplifying -- another person's contribution, while giving attribution to that person, enhances the status of both parties, according to "Amplifying Voice in Organizations," ...
2021-05-10
Due to their complexity and microscopic scale, plant-microbe interactions can be quite elusive. Each researcher focuses on a piece of the interaction, and it is hard to find all the pieces let alone assemble them into a comprehensive map to find the hidden treasures within the plant microbiome. This is the purpose of review, to take all the pieces from all the different sources and put them together into something comprehensive that can guide researchers to hidden clues and new associations that unlock the secrets of a system. Like any good treasure map, there are still gaps in the knowledge and the searcher must be clever enough to fill in those gaps to find the "X". Without a map, there is only aimless wandering, but with a map, there is hope of finding the hidden ...
2021-05-10
When a loved one dies, memories of that person become particularly valuable in connecting the mourners with the deceased. A new Weill Cornell Medicine online application, called Living Memory Home, offers a virtual and personal memorial space that allows mourners to deposit their memories and feelings about their loss and honor their loved one.
Living Memory Home users are able to create a memorial space that they can personalize with photos and messages. They can customize a virtual cabin and choose an appropriate view. The curated set of questions prompt users to write memories ...
2021-05-10
AMES, Iowa - New variants of the SARS-CoV-2 virus most likely will necessitate the development of more vaccine options in the years ahead, and a biomedical scientist at Iowa State University believes the "key" to that development lies in the way the virus binds to human cells.
Michael Cho, a professor of biomedical sciences at Iowa State, is studying how to develop COVID-19 vaccines that target SARS-CoV-2's receptor-binding domain, or the part of the virus that docks with the host cellular receptor, angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2). This docking process allows the virus access to the host's cells, which leads to infection.
Cho was the lead author of a study recently published in the peer-reviewed scientific journal Frontiers in Immunology detailing the ability of a vaccine ...
2021-05-10
Unlike the oscillations of sound waves, the oscillations of light are so fast that extremely complex equipment is needed to observe them directly. However, it is possible to measure the frequencies of these oscillations indirectly with frequency combs. These combs are made up of a set of regularly spaced "teeth" where each tooth corresponds to a frequency. Used as a graduated ruler, they offer the possibility of measuring an optical frequency with great precision. This makes it possible, among other things, to measure variations in the distance between the Earth and the Moon with an accuracy ...
2021-05-10
MADISON - By engineering a short chunk of protein, or peptide, that can prevent the attachment of human parainfluenza viruses to cells, researchers have improved a method in rodent models intended to help keep children healthy.
Human parainfluenza viruses, or HPIVs, are the leading cause of childhood respiratory infections, responsible for 30% to 40% of illnesses like croup and pneumonia. The viruses also affect the elderly and people with compromised immune systems.
To sicken people, HPIVs must latch onto cells and inject their genetic material to start making new viruses. HPIV3 is the most prevalent among these viruses. ...
2021-05-10
Autistic people have far greater risks of long term physical health conditions than others, but the reasons for this remain unclear. New research from the University of Cambridge suggests that unhealthy lifestyle habits may be an important contributing factor. The results are published today in the journal Molecular Autism.
Earlier research suggests that autistic people die 16-35 years younger than expected, and that greater health problems may contribute to this risk. The present study is the first to consider the diet, exercise, and sleep patterns of autistic adults and how these patterns may relate to health outcomes.
The team at the Autism Research Centre in Cambridge developed an anonymous, online survey about lifestyle choices and daily habits, personal medical history, ...
2021-05-10
The Covid-19 pandemic, like many other health crises, has had unequal effects on the U.S. population, with communities of color often hit the hardest. A new study co-authored by an MIT professor identifies a related challenge: Different social groups have different reactions to the fact that Covid-19 has generated those health inequities.
More specifically, the study, based on a multilayered survey of U.S. residents, finds a divergence among racial groups when people are informed about the varying effects of the pandemic. Upon learning more about the social distribution of Covid-19, Black Americans tend to gain a better understanding of their risk. But among white Americans given the same information, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] How Legionella makes itself at home
Protein remodels intracellular membrane to help bacteria survive in host cells