What does your voice say about you?
International research team led by Göttingen University investigates links between personality and vocal characteristics
2021-05-12
(Press-News.org) Everyone has at some point been charmed by the sound of a person's voice: but can we believe our ears? What can a voice really reveal about our character? Now an international research team led by the University of Göttingen has shown that people seem to express at least some aspects of their personality with their voice. The researchers discovered that a lower pitched voice is associated with individuals who are more dominant, extrovert and higher in sociosexuality (more interested in casual sex). The findings were true for women as well as for men. The results were published in the Journal of Research in Personality.
The researchers analysed data from over 2,000 participants and included information from four different countries. Participants filled in questionnaires about themselves to measure personality and provided recordings of their voice so that the pitch could be measured using a computer programme. This is the first time that an objective digital measure of voice pitch has been used in a study of this kind, rather than subjective ratings of how "high" or "deep" a voice might sound. The researchers measured "sociosexuality" by collecting responses about sexual behaviour, attitude and desire. They also collected data to provide ratings of dominance and other character traits such as neuroticism, extraversion, openness to experience, agreeableness and conscientiousness. The number of participants helps to confirm the robustness of the findings: the study involves the largest number to date compared to similar research in this theme.
The researchers found that people with lower pitched voices were more dominant, extroverted and higher in sociosexuality (eg were more interested in sex outside a relationship). However, the relationship between voice pitch and other personality traits (such as agreeableness, neuroticism, conscientiousness or openness) seems less clear. It is possible that these traits are not expressed in the pitch of voices. The researchers found no difference between men and women.
"People's voices can make a huge and immediate impression on us," explains Dr Julia Stern, at the University of Göttingen's Biological Personality Psychology Group. "Even if we just hear someone's voice without any visual clues - for instance on the phone - we know pretty soon whether we're talking to a man, a woman, a child or an older person. We can pick up on whether the person sounds interested, friendly, sad, nervous, or whether they have an attractive voice. We also start to make assumptions about trust and dominance." This led Stern to question whether these assumptions were justified. "The first step was to investigate whether voices are, indeed, related to people's personality. And our results suggest that people do seem to express some aspects of their personality with their voice."
This study was conducted as a "registered report" which means it benefits from peer review from other researchers at a very early stage and was accepted for publication independent of the results. It is one of the new indicators of quality being developed to make science more transparent and reliable.
INFORMATION:
Original publication: Stern J et al, "Do voices carry valid information about a speaker's personality?" Journal of Research in Personality. Doi: 10.1016/j.jrp.2021.104092
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrp.2021.104092
Contact:
Dr Julia Stern
University of Göttingen
Georg-Elias-Müller-Institute of Psychology
Biological Personality Psychology Group
Goßlerstraße 14, 37073 Göttingen, Germany
Email: julia.stern@psych.uni-goettingen.de
http://www.psych.uni-goettingen.de/en/biopers/team/stern
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-12
In Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS), the progressive death of neurons that control body movement leads to paralysis of muscles in the limbs and gradually of the whole body, which ultimately makes it impossible to breathe. ALS is currently untreatable, and its cause is unknown.
It is known, however, that in 10% of affected individuals there is a strong genetic component, which causes the disease to occur in several members of a single family. In about half of these cases of familial ALS, the origin lies in a gene called C9ORF72. But why do mutations in this gene kill motor neurons?
The answer may have been found by the Genomic Instability Group headed by Óscar Fernández-Capetillo at the Spanish National Cancer Research Centre (CNIO), who discovered ...
2021-05-12
The property that makes fluorescent lights buzz could power a new generation of more efficient computing devices that store data with magnetic fields, rather than electricity.
A team led by University of Michigan researchers has developed a material that's at least twice as "magnetostrictive" and far less costly than other materials in its class. In addition to computing, it could also lead to better magnetic sensors for medical and security devices.
Magnetostriction, which causes the buzz of fluorescent lights and electrical transformers, occurs when a material's shape and magnetic field are linked--that is, a change in shape causes a change in magnetic field. The property could be key to a new generation of computing devices called ...
2021-05-12
Trained to see patterns by analyzing thousands of chest X-rays, a computer program predicted with up to 80 percent accuracy which COVID-19 patients would develop life-threatening complications within four days, a new study finds.
Developed by researchers at NYU Grossman School of Medicine, the program used several hundred gigabytes of data gleaned from 5,224 chest X-rays taken from 2,943 seriously ill patients infected with SARS-CoV-2, the virus behind the infections.
The authors of the study, publishing in the journal npj Digital Medicine online May 12, cited the "pressing need" ...
2021-05-12
The 'missing link' that helped our ancestors to begin communicating with each other through language may have been iconic sounds, rather than charades-like gestures - giving rise to the unique human power to coin new words describing the world around us, a new study reveals.
It was widely believed that, in order to get the first languages off the ground, our ancestors first needed a way to create novel signals that could be understood by others, relying on visual signs whose form directly resembled the intended meaning.
However, an international research team, led by experts from the University of Birmingham and the Leibniz-Centre General Linguistics (ZAS), Berlin, have discovered that iconic ...
2021-05-12
Lancaster scientists have demonstrated that other physicists' recent "discovery" of the field effect in superconductors is nothing but hot electrons after all.
A team of scientists in the Lancaster Physics Department have found new and compelling evidence that the observation of the field effect in superconducting metals by another group can be explained by a simple mechanism involving the injection of the electrons, without the need for novel physics.
Dr Sergey Kafanov, who initiated this experiment, said: "Our results unambiguously refute the claim of the electrostatic field effect ...
2021-05-12
Touchscreens are notoriously difficult to type on. Since we can't feel the keys, we rely on the sense of sight to move our fingers to the right places and check for errors, a combination of efforts we can't pull off at the same time. To really understand how people type on touchscreens, researchers at Aalto University and the Finnish Center for Artificial Intelligence (FCAI) have created the first artificial intelligence model that predicts how people move their eyes and fingers while typing.
The AI model can simulate how a human user would type any sentence on any keyboard design. It makes errors, detects them -- though not always immediately -- and corrects them, very much like ...
2021-05-12
Philadelphia, May 12, 2021 - The COVID-19 pandemic has resulted in an abrupt change in healthcare delivery, including a shift from in-person visits to telemedicine. However, a Canadian survey found that a significant proportion of cardiology trainees are uncomfortable with using telemedicine and feel that better preparation for new-tech medicine is needed. Experts draw attention to the need for a telemedicine curriculum that includes supervision to prepare trainees for the expanding role of telemedicine in cardiovascular care. Survey results are published in the Canadian Journal of Cardiology.
"Our outpatient care shifted almost overnight from in-person visits to providing care to patients via telephone or video platforms (known as telemedicine) as a result ...
2021-05-12
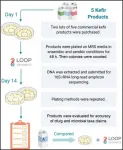
Philadelphia, May 12, 2021 - In recent years there has been an increased interest in the consumption of kefir, a fermented dairy beverage, because there is some evidence that it has health benefits and its affordability. A new study by researchers from the University of Illinois and The Ohio State University, published in JDS Communications, found that 66 percent of the commercial kefir products studied overstated microorganism density and 80 percent contained bacterial species that were not included on the label, potentially misleading consumers.
Senior author Kelly S. Swanson, PhD, University of Illinois, Urbana, ...
2021-05-12
A new study led by the Centre for Nutraceuticals in the University of Westminster shows that pink drinks can help to make you run faster and further compared to clear drinks.
The researchers found that a pink drink can increase exercise performance by 4.4 per cent and can also increase a 'feel good' effect which can make exercise seem easier.
The study, published in the journal Frontiers in Nutrition, is the first investigation to assess the effect of drink colour on exercise performance and provides the potential to open a new avenue of future research in the field of sports drinks and exercise.
During the study participants were asked to run on a treadmill for 30 minutes at a self-selected speed ensuring their rate of exertion remained consistent. Throughout the exercise ...
2021-05-12
For college students under pressure, a dog may be the best stress fighter around.
Programs exclusively focused on petting therapy dogs improved stressed-out students' thinking and planning skills more effectively than programs that included traditional stress-management information, according to new Washington State University research.
The study was published today in the journal AERA Open, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Educational Research Association. The paper demonstrated that stressed students still exhibited these cognitive skills improvements up to six weeks after completion of the four-week-long program.
"It's a really powerful finding," said Patricia Pendry, associate professor in WSU's Department of ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] What does your voice say about you?
International research team led by Göttingen University investigates links between personality and vocal characteristics