Electromagnetic levitation whips nanomaterials into shape
Electromagnetic field directs shape formed by gas phase metal molecules
2021-05-11
(Press-News.org) In order for metal nanomaterials to deliver on their promise to energy and electronics, they need to shape up -- literally.
To deliver reliable mechanical and electric properties, nanomaterials must have consistent, predictable shapes and surfaces, as well as scalable production techniques. UC Riverside engineers are solving this problem by vaporizing metals within a magnetic field to direct the reassembly of metal atoms into predictable shapes. The research is published in The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters.
Nanomaterials, which are made of particles measuring 1-100 nanometers, are typically created within a liquid matrix, which is expensive for bulk production applications, and in many cases cannot make pure metals, such as aluminum or magnesium. More economical production techniquess typically involve vapor phase approaches to create a cloud of particles condensing from the vapor. These suffer from a lack of control.
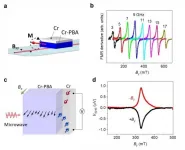
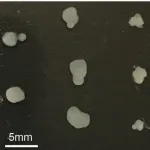
Reza Abbaschian, a distinguished professor of mechanical engineering; and Michael Zachariah, a distinguished professor of chemical and environmental engineering at UC Riverside's Marlan and Rosemary Bourns College of Engineering; joined forces to create nanomaterials from iron, copper, and nickel in a gas phase. They placed solid metal within a powerful electromagnetic levitation coil to heat the metal beyond its melting point, vaporizing it. The metal droplets levitated in the gas within the coil and moved in directions determined by their inherent reactions to magnetic forces. When the droplets bonded, they did so in an orderly fashion that the researchers learned they could predict based on the type of metal and how and where they applied the magnetic fields.
Iron and nickel nanoparticles formed string-like aggregates while copper nanoparticles formed globular clusters. When deposited on a carbon film, iron and nickel aggregates gave the film a porous surface, while carbon aggregates gave it a more compact, solid surface. The qualities of the materials on the carbon film mirrored at larger scale the properties of each type of nanoparticle.
Because the field can be thought of as an "add-on," this approach could be applied to any vapor-phase nanoparticle generation source where the structure is important, such as fillers used in polymer composites for magnetic shielding, or to improve electrical or mechanical properties.
"This 'field directed' approach enables one to manipulate the assembly process and change the architecture of the resulting particles from high fractal dimension objects to lower dimension string-like structures. The field strength can be used to manipulate the extent of this arrangement," Zachariah said.
INFORMATION:
Abbaschian and Zachariah were joined in the research by Pankaj Ghildiyal, Prithwish Biswas, Steven Herrera, George W. Mulholland, and Yong Yang. The paper, "Magnetic-field directed vapor-phase assembly of low fractal dimension metal nanostructures: experiment and theory," is available here.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-11
Almost half (47.5%) of women with babies aged six months or younger met the threshold for postnatal depression during the first COVID-19 lockdown, more than double average rates for Europe before the pandemic (23%), finds a new study led by UCL researchers.
Women described feelings of isolation, exhaustion, worry, inadequacy, guilt, and increased stress. Many grieved for what they felt were lost opportunities for them and their baby, and worried about the developmental impact of social isolation on their new little one.
Those whose partners were unable or unavailable to help with parenting and domestic ...
2021-05-11
Air quality in Spain temporarily improved during the first wave of COVID-19, largely as a result of mobility restrictions. Until recently, however, the effect of this improvement on the health of the population was poorly understood. A new study led by the Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal), a centre supported by the "la Caixa" Foundation, together with the Barcelona Supercomputing Center (BSC-CNS), has estimated that this improvement in air quality prevented around 150 premature deaths in Spain's provincial capital cities.
Several analyses have estimated the mortality reduction from improved ...
2021-05-11
The tightly defined ratios of metals in MOFs makes them ideal starting materials for novel catalyst creation.
Heating bimetallic metal organic frameworks (MOFs) until their porous structure collapses into nanoparticles can be a highly effective way to make catalysts. This novel approach to catalyst design has now been used by KAUST and Spanish researchers to make a robust catalyst that converts carbon dioxide (CO2) into carbon monoxide (CO) gas with unprecedented selectivity.
The benefit of this method pioneered at KAUST is that it can generate mixed metal catalytic nanoparticles that have proven challenging or impossible to make by conventional means.
Capturing ...
2021-05-11
Published today in Nature Communications, the team from the Peter Doherty Institute for Infection and Immunity (Doherty Institute), Alfred Health and Monash University sought to understand which patients would recover quickly from influenza and which would become severely ill.
The four-year project took samples from patients hospitalised with influenza at up to five time points during their hospital stay, and 30 days after discharge. They analysed the breadth of the immune response, enabling them to describe the specific roles of several different types of immune cells, including killer and helper T cells, B cells and innate cells.
University of Melbourne Dr Oanh Nguyen, Research Fellow at the Doherty Institute, said two significant findings of the research include understanding ...
2021-05-11
A group of researchers from Osaka University developed a quadruped robot platform that can reproduce the neuromuscular dynamics of animals (Figure 1), discovering that a steady gait and experimental behaviors of walking cats emerged from the reflex circuit in walking experiments on this robot. Their research results were published in Frontiers in Neurorobotics.
It was thought that a steady gait in animals is generated by complex nerve systems in the brain and spinal marrow; however, recent research shows that a steady gait is produced by the reflex circuit alone. Scientists discovered a candidate of reflex circuit to generate the steady walking motion ...
2021-05-11
Dr. HAN Fangpu's group from the Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences reports the identification and functional study of the maize Knl1 gene in an article published online in PNAS. The gene is a major component of the KMN network that links centromeric DNA and the plus-ends of spindle microtubules. It also plays an important role in kinetochore protein recruitment.
The kinetochore complex that assembles on the centromeres mediates the proper partitioning of chromosomes to daughter cells during the cell cycle. However, kinetochore proteins undergo frequent mutations and coevolve with their interaction partners, leading to great diversity in kinetochore composition in eukaryotes.
Functional ...
2021-05-11
A team of researchers, affiliated with UNIST has recently introduced a new class of magnetic materials for spin caloritronics. Published in the February 2021 issue of Nature Communications, the demonstrated STE applications of a new class of magnets will pave the way for versatile recycling of ubiquitous waste heat. This breakthrough has been led by Professor Jung-Woo Yoo and his research team in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at UNIST.
Spin thermoelectrics is an emerging thermoelectric technology that offers energy harvesting from waste heat. ...
2021-05-11
Like many around the world, the lab of Professor Mriganka Sur in The Picower Institute for Learning and Memory at MIT has embraced the young technology of cerebral organoids, or "minibrains," for studying human brain development in health and disease. By making a surprising finding about a common practice in the process of growing the complex tissue cultures, the lab has produced both new guidance that can make the technology better, and also new insight into the important roles a prevalent enzyme takes in natural brain development.
To make organoids, scientists take skin cells from a donor, induce them to become stem cells and then culture those in a bioreactor, guiding their development with the addition of growth ...
2021-05-11
COLUMBUS, Ohio - People are more persuaded by the actual messages contained in social media posts than they are by how many others viewed the posts, a new study suggests.
Researchers found that when people watched YouTube videos either for or against e-cigarette use, their level of persuasion wasn't directly affected by whether the video said it was viewed by more than a million people versus by fewer than 20.
What mattered for persuasion was viewers' perception of the message as truthful and believable.
"There wasn't a bandwagon effect in which people were persuaded by a video just because ...
2021-05-11
An international team of researchers at Great Ormond Street Hospital (GOSH), and University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) have developed a gene therapy that successfully treated 48 out of 50 children with a form of severe combined immunodeficiency that leaves them without an immune system.
Severe combined immunodeficiency due to adenosine deaminase deficiency, also known as ADA-SCID, is a rare, life-threatening disease that prevents children from living a normal life. It is caused by mutations in the gene that creates the enzyme adenosine deaminase, which is essential to a functioning immune system.
Children with ADA-SCID have no immune system and, if left untreated, the condition can be fatal within the first two years of life. Day-to-day activities ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Electromagnetic levitation whips nanomaterials into shape
Electromagnetic field directs shape formed by gas phase metal molecules