Jab-free dengue immunity could be just a click away
2021-05-13
(Press-News.org) A dengue virus vaccine candidate has passed an important milestone, with promising results in animal model testing providing hope to the 390 million people infected every year.
The University of Queensland-developed vaccine candidate, applied to the skin via the high-density microarray patch (HD-MAP), has produced a protective immune response in dengue-infected mice.
UQ PhD candidate Jovin Choo said the result could lead to a readily administered vaccine that could help halt the devastation of dengue fever globally.
"Dengue is the most significant mosquito-borne viral disease in the world's tropical zone, infecting 390 million and killing 25,000 annually, resulting in annual estimated economic cost of $8.9 billion," Ms Choo said.
"While a dengue vaccine technically already exists, it's only licensed to be used in certain countries where Dengue virus is endemic - and with restricted use.
"So to properly fight this terrible disease, we've engineered a vaccine candidate based on a platform technology that uses an Australian insect virus called Binjari virus."
UQ researchers merged the Binjari and dengue viruses making what's known as a chimeric virus - an artificial virus - to build the basis of the vaccine which has resulted in some great benefits.
"For instance, the particles exactly mimic the surface of their dengue counterpart, which induces a strong, authentic and protective immune response," Ms Choo said.
"Also, it allows us to very easily manufacture high yields of the vaccine candidate in mosquito cell culture.
"And it only grows in insect cells, and not mammalian cells, making it extremely safe."
UQ's Dr David Muller, one of the senior authors of the research, said another advantage was that the candidate could offer potent antibody responses when delivered via the UQ-developed, Vaxxas Pty Ltd commercialised, HD-MAP system.
"Using the microarray patch, we're able to employ needle-free delivery of the vaccine to the immune cell-rich layers of the skin with just a click," he said.
"This targeted delivery allows us to achieve potent neutralising antibody responses using a fraction of a typical dose delivered by injection.
"The ease of administration, coupled with lower dose amounts means that the patch could provide both an efficient and inexpensive vaccination option."
UQ's Dr Jody Hobson-Peters said this was only the start with the research team looking to apply these techniques more widely.
"There are four variations of dengue that are closely related, all of which can cause severe disease," Dr Peters said.
"So we're now expanding our ongoing pre-clinical studies to all four of these forms of dengue virus.
"And we're also looking to adapt this technology to other viruses, like Zika virus, West Nile virus and Japanese encephalitis virus.
"These are daunting diseases but cheap, easy and accessible vaccinations for them might one day be just a click away."
INFORMATION:
The research is published in npj Vaccines (DOI: 10.1038/s41541-021-00328-1).
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-13
LOS ALAMOS, N.M., May 12, 2021--A new theorem from the field of quantum machine learning has poked a major hole in the accepted understanding about information scrambling.
"Our theorem implies that we are not going to be able to use quantum machine learning to learn typical random or chaotic processes, such as black holes. In this sense, it places a fundamental limit on the learnability of unknown processes," said Zoe Holmes, a post-doc at Los Alamos National Laboratory and coauthor of the paper describing the work published today in Physical Review Letters.
"Thankfully, because most physically interesting processes are sufficiently simple or structured so that they do not resemble ...
2021-05-13
A new study, by researchers from Simon Fraser University and the Department of Fisheries and Oceans, reveals the trade-offs of fish biodiversity--its costs and benefits to mixed-stock fisheries--and points to a potential way to harness the benefits while avoiding costs to fishery performance.
Many Pacific salmon fisheries catch fish that come from multiple stocks (management units), often representing locally-adapted populations, in so-called mixed-stock fisheries. Fish are intercepted in the ocean as they migrate along the coast, returning to different rivers to spawn.
The study used computer models of hypothetical fisheries and case studies of three actual sockeye salmon fisheries, including BC's Fraser River fishery, to explore how fish biodiversity within mixed-stock ...
2021-05-13
PASADENA, Calif. -- Among cancer patients with health coverage in Southern California, those who were diagnosed and treated at Kaiser Permanente, an integrated health care organization, had better survival rates, especially Black and Latino patients, according to Kaiser Permanente research published in The American Journal of Managed Care.
"Kaiser Permanente is committed to finding and addressing health care inequities," said the study's senior author, Reina Haque, PhD, a cancer epidemiologist in the Kaiser Permanente Southern California Department of Research & Evaluation. "We investigated survival among insured patients with cancer ...
2021-05-13
SAN FRANCISCO, CA--May 12, 2021--Following the minuscule movements of every cell in a petri dish would be a painstaking task for any human. But teach a set of computer programs to do the job, and they can complete it quickly and even observe things that the human eye would miss.
Scientists at Gladstone Institutes have developed such an approach, which uses "neural nets"--artificial intelligence programs that can detect patterns--to analyze the locations of hundreds of cells growing together in a colony. When they applied the technique to a group of stem cells, the program revealed that a small number of cells act as "leaders," able to direct the movements of their neighbors.
"This technique gives us a much more comprehensive view of how cells behave, how they work cooperatively, and how ...
2021-05-13
White evangelicals are best persuaded to mask up through messages that stress the Christian doctrine of "love thy neighbor," according to a UCR-authored study published Tuesday.
The study yielded a second effective way to persuade white evangelicals - but only if they are Republican. That is, messaging from former President Donald Trump that aligns mask-wearing with patriotism.
The lessons learned from the study can be borrowed for pro-vaccine messaging, said study author Jennifer Merolla, a UCR professor of political science.
About 45% of white evangelicals do not plan on getting vaccinated against COVID-19, according to a Pew Research Center poll. Health officials have said persuading the 41 million white evangelical ...
2021-05-13
A person's stance on abortion is linked to their, often inaccurate, belief about when a fetus can feel pain, a University of Otago study has found.
Lead author Emma Harcourt, PhD candidate in Otago's Centre for Science Communication, says misinformation about abortion and pregnancy is common and potentially harmful.
"The current medical consensus is that it is unlikely that fetal pain perception is possible before the 29th or 30th weeks of pregnancy. However, we found that most people believe that the capacity to feel pain develops much earlier and that this was particularly evident in participants with anti-abortion views," she says.
The study, published in The Australian and New Zealand Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, recruited 374 ...
2021-05-13
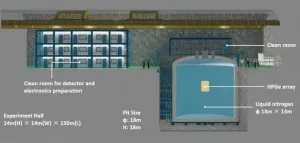
Numerous compelling evidences from astroparticle physics and cosmology indicate that the major matter component in the Universe is dark matter, accounting for about 85% with the remaining 15% is the ordinary matter. Nevertheless, people still know little about the dark matter, including its mass and other properties. Many models predict dark matter particles could couple to ordinary particle at weak interaction level, so it is possible to capture the signal of dark matter particle in the direct detection experiment. The scientific goals of the China ...
2021-05-13
The evolution of ankle and foot bones into different shapes and sizes helped mammals adapt and thrive after the extinction of the dinosaurs, a study suggests.
A surge of evolution following the mass extinction 66 million years ago enabled mammals to diversify and prosper during a period of major global change, researchers say.
Analysis of bones that form part of the ankle and the heel of the foot reveal that mammals during this time - the Paleocene Period - were less primitive than previously thought.
Palaeontologists from the University of Edinburgh made the discovery by comparing the anatomy of Paleocene mammals with species from the earlier Cretaceous ...
2021-05-13
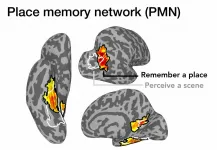
As we move through the world, what we see is seamlessly integrated with our memory of the broader spatial environment. How does the brain accomplish this feat? A new study from Dartmouth College reveals that three regions of the brain in the posterior cerebral cortex, which the researchers call "place-memory areas," form a link between the brain's perceptual and memory systems. The findings are published in Nature Communications.
"As we navigate our surroundings, information enters the visual cortex and somehow ends up as knowledge of where we are - the question is where this transformation into spatial ...
2021-05-13
A research group has developed an ion-selective smart porous membrane that can respond to outer stimuli, potentially paving the way for new applications in molecular separation and sensing applications.
Porous thin films have attracted the attention of scientists because of their potential use in sensors, energy harvesting, and ion/molecular separation.
Nanostructure properties, such as pore size, thickness, and film density, affect molecular selectivity and molecular permeability. Surface properties also have a significant impact on molecular selectivity.
Thus it is important to be able to control both the 3D nanostructures and surface properties of ultrathin porous films.
Previous research shed light on smart porous membranes, which are covered with molecules that can respond ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Jab-free dengue immunity could be just a click away