Even when they include them, gifted programs aren't serving Black or low-income kids
2021-05-10
(Press-News.org) After years of criticism for their lack of diversity, programs for high achievers may not be adequately serving their Black and low-income students, a new study shows.
"The potential benefits aren't equally distributed," said lead author and University of Florida College of Education professor Christopher Redding, Ph.D., who evaluated data from gifted programs in elementary schools nationwide. "The conversation up to this point has been about access, with less emphasis on how students perform once in gifted programs."
While academic achievement gains for students overall were modest -- going from the 78th to 80th percentile in reading and rising only a third as much in math -- low-income and Black gifted students, on average, saw no achievement gains. When the researchers looked at factors beyond scores, including engagement, attendance, and whether a student left or stayed in a school, they found little evidence to suggest gifted participation influenced those measures for any group.
"We're not saying these programs don't have benefits," Redding said. "But as states and school districts evaluate them, we need to ask, 'How can we do this best both for all gifted students and for diverse student populations?'"
A barrier to effectively serving a diverse gifted population could be the programs' content. If the curriculum only reflects the affluent, predominantly white population that gifted has traditionally served, it might not meet the needs of its other students, Redding says. As a success story, he points to the example of Illinois' second-largest school district, which diversified its curriculum -- but the impetus for that shift was a federal class-action suit.
"Unfortunately, unless there's this strong pressure from the courts, lots of districts aren't taking these steps that could be taken," Redding said.
Another culprit could be the structure of the programs. While some students receive all-day gifted instruction, others might only get an hour every other week. In "light touch" programs like those, a better option might be what education researchers call acceleration: skipping a grade or taking fifth grade math while in fourth grade, for example.
Redding doesn't want to see gifted programs go away, but he wants educators to take a hard look at how their curriculum meshes with the students they're trying to reach -- and for policymakers to have a better understanding of what the programs are actually achieving.
"It's not just about access," he said.
INFORMATION:
The study, done with Jason A. Grissom of Vanderbilt University, was published in the journal Educational Evaluation and Policy Analysis.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-10
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- Log on to any app store, and parents will find hundreds of options for children that claim to be educational. But new research suggests these apps might not be as beneficial to children as they seem.
A new study analyzed some of the most downloaded educational apps for kids using a set of four criteria designed to evaluate whether an app provides a high-quality educational experience for children. The researchers found that most of the apps scored low, with free apps scoring even lower than their paid counterparts on some criteria.
Jennifer Zosh, associate professor of human development ...
2021-05-10
Recurrent, metastatic breast cancer resists treatment and is usually fatal.
These tumors often have low numbers of immune cells in them, which renders immune therapies less effective for the disease.
This preclinical study suggests that drugs called CDK4 and CDK6 inhibitors may make immune-cell therapies an effective option for treating recurrent ER-positive metastatic breast cancer.
COLUMBUS, Ohio - A class of drugs that inhibits breast cancer progression when used with hormonal therapy might also boost the effectiveness of immune therapy in cases of recurrent, metastatic breast cancer, according to a new study led by researchers at The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center - Arthur G. James Cancer Hospital ...
2021-05-10
A new survey led by researchers from North Carolina State University found that the future of hunting in the United States might look different than it has in the past.
In The Journal of Wildlife Management, researchers reported findings from a nationwide survey of college students' interest and participation in hunting. They found current, active hunters were more likely to be white, male and from rural areas, and to have family members who hunted. But they also found a group of potential hunters - with no hunting experience but an interest in trying it - who were more diverse in terms of gender, ...
2021-05-10
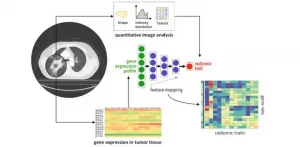
Despite our remarkable advances in medicine and healthcare, the cure to cancer continues to elude us. On the bright side, we have made considerable progress in detecting several cancers in earlier stages, allowing doctors to provide treatments that increase long-term survival. The credit for this is due to "integrated diagnosis," an approach to patient care that combines molecular information and medical imaging data to diagnose the cancer type and, eventually, predict treatment outcomes.
There are, however, several intricacies involved. The correlation of molecular patterns, such as gene expression and mutation, with image features (e.g., how a tumor appears in a CT scan), is ...
2021-05-10
HOUSTON - (May 10, 2021) - Implants that require a steady source of power but don't need wires are an idea whose time has come.
Now, for therapies that require multiple, coordinated stimulation implants, their timing has come as well.
Rice University engineers who developed implants for electrical stimulation in patients with spinal cord injuries have advanced their technique to power and program multisite biostimulators from a single transmitter.
A peer-reviewed paper about the advance by electrical and computer engineer Kaiyuan Yang and his colleagues at Rice's Brown School of Engineering won the best paper award at the IEEE's Custom Integrated Circuits Conference, held virtually in the last ...
2021-05-10
According to the International Whaling Commission, whale-watching tourism generates more than $2.5 billion a year. After the COVID-19 pandemic, this relatively safe outdoor activity is expected to rebound. Two new studies funded by a collaborative initiative between the Smithsonian Tropical Research Institute (STRI) in Panama and Arizona State University (ASU) show how science can contribute to whale watching practices that ensure the conservation and safety of whales and dolphins.
"The Smithsonian's role is to provide scientific advice to policy makers as they pioneer management strategies to promote whale conservation," said STRI marine biologist, Hector Guzmán, whose previous work led the International Maritime Organization to establish shipping corridors ...
2021-05-10
ATLANTA--Gestures--such as pointing or waving--go hand in hand with a child's first words, and twins lag behind single children in producing and using those gestures, two studies from Georgia State University psychology researchers show.
Twins produce fewer gestures and gesture to fewer objects than other children, said principal researcher Seyda Ozcaliskan, an associate professor in the Department of Psychology. Language use also lags for twins, and language--but not gesture--is also affected by sex, with girls performing better than boys, Ozcaliskan said.
"The implications are fascinating," said Ozcaliskan. ...
2021-05-10
MISSOULA - University of Montana Professor Mark Hebblewhite has joined an international team of 92 scientists and conservationists to create the first-ever global atlas of ungulate (hoofed mammal) migrations.
Working in partnership with the Convention on the Conservation of Migratory Species of Wild Animals, a U.N. treaty, the Global Initiative on Ungulate Migration (GIUM) launches May 7 with the publication of a commentary in Science titled " END ...
2021-05-10
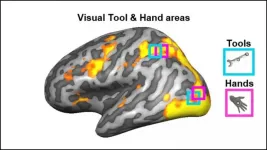
Visual brain areas involved in processing hands also encode information about the correct way to hold tools, according to new research published in JNeurosci.
Each part of the brain's visual system activates in response to a certain type of item -- whether it's faces, tools, objects, or hands. Scientists assumed the brain segregates visual information in this way to optimize motor actions with tools. Yet most studies investigating the brain mechanisms for tool grasping used images of tools or hands, and no actual hand movements were performed.
Knights et al. used fMRI to measure the brain activity of participants as they grasped 3D-printed kitchen tools (spoon, knife, and pizza cutter) and similar-sized non-tools. ...
2021-05-10
Researchers at the University of East Anglia have made an astonishing discovery about how our brains control our hands.
They used MRI data to study which parts of the brain are used when we handle tools, such as a knives.
They read out the signal from certain brain regions and tried to distinguish when participants handled tools appropriately for use.
Humans have used tools for millions of years, but this research is the first to show that actions such grasping a knife by its handle for cutting are represented by brain areas that also represent images of human hands, our primary 'tool' for interacting with the world.
The research ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Even when they include them, gifted programs aren't serving Black or low-income kids