(Press-News.org) CHICAGO --- A new Northwestern Medicine study of placentas from patients who received the COVID-19 vaccine during pregnancy found no evidence of injury, adding to the growing literature that COVID-19 vaccines are safe in pregnancy.
"The placenta is like the black box in an airplane. If something goes wrong with a pregnancy, we usually see changes in the placenta that can help us figure out what happened," said corresponding author Dr. Jeffery Goldstein, assistant professor of pathology at Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine and a Northwestern Medicine pathologist. "From what we can tell, the COVID vaccine does not damage the placenta."
The study will be published May 11 in the journal Obstetrics & Gynecology. To the authors' knowledge, it is the first study to examine the impact of the COVID vaccines on the placenta.
"We have reached a stage in vaccine distribution where we are seeing vaccine hesitancy, and this hesitancy is pronounced for pregnant people," said study co-author Dr. Emily Miller, Northwestern Medicine maternal fetal medicine physician and assistant professor of obstetrics and gynecology at Feinberg. "Our team hopes these data, albeit preliminary, can reduce concerns about the risk of the vaccine to the pregnancy."
The study authors collected placentas from 84 vaccinated patients and 116 unvaccinated patients who delivered at Prentice Women's Hospital in Chicago and pathologically examined the placentas whole and microscopically following birth. Most patients received vaccines - either Moderna or Pfizer - during their third trimester.
Last May, Goldstein, Miller and collaborators from Northwestern and Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children's Hospital of Chicago published a study that found placentas of women who tested positive for the COVID-19 virus while pregnant showed evidence of injury (abnormal blood flow between mother and baby in utero). Pregnant patients who want to get vaccinated to avoid contracting the disease should feel safe doing so, Miller said.
"We are beginning to move to a framework of protecting fetuses through vaccination, rather than from vaccination," Miller said.
In April, the scientists published a study showing pregnant women make COVID antibodies after vaccination and successfully transfer them to their fetuses.
"Until infants can get vaccinated, the only way for them to get COVID antibodies is from their mother," Goldstein said.
The placenta's role in the immune system
The placenta is the first organ that forms during pregnancy. It performs duties for most of the fetus' organs while they're still forming, such as providing oxygen while the lungs develop and nutrition while the gut is forming.
Additionally, the placenta manages hormones and the immune system, and tells the mother's body to welcome and nurture the fetus rather than reject it as a foreign intruder.
"The Internet has amplified a concern that the vaccine might trigger an immunological response that causes the mother to reject the fetus," Goldstein said. "But these findings lead us to believe that doesn't happen."
The scientists also looked for abnormal blood flow between the mother and fetus and problems with fetal blood flow - both of which have been reported in pregnant patients who have tested positive for COVID.
The rate of these injuries was the same in the vaccinated patients as for control patients, Goldstein said. The scientists also examined the placentas for chronic histiocytic intervillositis, a complication that can happen if the placenta is infected, in this case, by SARS-CoV-2. Although this study did not find any cases in vaccinated patients, it's a very rare condition that requires a larger sample size (1,000 patients) to differentiate between vaccinated and unvaccinated patients.
INFORMATION:
Other Northwestern study authors include Dr. Elisheva Shanes and Chiedza Mupanomunda. Dr. Leena B. Mithal and Sebastian Otero from Lurie Children's Hospital also are study authors.
The study was funded by The Friends of Prentice, the Stanley Manne Children's Research Institute, the National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering (grant number K08EB030120) and the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (grant number K23AI139337), part of the National Institutes of Health.
TORONTO, ON - Geoscientists at the University of Toronto (U of T) and Istanbul Technical University have discovered a new process in plate tectonics which shows that tremendous damage occurs to areas of Earth's crust long before it should be geologically altered by known plate-boundary processes, highlighting the need to amend current understandings of the planet's tectonic cycle.
Plate tectonics, an accepted theory for over 60 years that explains the geologic processes occurring below the surface of Earth, holds that its outer shell is fragmented into continent-sized blocks of solid rock, called "plates," that slide over Earth's mantle, the rocky inner layer above ...
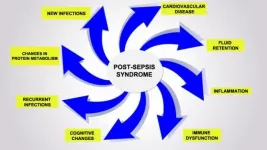
An article published in Frontiers in Immunology suggests that sepsis can cause alterations in the functioning of defense cells that persist even after the patient is discharged from hospital. This cellular reprogramming creates a disorder the authors call post-sepsis syndrome, whose symptoms include frequent reinfections, cardiovascular alterations, cognitive disabilities, declining physical functions, and poor quality of life. The phenomenon explains why so many patients who survive sepsis die sooner after hospital discharge than patients with other diseases or suffer from post-sepsis syndrome, immunosuppression ...
COVID-19 has had a significant impact since the pandemic was declared by WHO in 2020, with over 3 million deaths and counting, Researchers and medical teams have been hard at work at developing strategies to control the spread of the infection, caused by SARS-COV-2 virus and treat affected patients. Of special interest to the global population is the developments of vaccines to boost human immunity against SARS-COV-2, which are based on our understanding of how the viral proteins work during the infection in host cells. Two vaccines, namely the Pfizer/BioINtech and Oxford/AZ vaccine rely on the use of delivering the gene that encodes the viral spike protein either as an mRNA or through an adenovirus vector to promote the production of relevant antibodies. The use of monoclonal ...
In order to make meaningful gains in cardiovascular disease care, primary care medical practices should adopt a set of care improvements specific to their practice size and type, according to a new study from the national primary care quality improvement initiative EvidenceNOW. High blood pressure and smoking are among the biggest risk factors associated with cardiovascular disease. Primary care physicians help patients manage high blood pressure and provide smoking cessation interventions.
Researchers found that there is no one central playbook for all types of practices, but they did identify ...
Although new family medicine graduates intend to provide a broader scope of practice than their senior counterparts, individual family physicians' scope of practice has been decreasing, with fewer family physicians providing basic primary care services, such pediatric and prenatal care. Russell et al conducted a study to explore family medicine graduates' attitudes and perspectives on modifiable and non-modifiable factors that influenced their scope of practice and career choices. The authors conducted five focus group discussions with 32 family physicians and explored their attitudes and perspectives on their desired and actual scope of practice. Using a conceptual framework ...
In the decade since the advent of CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing, researchers have used the technology to delete or change genes in a growing number of cell types. Now, researchers at Gladstone Institutes and UC San Francisco (UCSF) have added human monocytes--white blood cells that play key roles in the immune system--to that list.
The team has adapted CRISPR-Cas9 for use in monocytes and shown the potential utility of the technology for understanding how the human immune system fights viruses and microbes. Their results were published online today in the journal Cell Reports.
"These experiments set the stage for many more studies on the interactions between major infectious diseases and human immune cells," says senior author Alex Marson, MD, PhD, director of the Gladstone-UCSF Institute ...
Pregnant women who develop severe COVID-19 infections that require hospitalization for pneumonia and other complications may not be more likely to die from these infections than non-pregnant women. In fact, they may have significantly lower death rates than their non-pregnant counterparts. That is the finding of a new study published today in the Annals of Internal Medicine conducted by researchers at the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM).
The study examined medical records from nearly 1,100 pregnant women and more than 9,800 non-pregnant patients aged 15 to 45 who were hospitalized with COVID-19 and pneumonia. Slightly less than 1 percent of the pregnant patients died from COVID-19 compared to 3.5 percent of non-pregnant patients, according to the study findings.
There ...
New York, NY--May 11, 2021--Widely used to monitor and map biological signals, to support and enhance physiological functions, and to treat diseases, implantable medical devices are transforming healthcare and improving the quality of life for millions of people. Researchers are increasingly interested in designing wireless, miniaturized implantable medical devices for in vivo and in situ physiological monitoring. These devices could be used to monitor physiological conditions, such as temperature, blood pressure, glucose, and respiration for both diagnostic and therapeutic ...
2003 was a big year for virologists. The first giant virus was discovered in this year, which shook the virology scene, revising what was thought to be an established understanding of this elusive group and expanding the virus world from simple, small agents to forms that are as complex as some bacteria. Because of their link to disease and the difficulties in defining them--they are biological entities but do not fit comfortably in the existing tree of life--viruses incite the curiosity of many people.
Scientists have long been interested in how viruses evolved, especially when it comes to giant viruses that can produce new viruses with very little help from the host--in contrast to most small viruses, which utilize the host's machinery to replicate. ...
Surgical cesarean births can expose new mothers to a range of health complications, including infection, blood clots and hemorrhage. As part of Healthy People 2020 and other maternal health objectives, the state of California exerted pressure to reduce cesarean deliveries, and statewide organizations established quality initiatives in partnership with those goals. In this study, researchers from Stanford University and the University of Chicago examined unit culture and provider mix differences on hospital and delivery units to identify characteristics of units that successfully reduced their cesarean delivery rates. The mixed-methods study surveyed ...