(Press-News.org) COLUMBUS, Ohio - People are more persuaded by the actual messages contained in social media posts than they are by how many others viewed the posts, a new study suggests.
Researchers found that when people watched YouTube videos either for or against e-cigarette use, their level of persuasion wasn't directly affected by whether the video said it was viewed by more than a million people versus by fewer than 20.
What mattered for persuasion was viewers' perception of the message as truthful and believable.
"There wasn't a bandwagon effect in which people were persuaded by a video just because a lot of other people watched it," said Hyunyi Cho, lead author of the study and professor of communication at The Ohio State University.
"The message itself was most important for persuasion."
The study will appear in the June 2021 issue of the journal Media Psychology.
The study involved 819 demographically diverse American adults aged 18-35.
Most of them were shown two YouTube videos either for or against vaping. The pro-vaping videos were commercials for e-cigarette brands. The anti-vaping videos were public service announcements produced by anti-smoking nonprofit organizations.
The researchers, though, manipulated the view numbers that participants saw for the videos. Participants saw view numbers either around 10, 100, 100,000 or 1,000,000.
Participants rated how persuasive the videos were to them: whether they affected their curiosity about e-cigarettes, positive attitude toward e-cigarette use, and susceptibility to using e-cigarettes in the future.
Results showed that participants were more persuaded when they rated them as more truthful and believable. The number of views that the video had did not have a direct impact on how much they were persuaded.
Participants were also asked how much they thought the videos they watched would influence other young adults, Cho said.
Results showed that how participants themselves viewed the videos - whether they thought the videos were believable and truthful - was directly related to their estimation of the videos' impact on other people.
"People focused more on self-related factors - how they felt about the video - when considering how much influence it would have on others," Cho said.
"They concentrated less on other-focused factors - such as view numbers - as a reason why a video might be persuasive."
In addition, participants in the study didn't think that mass media would have as far of a reach as social media would.
Some participants saw the videos in a mock TV condition rather than in the YouTube condition. Overall, participants in the TV condition estimated the videos would have fewer views than did the participants in the YouTube condition.
"Social media may be seen as more pervasive than mass media like television because sites like YouTube do not have the same geographic boundaries as mass media may have," Cho said.
Overall, the results suggest that people should not equate popularity of YouTube videos and other social media posts with how many people find their messages persuasive or are persuaded by them, Cho said.
"We may choose to watch a YouTube video because it has a lot of views, but that is different from whether we are persuaded by the message," she said.
INFORMATION:
The research was supported in part by the National Institutes of Health.
Contact: Hyunyi Cho, Cho.919@osu.edu
Written by Jeff Grabmeier, 614-292-8457; Grabmeier.1@osu.edu
An international team of researchers at Great Ormond Street Hospital (GOSH), and University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) have developed a gene therapy that successfully treated 48 out of 50 children with a form of severe combined immunodeficiency that leaves them without an immune system.
Severe combined immunodeficiency due to adenosine deaminase deficiency, also known as ADA-SCID, is a rare, life-threatening disease that prevents children from living a normal life. It is caused by mutations in the gene that creates the enzyme adenosine deaminase, which is essential to a functioning immune system.
Children with ADA-SCID have no immune system and, if left untreated, the condition can be fatal within the first two years of life. Day-to-day activities ...
An experimental form of gene therapy developed by a team of researchers from UCLA and Great Ormond Street Hospital in London has successfully treated 48 of 50 children born with a rare and deadly inherited disorder that leaves them without an immune system.
Severe combined immunodeficiency due to adenosine deaminase deficiency, or ADA-SCID, is caused by mutations in the ADA gene that creates the enzyme adenosine deaminase, which is essential to a functioning immune system. For children with the condition, even day-to-day activities like going to school or playing with friends can lead to dangerous, life-threatening infections. If untreated, ADA-SCID can be fatal within the first two years of life.
The investigational gene therapy method involves first collecting ...
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- In early 2020, a few months after the Covid-19 pandemic began, scientists were able to sequence the full genome of the virus that causes the infection, SARS-CoV-2. While many of its genes were already known at that point, the full complement of protein-coding genes was unresolved.
Now, after performing an extensive comparative genomics study, MIT researchers have generated what they describe as the most accurate and complete gene annotation of the SARS-CoV-2 genome. In their study, which appears today in Nature Communications, they confirmed ...
A receptor that helps conserve energy when food is scarce may be the key to a safer approach to treating diet-induced obesity, research led by the Garvan Institute of Medical Research has revealed.
In a study using experimental models and fat tissue biopsies from obese individuals, the team revealed that blocking a specific receptor of the molecule neuropeptide Y (NPY), which helps our body regulate its heat production, could increase fat metabolism and prevent weight gain.
"The Y1 receptor acts as a 'brake' for heat generation in the body. In our study, we found that blocking this receptor in fat tissues transformed the 'energy-storing' fat into 'energy-burning' fat, which ...
The first comprehensive comparison of 'degrowth' scenarios with established pathways to limit climate change highlights the risk of over-reliance on carbon dioxide removal, renewable energy and energy efficiency to support continued global growth - which is assumed in established global climate modelling.
Degrowth focuses on the global North and is defined as an equitable, democratic reduction in energy and material use while maintaining wellbeing. A decline in GDP is accepted as a likely outcome of this transition.
The new modelling by the University of Sydney and ETH Zürich includes high growth/technological change and scenarios summarised ...
Diamonds are sometimes described as messengers from the deep earth; scientists study them closely for insights into the otherwise inaccessible depths from which they come. But the messages are often hard to read. Now, a team has come up with a way to solve two longstanding puzzles: the ages of individual fluid-bearing diamonds, and the chemistry of their parent material. The research has allowed them to sketch out geologic events going back more than a billion years--a potential breakthrough not only in the study of diamonds, but of planetary evolution.
Gem-quality diamonds are nearly pure lattices of carbon. This elemental purity ...
Saw-toothed grain beetles live in a symbiotic association with bacteria. Their bacterial partners provide important building blocks for the formation of the insect's exoskeleton, which protects the beetles from their enemies as well as from desiccation. In a new study, a team of scientists from the Johannes Gutenberg University in Mainz, the Max Planck Institute for Chemical Ecology in Jena, and the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology in Japan demonstrates that glyphosate inhibits the symbiotic bacteria of the grain beetle. Beetles exposed to the weedkiller no longer receive the building blocks they need from the bacteria. The study shows that glyphosate has the potential to harm insects indirectly by targeting their bacterial partners ...
When horseradish flea beetles feed on their host plants, they take up not only nutrients but also mustard oil glucosides, the characteristic defense compounds of horseradish and other brassicaceous plants. Using these mustard oil glucosides, the beetles turn themselves into a "mustard oil bomb" and so deter predators. A team of researchers from the Max Planck Institute for Chemical Ecology in Jena, Germany, has now been able to demonstrate how the beetle regulates the accumulation of mustard oil glucosides in its body. The beetles have special transporters in the excretory system that prevent the excretion of mustard ...
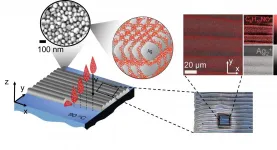
Inks containing metal nanoparticles are among the most commonly-used conductive materials for printed electronics. Ink-jetting layers of MNP materials allows for unpreceded design flexibility, rapid processing and 3D printing of functional electronic devices such as sensors, solar panels, LED displays, transistors and smart textiles.
Inkjet 3D printing of metals typically form a solid printed object via a two-step process: solvent evaporation upon printing (pinning) and subsequent low-temperature consolidation of nanoparticles (sintering). The low temperature is important as in many applications the nanoparticles are co-printed with ...
Researchers at the University of California San Diego have laid the groundwork for a potential new type of gene therapy using novel CRISPR-based techniques.
Working in fruit flies and human cells, research led by UC San Diego Postdoctoral Scholar Zhiqian Li in Division of Biological Sciences Professor Ethan Bier's laboratory demonstrates that new DNA repair mechanisms could be designed to address the effects of debilitating diseases and damaged cell conditions.
The scientists developed a novel genetic sensor called a "CopyCatcher," which capitalizes on CRISPR-based gene drive technology, to detect instances in which a genetic element is copied precisely from one chromosome to another throughout cells in ...