(Press-News.org) Researchers from University of Maryland, North Carolina State University, National Taiwan University, Oxford University, Kings College London, and Perceptronics Solutions, Inc. published a new paper in the Journal of Marketing that examines how artificial intelligence (AI)-based text analysis of social media can monitor the extent to which brand reputation rises and falls over time.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled "Real-Time Brand Reputation Tracking using Social Media" and is authored by Roland Rust, William Rand, Ming-Hui Huang, Andrew Stephen, Gillian Brooks, and Timur Chabuk.
Organizations' brand reputations can rise and fall based on brand-related events. For example, when Goya CEO Robert Unanue suggested that the 2020 U.S. presidential election was fraudulent, that controversial assertion likely offended a large segment of the population. How can we tell? This research team demonstrates that using artificial intelligence (AI)-based text analysis of social media can monitor the extent to which brand reputation rises and falls over time. What's more, merging this social media monitoring with the Rust-Zeithaml-Lemon customer equity drivers can show exactly which dimensions of brand reputation are changing.
All marketers know that brands are important and that stakeholders' views of the brand are reflective of many different factors. Also, brand reputation may rise or fall over time, due to events that affect the brand. The fact that brand reputation is not constant makes it essential for companies to monitor their brands continuously, to determine whether a brand's reputation is changing, and to evaluate which aspects of the brand are causing these changes. Survey-based approaches exist, but surveying stakeholders on a daily basis is generally too expensive to be practical. Another approach is to infer what is happening to brand reputation by mining social media. Automatic, AI-based text analysis of social media posts is a realistic alternative.
Because Twitter is widely used by people to express opinions about brands and is often monitored by the public, the research team chose it as the platform to explore and baseline results. By analyzing millions of Twitter tweets, they demonstrate that their brand reputation tracker accurately reflected major brand events in real-time. For example, when it was revealed that Facebook had improperly shared personal information with an outside company (Cambridge Analytica), the brand tracker reflected that right away with a decline in brand reputation. On the positive side, when Google added new features, its brand reputation ratings went up.
Rust says that "It is one thing to know that brand reputation is improving or declining, but another thing entirely to figure out why. To ensure the actionability of our brand reputation tracker, we sorted the tweets according to the Rust-Zeithaml-Lemon customer equity drivers, which have been applied by many Fortune 500 companies. These three drivers, along with their sub-drivers, help managers know where to focus, making the brand tracker managerially relevant and actionable." The three main drivers of customer equity according to this framework are value, brand, and relationship. The value driver considers the rational or objective aspects of the brand, such as price, quality, or convenience. The brand driver considers the emotional or subjective aspects of the brand, such as attitude toward the brand, or perceptions of the brand's ethics. The relationship driver focuses on the aspects of the brand that create switching costs, such as loyalty programs or knowledge of the brand.
Rand explains that "Our brand reputation tracker is unique in that it can reflect the impact of brand events in real-time and connect them in a more granular way to managerially specific drivers of brand reputation. Managers can use it to drive programs that enhance their brands' standing with customers, forging deeper relationships and ultimately delivering more revenues to their bottom line."
INFORMATION:
Full article and author contact information available at: https://doi.org/10.1177/0022242921995173
About the Journal of Marketing
The Journal of Marketing develops and disseminates knowledge about real-world marketing questions useful to scholars, educators, managers, policy makers, consumers, and other societal stakeholders around the world. Published by the American Marketing Association since its founding in 1936, JM has played a significant role in shaping the content and boundaries of the marketing discipline. Christine Moorman (T. Austin Finch, Sr. Professor of Business Administration at the Fuqua School of Business, Duke University) serves as the current Editor in Chief.
https://www.ama.org/jm
About the American Marketing Association (AMA)
As the largest chapter-based marketing association in the world, the AMA is trusted by marketing and sales professionals to help them discover what is coming next in the industry. The AMA has a community of local chapters in more than 70 cities and 350 college campuses throughout North America. The AMA is home to award-winning content, PCM professional certification, premiere academic journals, and industry-leading training events and conferences.
https://www.ama.org
INDIANAPOLIS -- Artificial intelligence (AI)-driven healthcare has the potential to transform medical decision-making and treatment, but these algorithms must be thoroughly tested and continuously monitored to avoid unintended consequences to patients.
In a JAMA Network Open Invited Commentary, Regenstrief Institute President and Chief Executive Officer and Indiana University School of Medicine Associate Dean for Informatics and Health Services Research Peter Embí, M.D., M.S., strongly stated the importance of algorithmovigilance to address inherent biases in healthcare algorithms and their deployment. ...
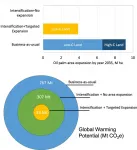
A global team of researchers recently released the results of a 'data-rich' modeling approach designed to illustrate a range of what-if scenarios for future oil palm plantation development in Indonesia. The study provides new insight into crop production strategies available to an industry facing increasing scrutiny.
Oil palm production is challenged by global and domestic concerns related to how it operates within its tropical rainforest environment, which is highly valued for its contribution to climate change mitigation potential and biodiversity protection. The study sheds new light on the future implications of maintaining business-as-usual ...
ROCHESTER, Minn. -- Patients diagnosed with post-COVID-19 syndrome, also known as "PCS," "COVID-19 long-haul syndrome" and "Post-Acute Sequelae of SARS COV-2," experience symptoms such as mood disorders, fatigue and perceived cognitive impairment that can negatively affect returning to work and resuming normal activities, according to a Mayo Clinic study published in Mayo Clinic Proceedings.
The study reports on the first 100 patients to participate in Mayo Clinic's COVID-19 Activity Rehabilitation program (CARP), one of the first multidisciplinary programs established to evaluate ...
A 'slow-motion' earthquake lasting 32 years - the slowest ever recorded - eventually led to the catastrophic 1861 Sumatra earthquake, researchers at the Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore) have found.
The NTU research team says their study highlights potential missing factors or mismodelling in global earthquake risk assessments today.
'Slow motion' earthquakes or 'slow slip events' refer to a type of long, drawn-out stress release phenomenon in which the Earth's tectonic plates slide against one another without causing major ground shaking or destruction. They typically involve movements of between ...
New research at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden suggests a link between psychosis and a genetic change that affects the brain's immune system. The study published in Molecular Psychiatry may impact the development of modern medicines for bipolar disorder or schizophrenia.
Psychosis affects approximately 2-3 per cent of the population and is characterized by a change in the perception of reality, often with elements of hallucinations and paranoid reactions.
Most of the people affected are patients with schizophrenia, but people with bipolar disorder may also experience psychotic symptoms.
The antipsychotics available today often have insufficient efficacy, and for patients, ...
Anyone who's raised a child or a pet will know just how fast and how steady their growth seems to be. You leave for a few days on a work trip and when you come home the child seems to have grown 10cm! That's all well and good for the modern household, but how did dinosaurs grow up? Did they, too, surprise their parents with their non-stop growth?
A new study lead by Dr Kimberley Chapelle of the American Museum of Natural History in New York City and Honorary Research Fellow at the University of the Witwatersrand suggests NOT. At least for one iconic southern African dinosaur species. By looking at the fossil ...
Can you feel the heat? To a thermal camera, which measures infrared radiation, the heat that we can feel is visible, like the heat of a traveler in an airport with a fever or the cold of a leaky window or door in the winter.
In a paper published in Proceedings of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, an international group of applied mathematicians and physicists, including Fernando Guevara Vasquez and Trent DeGiovanni from the University of Utah, report a theoretical way of mimicking thermal objects or making objects invisible to thermal measurements. And it doesn't ...
A study across 55 hospitals in Queensland, Australia suggests that a recent state policy to introduce a minimum ratio of one nurse to four patients for day shifts has successfully improved patient care, with a 7% drop in the chance of death and readmission, and 3% reduction in length of stay for every one less patient a nurse has on their workload.
The study of more than 400,000 patients and 17,000 nurses in 27 hospitals that implemented the policy and 28 comparison hospitals is published in The Lancet. It is the first prospective evaluation of the ...
CHICAGO --- A new Northwestern Medicine study of placentas from patients who received the COVID-19 vaccine during pregnancy found no evidence of injury, adding to the growing literature that COVID-19 vaccines are safe in pregnancy.
"The placenta is like the black box in an airplane. If something goes wrong with a pregnancy, we usually see changes in the placenta that can help us figure out what happened," said corresponding author Dr. Jeffery Goldstein, assistant professor of pathology at Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine and a Northwestern Medicine pathologist. "From what we can tell, the COVID vaccine does not damage the placenta."
The study will be published May 11 in the journal Obstetrics ...
TORONTO, ON - Geoscientists at the University of Toronto (U of T) and Istanbul Technical University have discovered a new process in plate tectonics which shows that tremendous damage occurs to areas of Earth's crust long before it should be geologically altered by known plate-boundary processes, highlighting the need to amend current understandings of the planet's tectonic cycle.
Plate tectonics, an accepted theory for over 60 years that explains the geologic processes occurring below the surface of Earth, holds that its outer shell is fragmented into continent-sized blocks of solid rock, called "plates," that slide over Earth's mantle, the rocky inner layer above ...