Researchers reveal how PIF proteins regulate cytokinesis
2021-05-11
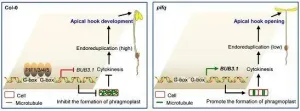
(Press-News.org) To protect their newly formed fragile organs, dark-grown dicotyledonous plants form an apical hook when penetrating through the soil. The apical hook of pifq (pif1 pif3 pif4 pif5) mutant was fully opened, even in complete darkness, suggesting that PIF proteins are required for maintaining the apical hook in the darkness and are involved in regulation of the apical hook opening. But the underlying mechanism for PIF proteins mediated apical hook development remains elusive.
To better understand how PIF proteins affect apical hook development, scientists from the Institute of Botany of the Chinese Academy of Sciences recently investigated their roles in an organ specific manner. The study was published in the journal Cell Reports on May 11.
The researchers performed organ-specific RNA-sequencing of the cotyledons, apical hooks and hypocotyls of etiolated Col-0 and pifq mutant seedlings, respectively. Interestingly, the scientists found that the genes involved in the regulation of cell cycle were significantly enriched in differentially expressed genes (DEGs) of the cotyledons and apical hooks, but not in DEGs of the hypocotyls.
Transcriptomic analysis combined with previous ChIP-seq data reveal that BUB3.1 is a potential common target gene of PIF proteins. Indeed, the researchers demonstrated that PIF proteins directly bind to the promoter BUB3.1 and inhibit its transcription. Importantly, BUB3.1 overexpression in transgenic lines leads to a partial apical hook opening phenotype, indicating that the higher level of BUB3.1 in pifq mutant at least in part contributed to its apical hookless phenotype.
Previously, BUB3.1 was shown to majorly function in microtubule reorganization during cytokinesis through facilitating MAP65-3 to localize in the phragmoplast. Consistently, the phragmoplast could be clearly observed in dark-grown pifq and Col-0 etiolated seedlings exposed to light for only 6 hours, but not in the etiolated Col-0 seedlings. In addition, the researchers also showed that cell ploidy for cotyledons and apical hooks of pifq mutants is significantly lower than for the wild type. However, cell ploidy in the hypocotyl is not significantly different regardless of type, indicating that PIF proteins can regulate cytokinesis in an organ specific manner such as in the apical hook or cotyledons.
To further investigate the role of cytokinesis in the apical hook opening, the researchers applied caffeine, a well-known potent inhibitor of phragmoplast-based cytokinesis, to the wild type etiolated seedlings. Evidently, the researchers found that caffeine treatment significantly promotes the hook curvature of wild-type etiolated seedlings, suggesting cytokinesis might be involved into the apical hook development.
Altogether, this study reveals that PIF proteins can regulate cytokinesis in the apical hook and cytokinesis may affect the development of the apical hook. Hence, their work demonstate that PIF proteins may play organ-specific roles, in hypocotyl to regulate cell elongation, while in apical hook and cotyledons to regulate cell division.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-11
The Saker Falcon (Falco cherrug) is a bird of prey living in plains and forest-steppes in the West and semi-desert montane plateaus and cliffs in the East. The majority of its Central and Eastern European population is migratory and spends winters in the Mediterranean, the Near East and East Africa. With its global population estimated at 6,100-14,900 breeding pairs, the species is considered endangered according to the IUCN Red List.
In Bulgaria, the Saker Falcon, considered extinct as a breeding species since the early 2000s, was recovered in 2018 with the discovery of the first active nest from its new history in Bulgaria. The nest is built by two birds that were reintroduced back in 2015 as part of the first ever Saker Falcon reintroduction programme. The results of the 5-year programme ...
2021-05-11
Northern Chile is an ideal natural laboratory to study the origin of earthquakes. Here, the Pacific Nazca plate slides underneath the South American continental plate with a speed of about 65 millimetres per year. This process, known as subduction, creates strain between the two plates and scientists thus expected a mega-earthquake here sooner or later, like the last one in 1877. But although northern Chile is one of the focal points of global earthquake research, until now there was no comprehensive data set on the structure of the marine subsurface - until nature itself stepped in to help.
On 1 April 2014, a segment of the subduction zone ...
2021-05-11
St. Petersburg, like other cities in the Russian Federation, is actively participating in the establishment of the "Smart City" program, which will provide new services for residents of the megalopolis, increasing the safety of citizens. Digital services are essential for such a system.
Due to the Internet of Things (IoT) systems, the environment can adapt to the needs of humanity on its own accord. Cybersecurity threats are especially dangerous for such infrastructure.
Specialists from Peter the Great St.Petersburg Polytechnic University (SPbPU) developed the methodology for assessing cyber risks in intelligent systems of a Smart City. The developed methodology was tested on the "smart crossroads" ...
2021-05-11
A reliable projection of extreme El Niño frequency change in future warmer climate is critical to managing socio-economic activities and human health, strategic policy decisions, environmental and ecosystem managements, and disaster mitigations in many parts of the world. Unfortunately, long-standing common biases in CMIP5 models, despite enormous efforts on the numerical model development over the past decades, make it hard to achieve a reliable projection of the extreme El Niño frequency change in the future. While increasing attentions have been paid to estimate possible impacts of models' biases, it is not yet fully understood whether and how much models' common biases would impact the projection ...
2021-05-11
Using Zebrafish, researchers from the School of Neurobiology, Biochemistry and Biophysics at the Faculty of Life Sciences of Tel Aviv University have developed an advanced simulation of a key process in the brain - the activation of the stem cells responsible for generating neurons. The simulation revealed that the process, which until today was considered to be random, is in fact coordinated, thereby ensuring the normal production of neurons in the brain. According to the researchers, their findings add another layer of understanding to brain development, ...
2021-05-11
Ishikawa, Japan - History tells us that games are an inseparable facet of humanity, and mainly for good reasons. Advocates of video games laud their pros: they help develop problem-solving skills, socialize, relieve stress, and exercise the mind and body--all at the same time! However, games also have a dark side: the potential for addiction. The explosive growth of the video game industry has spawned all sorts of games targeting different groups of people. This includes digital adaptations of popular board games like chess, but also extends to gambling-type games like online casinos and betting on ...
2021-05-11
According to the British Heart Foundation, heart and circulatory diseases cause more than a quarter (27 per cent) of all deaths in the UK, which equates to more than 160,000 deaths each year - or one death every three minutes.
The research, published in the top science journal Advanced Science, found that injection of the trace mineral manganese could enhanced MRI scans so that they provided more accurate details of heart function than traditional MRI methods.
These findings, if confirmed in human subjects, could have major implications for the treatment of heart attack patients. The findings could also be of great use in the preclinical evaluation of treatments for patients who suffer from cardiac ischemia - a reduction in blood supply ...
2021-05-11
By combining two medications, researchers at Michigan Medicine optimized a therapy for people with gout, a condition that causes severe damage and disability if left untreated.
The study revealed how a second drug taken orally more than doubled the effectiveness of Pegloticase, an intravenous gout treatment used to dissolve crystalized uric acid in the joints when oral medications fail.
"Gout is a challenging disease to treat because there are only a handful of oral therapies to lower uric acid," says Puja Khanna, M.D., M.P.H., a rheumatologist at Michigan Medicine. "Now, we have a medication that works and gives us a ...
2021-05-11
New guidelines for coral reef restoration aiming to reduce the risk of flooding in tropical coastal communities have been set out in a new study that simulated the behavior of ocean waves travelling over and beyond a range of coral reef structures. Published in Frontiers in Marine Science, these guidelines hope to optimize restoration efforts not only for the benefit of the ecosystem, but also to protect the coast and people living on it.
"Our research reveals that shallow, energetic areas such as the upper fore reef and middle reef flat, typically characterized by physically-robust coral species, should be targeted for restoration to reduce coastal flooding," says Floortje Roelvink, lead author on the paper and researcher at Deltares, a Dutch research ...
2021-05-11
Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) in children and adolescents is associated with impaired education and worse general health later in life. Access to specialist treatment is often limited. According to a study from Centre for Psychiatry Research at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden and Region Stockholm, internet-delivered cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT) can be as effective as conventional CBT. The study, published in the prestigious journal JAMA, can help make treatment for OCD more widely accessible.
Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) is a potentially serious mental disorder that normally debuts in childhood.
Symptoms include intrusive thoughts that trigger anxiety ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Researchers reveal how PIF proteins regulate cytokinesis