INFORMATION:
Brand new physics of superconducting metals refuted by Lancaster physicists
2021-05-12
(Press-News.org) Lancaster scientists have demonstrated that other physicists' recent "discovery" of the field effect in superconductors is nothing but hot electrons after all.
A team of scientists in the Lancaster Physics Department have found new and compelling evidence that the observation of the field effect in superconducting metals by another group can be explained by a simple mechanism involving the injection of the electrons, without the need for novel physics.
Dr Sergey Kafanov, who initiated this experiment, said: "Our results unambiguously refute the claim of the electrostatic field effect claimed by the other group. This gets us back on the ground and helps maintain the health of the discipline."
The experimental team also includes Ilia Golokolenov, Andrew Guthrie, Yuri Pashkin and Viktor Tsepelin.
Their work is published in the latest issue of Nature Communications.
When certain metals are cooled to a few degrees above absolute zero, their electrical resistance vanishes - a striking physical phenomenon known as superconductivity. Many metals, including vanadium, which was used in the experiment, are known to exhibit superconductivity at sufficiently low temperatures.
For decades it was thought that the exceptionally low electrical resistance of superconductors should make them practically impervious to static electric fields, owing to the way the charge carriers can easily arrange themselves to compensate for any external field.
It therefore came as a shock to the physics community when a number of recent publications claimed that sufficiently strong electrostatic fields could affect superconductors in nanoscale structures - and attempted to explain this new effect with corresponding new physics. A related effect is well known in semiconductors and underpins the entire semiconductor industry.
The Lancaster team embedded a similar nanoscale device into a microwave cavity, allowing them to study the alleged electrostatic phenomenon at much shorter timescales than previously investigated. At short timescales, the team could see a clear increase in the noise and energy loss in the cavity - the properties strongly associated with the device temperature. They propose that at intense electric fields, high-energy electrons can "jump" into the superconductor, raising the temperature and therefore increasing the dissipation.
This simple phenomenon can concisely explain the origin of the "electrostatic field effect" in nanoscale structures, without any new physics.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
AI learns to type on a phone like humans
2021-05-12
Touchscreens are notoriously difficult to type on. Since we can't feel the keys, we rely on the sense of sight to move our fingers to the right places and check for errors, a combination of efforts we can't pull off at the same time. To really understand how people type on touchscreens, researchers at Aalto University and the Finnish Center for Artificial Intelligence (FCAI) have created the first artificial intelligence model that predicts how people move their eyes and fingers while typing.
The AI model can simulate how a human user would type any sentence on any keyboard design. It makes errors, detects them -- though not always immediately -- and corrects them, very much like ...
Telemedicine needs to be integrated into cardiology training, experts recommend
2021-05-12
Philadelphia, May 12, 2021 - The COVID-19 pandemic has resulted in an abrupt change in healthcare delivery, including a shift from in-person visits to telemedicine. However, a Canadian survey found that a significant proportion of cardiology trainees are uncomfortable with using telemedicine and feel that better preparation for new-tech medicine is needed. Experts draw attention to the need for a telemedicine curriculum that includes supervision to prepare trainees for the expanding role of telemedicine in cardiovascular care. Survey results are published in the Canadian Journal of Cardiology.
"Our outpatient care shifted almost overnight from in-person visits to providing care to patients via telephone or video platforms (known as telemedicine) as a result ...
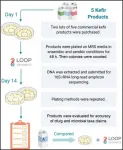
New study: Kefir package claims don't always accurately reflect composition of commercial products
2021-05-12
Philadelphia, May 12, 2021 - In recent years there has been an increased interest in the consumption of kefir, a fermented dairy beverage, because there is some evidence that it has health benefits and its affordability. A new study by researchers from the University of Illinois and The Ohio State University, published in JDS Communications, found that 66 percent of the commercial kefir products studied overstated microorganism density and 80 percent contained bacterial species that were not included on the label, potentially misleading consumers.
Senior author Kelly S. Swanson, PhD, University of Illinois, Urbana, ...
Pink drinks can help you run faster and further, study finds
2021-05-12
A new study led by the Centre for Nutraceuticals in the University of Westminster shows that pink drinks can help to make you run faster and further compared to clear drinks.
The researchers found that a pink drink can increase exercise performance by 4.4 per cent and can also increase a 'feel good' effect which can make exercise seem easier.
The study, published in the journal Frontiers in Nutrition, is the first investigation to assess the effect of drink colour on exercise performance and provides the potential to open a new avenue of future research in the field of sports drinks and exercise.
During the study participants were asked to run on a treadmill for 30 minutes at a self-selected speed ensuring their rate of exertion remained consistent. Throughout the exercise ...
Petting therapy dogs enhances thinking skills of stressed college students
2021-05-12
For college students under pressure, a dog may be the best stress fighter around.
Programs exclusively focused on petting therapy dogs improved stressed-out students' thinking and planning skills more effectively than programs that included traditional stress-management information, according to new Washington State University research.
The study was published today in the journal AERA Open, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Educational Research Association. The paper demonstrated that stressed students still exhibited these cognitive skills improvements up to six weeks after completion of the four-week-long program.
"It's a really powerful finding," said Patricia Pendry, associate professor in WSU's Department of ...
How social media and AI enable companies to track brand reputations in real-time
2021-05-12
Researchers from University of Maryland, North Carolina State University, National Taiwan University, Oxford University, Kings College London, and Perceptronics Solutions, Inc. published a new paper in the Journal of Marketing that examines how artificial intelligence (AI)-based text analysis of social media can monitor the extent to which brand reputation rises and falls over time.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled "Real-Time Brand Reputation Tracking using Social Media" and is authored by Roland Rust, William Rand, Ming-Hui Huang, Andrew Stephen, Gillian Brooks, ...
Eliminating bias from healthcare AI critical to improve health equity
2021-05-12
INDIANAPOLIS -- Artificial intelligence (AI)-driven healthcare has the potential to transform medical decision-making and treatment, but these algorithms must be thoroughly tested and continuously monitored to avoid unintended consequences to patients.
In a JAMA Network Open Invited Commentary, Regenstrief Institute President and Chief Executive Officer and Indiana University School of Medicine Associate Dean for Informatics and Health Services Research Peter Embí, M.D., M.S., strongly stated the importance of algorithmovigilance to address inherent biases in healthcare algorithms and their deployment. ...
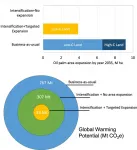
Defining climate-smart pathways towards tree crop yield intensification
2021-05-12
A global team of researchers recently released the results of a 'data-rich' modeling approach designed to illustrate a range of what-if scenarios for future oil palm plantation development in Indonesia. The study provides new insight into crop production strategies available to an industry facing increasing scrutiny.
Oil palm production is challenged by global and domestic concerns related to how it operates within its tropical rainforest environment, which is highly valued for its contribution to climate change mitigation potential and biodiversity protection. The study sheds new light on the future implications of maintaining business-as-usual ...
Fatigue, mood disorders associated with post-COVID-19 syndrome
2021-05-12
ROCHESTER, Minn. -- Patients diagnosed with post-COVID-19 syndrome, also known as "PCS," "COVID-19 long-haul syndrome" and "Post-Acute Sequelae of SARS COV-2," experience symptoms such as mood disorders, fatigue and perceived cognitive impairment that can negatively affect returning to work and resuming normal activities, according to a Mayo Clinic study published in Mayo Clinic Proceedings.
The study reports on the first 100 patients to participate in Mayo Clinic's COVID-19 Activity Rehabilitation program (CARP), one of the first multidisciplinary programs established to evaluate ...
NTU study of ancient corals in Indonesia reveals slowest earthquake ever recorded
2021-05-12
A 'slow-motion' earthquake lasting 32 years - the slowest ever recorded - eventually led to the catastrophic 1861 Sumatra earthquake, researchers at the Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore) have found.
The NTU research team says their study highlights potential missing factors or mismodelling in global earthquake risk assessments today.
'Slow motion' earthquakes or 'slow slip events' refer to a type of long, drawn-out stress release phenomenon in which the Earth's tectonic plates slide against one another without causing major ground shaking or destruction. They typically involve movements of between ...