(Press-News.org) ROCHESTER, Minn. -- Patients diagnosed with post-COVID-19 syndrome, also known as "PCS," "COVID-19 long-haul syndrome" and "Post-Acute Sequelae of SARS COV-2," experience symptoms such as mood disorders, fatigue and perceived cognitive impairment that can negatively affect returning to work and resuming normal activities, according to a Mayo Clinic study published in Mayo Clinic Proceedings.
The study reports on the first 100 patients to participate in Mayo Clinic's COVID-19 Activity Rehabilitation program (CARP), one of the first multidisciplinary programs established to evaluate and treat patients with post-COVID-19 syndrome. The patients were evaluated and treated between June 1 and Dec. 31, 2020. They had a mean age of 45, and 68% were female. They were evaluated a mean of 93 days after infection.
The most common symptom of patients seeking evaluation for post-COVID-19 syndrome was fatigue. Of the patients in the study, 80% reported unusual fatigue, while 59% had respiratory complaints and a similar percentage had neurologic complaints. More than one-third of patients reported difficulties performing basic activities of daily living, and only 1 in 3 patients had returned to unrestricted work activity.
"Most patients in the study had no preexisting comorbidities prior to COVID-19 infection, and many did not experience symptoms related to COVID-19 that were severe enough to require hospitalization," says Greg Vanichkachorn, M.D., medical director of Mayo Clinic's COVID-19 Activity Rehabilitation program and first author of the study. "Most of the patients had normal or nondiagnostic lab and imaging results, despite having debilitating symptoms. That's among the challenges of diagnosing PCS in a timely way and then responding effectively."
Nonetheless, the symptoms often resulted in significant negative effects as patients tried to return to normal daily activities, including work. "Most patients with whom we worked required physical therapy, occupational therapy or brain rehabilitation to address the perceived cognitive impairment," says Dr. Vanichkachorn. "While many patients had fatigue, more than half also reported troubles with thinking, commonly known as 'brain fog.' And more than one-third of patients had trouble with basic activities of life. Many could not resume their normal work life for at least several months."
Mayo Clinic developed the COVID-19 Activity Rehabilitation program at Mayo Clinic in Rochester in June 2020 to care for patients experiencing persistent symptoms after COVID-19 infection. In addition to Dr. Vanichkachorn, Mayo Clinic staff from many specialty fields are involved in diagnostics and treatment. Among services provided are psychosocial support for patients who frequently report feelings of abandonment, guilt and frustration during initial evaluation.
Mayo Clinic is conducting intensive research on post-COVID-19 syndrome, in part to better define how the condition presents across different socioeconomic groups and ethnicities. Prolonged symptoms, such as those experienced with post-COVID-19 syndrome, have been reported in prior epidemics.
"As the pandemic continues, we expect to see more patients who experience symptoms long after infection, and health care providers need to prepare for this, know what to look for, and know how to best provide for their patients' needs," says Dr. Vanichkachorn.
Patients who have recovered from acute infection shouldn't wait to be evaluated if they are experiencing prolonged symptoms, though Dr. Vanichkachorn says providers should be judicious in recommending expensive diagnostic tests, which often aren't covered by insurance and don't reveal significant information.
INFORMATION:
The authors of the study have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
About Mayo Clinic Proceedings
Mayo Clinic Proceedings is a monthly peer-reviewed journal that publishes original articles and reviews dealing with clinical and laboratory medicine, clinical research, basic science research, and clinical epidemiology. Mayo Clinic Proceedings is sponsored by the Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research as part of its commitment to physician education.
About Mayo Clinic
Mayo Clinic is a nonprofit organization committed to innovation in clinical practice, education and research, and providing compassion, expertise and answers to everyone who needs healing. Visit the Mayo Clinic News Network for additional Mayo Clinic news. For information on COVID-19, including Mayo Clinic's Coronavirus Map tracking tool, which has 14-day forecasting on COVID-19 trends, visit the Mayo Clinic COVID-19 Resource Center.
Media contact:
Heather Carlson Kehren, Mayo Clinic Public Affair, newsbureau@mayo.edu
A 'slow-motion' earthquake lasting 32 years - the slowest ever recorded - eventually led to the catastrophic 1861 Sumatra earthquake, researchers at the Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore) have found.
The NTU research team says their study highlights potential missing factors or mismodelling in global earthquake risk assessments today.
'Slow motion' earthquakes or 'slow slip events' refer to a type of long, drawn-out stress release phenomenon in which the Earth's tectonic plates slide against one another without causing major ground shaking or destruction. They typically involve movements of between ...
New research at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden suggests a link between psychosis and a genetic change that affects the brain's immune system. The study published in Molecular Psychiatry may impact the development of modern medicines for bipolar disorder or schizophrenia.
Psychosis affects approximately 2-3 per cent of the population and is characterized by a change in the perception of reality, often with elements of hallucinations and paranoid reactions.
Most of the people affected are patients with schizophrenia, but people with bipolar disorder may also experience psychotic symptoms.
The antipsychotics available today often have insufficient efficacy, and for patients, ...
Anyone who's raised a child or a pet will know just how fast and how steady their growth seems to be. You leave for a few days on a work trip and when you come home the child seems to have grown 10cm! That's all well and good for the modern household, but how did dinosaurs grow up? Did they, too, surprise their parents with their non-stop growth?
A new study lead by Dr Kimberley Chapelle of the American Museum of Natural History in New York City and Honorary Research Fellow at the University of the Witwatersrand suggests NOT. At least for one iconic southern African dinosaur species. By looking at the fossil ...
Can you feel the heat? To a thermal camera, which measures infrared radiation, the heat that we can feel is visible, like the heat of a traveler in an airport with a fever or the cold of a leaky window or door in the winter.
In a paper published in Proceedings of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, an international group of applied mathematicians and physicists, including Fernando Guevara Vasquez and Trent DeGiovanni from the University of Utah, report a theoretical way of mimicking thermal objects or making objects invisible to thermal measurements. And it doesn't ...
A study across 55 hospitals in Queensland, Australia suggests that a recent state policy to introduce a minimum ratio of one nurse to four patients for day shifts has successfully improved patient care, with a 7% drop in the chance of death and readmission, and 3% reduction in length of stay for every one less patient a nurse has on their workload.
The study of more than 400,000 patients and 17,000 nurses in 27 hospitals that implemented the policy and 28 comparison hospitals is published in The Lancet. It is the first prospective evaluation of the ...
CHICAGO --- A new Northwestern Medicine study of placentas from patients who received the COVID-19 vaccine during pregnancy found no evidence of injury, adding to the growing literature that COVID-19 vaccines are safe in pregnancy.
"The placenta is like the black box in an airplane. If something goes wrong with a pregnancy, we usually see changes in the placenta that can help us figure out what happened," said corresponding author Dr. Jeffery Goldstein, assistant professor of pathology at Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine and a Northwestern Medicine pathologist. "From what we can tell, the COVID vaccine does not damage the placenta."
The study will be published May 11 in the journal Obstetrics ...
TORONTO, ON - Geoscientists at the University of Toronto (U of T) and Istanbul Technical University have discovered a new process in plate tectonics which shows that tremendous damage occurs to areas of Earth's crust long before it should be geologically altered by known plate-boundary processes, highlighting the need to amend current understandings of the planet's tectonic cycle.
Plate tectonics, an accepted theory for over 60 years that explains the geologic processes occurring below the surface of Earth, holds that its outer shell is fragmented into continent-sized blocks of solid rock, called "plates," that slide over Earth's mantle, the rocky inner layer above ...
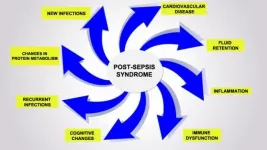
An article published in Frontiers in Immunology suggests that sepsis can cause alterations in the functioning of defense cells that persist even after the patient is discharged from hospital. This cellular reprogramming creates a disorder the authors call post-sepsis syndrome, whose symptoms include frequent reinfections, cardiovascular alterations, cognitive disabilities, declining physical functions, and poor quality of life. The phenomenon explains why so many patients who survive sepsis die sooner after hospital discharge than patients with other diseases or suffer from post-sepsis syndrome, immunosuppression ...
COVID-19 has had a significant impact since the pandemic was declared by WHO in 2020, with over 3 million deaths and counting, Researchers and medical teams have been hard at work at developing strategies to control the spread of the infection, caused by SARS-COV-2 virus and treat affected patients. Of special interest to the global population is the developments of vaccines to boost human immunity against SARS-COV-2, which are based on our understanding of how the viral proteins work during the infection in host cells. Two vaccines, namely the Pfizer/BioINtech and Oxford/AZ vaccine rely on the use of delivering the gene that encodes the viral spike protein either as an mRNA or through an adenovirus vector to promote the production of relevant antibodies. The use of monoclonal ...
In order to make meaningful gains in cardiovascular disease care, primary care medical practices should adopt a set of care improvements specific to their practice size and type, according to a new study from the national primary care quality improvement initiative EvidenceNOW. High blood pressure and smoking are among the biggest risk factors associated with cardiovascular disease. Primary care physicians help patients manage high blood pressure and provide smoking cessation interventions.
Researchers found that there is no one central playbook for all types of practices, but they did identify ...