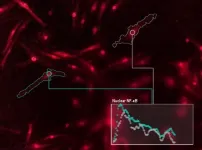
(Press-News.org) UCLA life scientists have identified six "words" that specific immune cells use to call up immune defense genes -- an important step toward understanding the language the body uses to marshal responses to threats.
In addition, they discovered that the incorrect use of two of these words can activate the wrong genes, resulting in the autoimmune disease known as Sjögren's syndrome. The research, conducted in mice, END
UCLA scientists decode the 'language' of immune cells
The advance, researchers say, is like the discovery of the Rosetta stone and could eventually lead to new treatments for diseases
2021-05-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study finds ghost forest 'tree farts' contribute to greenhouse gas emissions
2021-05-12
A new study from North Carolina State University finds that greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from standing dead trees in coastal wetland forests - colloquially called "tree farts" - need to be accounted for when assessing the environmental impact of so-called "ghost forests."
In the study, researchers compared the quantity and type of GHG emissions from dead tree snags to emissions from the soil. While snags did not release as much as the soils, they did increase GHG emissions of the overall ecosystem by about 25 percent. Researchers say the findings show snags are important for understanding the total environmental impact of the spread of dead trees in coastal wetlands, known as ghost forests, ...
A delicate balance: Learning new ways that gut microbes educate the immune system
2021-05-12
The immune system's main job is identifying things that can make us sick. In the language of immunology, this means distinguishing "self" from "non-self": The cells of our organs are self, while disease-causing bacteria and viruses are non-self.
But what about the billions of bacteria that live in our guts and provide us with benefits like digesting food and making vitamins? Are they friend or foe?
This isn't only a philosophical question. An immune system that mistakes our good gut bacteria for an enemy can cause a dangerous type of inflammation in the intestines called colitis. An immune system that looks the other way while gut microbes spill past their assigned borders is equally dangerous. Understanding ...
How the body builds a healthy relationship with 'good' gut bacteria
2021-05-12
Our body's relationship with bacteria is complex. While infectious bacteria can cause illness, our gut is also teaming with "good" bacteria that aids nutrition and helps keep us healthy. But even the "good" can have bad effects if these bacteria end up in tissues and organs where they're not supposed to be.
Now, research published in END ...
'Opioid treatment deserts' abound, study finds
2021-05-12
COLUMBUS, Ohio - Neighborhoods without opioid treatment providers likely serve as a widespread barrier to care for those who are ready to seek help, a new study has found.
The study, led by researchers at The Ohio State University, appears today (May 12, 2021) in the journal PLOS ONE.
"The study identified clear opioid treatment deserts that undoubtedly stand in the way of access to needed care and that likely exist throughout the state and the nation. These are areas where treatment providers should be setting up shop - we need a surge of resources into these areas," said Ayaz Hyder, an assistant professor in Ohio State's College of Public Health ...
Elephant seals' extreme diving allows them to exploit deep ocean niche
2021-05-12
Elephant Seals' Extreme Diving Allows Them to Exploit Deep Ocean Niche
Using data captured by video cameras and smart accelerometers attached to female elephant seals, Taiki Adachi and colleagues show that the animals spend at least 80% of their day foraging for fish, feeding between 1,000 and 2,000 times per day. The unique glimpse at elephant seal foraging strategy shows how these large marine mammals exploit a unique ocean niche filled with small fish. The findings also may offer a way to monitor the health of the mesopelagic zone, the dark and cold ocean "twilight zone" ecosystem at 200 to 1,000 meters deep. Small mesopelagic fish dominate the world's ocean ...
Johns Hopkins develops device for fast gonorrhea diagnosis
2021-05-12
A Johns Hopkins University-led team has created an inexpensive portable device and cellphone app to diagnose gonorrhea in less than 15 minutes and determine if a particular strain will respond to frontline antibiotics.
The invention improves on traditional testing in hospital laboratories and clinics, which typically takes up to a week to deliver results--time during which patients can unknowingly spread their infections. The team's results appear today in Science Translational Medicine.
"Our portable, inexpensive testing platform has the potential to change the game when it comes to diagnosing and enabling rapid treatment of sexually transmitted infections," said team leader Tza-Huei Wang, a professor of mechanical engineering ...
Genetic risk of heart disease may be due to low Omega 3-linked biomarker
2021-05-12
People who are genetically more likely to suffer from cardiovascular diseases may benefit from boosting a biomarker found in fish oils, a new study suggests.
In a genetic study in 1,886 Asian Indians published in PLOS ONE today (Wednesday 12 May), scientists have identified the first evidence for the role of adiponectin, an obesity-related biomarker, in the association between a genetic variation called omentin and cardiometabolic health.
The team, led by Professor Vimal Karani from the University of Reading, observed that the role of adiponectin was linked to cardiovascular disease markers that were independent of common and central obesity among the Asian Indian population. ...
We need herd immunity against COVID-19 vaccine misinformation
2021-05-12
Misleading claims about COVID-19 vaccines can negatively impact public confidence in immunisation uptake, a new UNSW Sydney study reveals.
A new study published in the scientific journal PLOS ONE revealed over 103 million people globally liked, shared, retweeted or reacted with an emoji to misinformation and conspiracy theories about COVID-19 vaccines.
In 2020, a social media post claiming, "a new vaccine for COVID-19 will alter a person's DNA and result in them becoming genetically modified" was circulated on Facebook accounts in Australia. Up until August 21, 2020, this false claim had attracted 360 shares and was viewed 32,000 times.
The study, led by UNSW researchers, ...
How imperfect memory causes poor choices
2021-05-12
Quick: Pick your three favorite fast-food restaurants.
If you're like many people, McDonald's, Wendy's, and Burger King may come to mind--even if you much prefer In-N-Out or Chick-fil-A.
A new study from UC Berkeley's Haas School of Business and UC San Francisco's Department of Neurology found that when it comes to making choices, we surprisingly often forget about the things we like best and are swayed by what we remember. The paper, publishing this week in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, combines insights from economics and psychology with decision-making experiments and fMRI brain scans to examine how our imperfect memories affect our decision making.
"Life is not a multiple-choice test," says Berkeley ...
All gas, no brakes: Testosterone may act as 'brake pedal' on immune response
2021-05-12
Autoimmune diseases have something in common with horses, bachelor's degrees and daily flossing habits: women are more likely to have them.
One reason for autoimmune diseases' prevalence in women may be sex-based differences in inflammation. In a new study, West Virginia University researcher Jonathan Busada investigated how sex hormones affect stomach inflammation in males and females. He found that androgens--or male sex hormones--may help to keep stomach inflammation in check.
"Stomach cancer is primarily caused by rampant inflammation," said Busada, an assistant professor in the School of ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Increased risk of bullying in open-plan offices
Frequent scrolling affects perceptions of the work environment
Brain activity reveals how well we mentally size up others
Taiwanese and UK scientists identify FOXJ3 gene linked to drug-resistant focal epilepsy
Pregnancy complications impact women’s stress levels and cardiovascular risk long after delivery
Spring fatigue cannot be empirically proven
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
[Press-News.org] UCLA scientists decode the 'language' of immune cellsThe advance, researchers say, is like the discovery of the Rosetta stone and could eventually lead to new treatments for diseases