Tests of bitumen pave way to rational approaches in road building
A research conducted by Kazan Federal University was published in Scientific Reports
2021-05-13
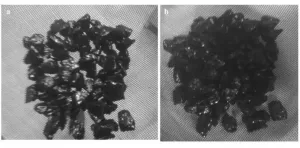
(Press-News.org) First co-author, Junior Research Associate of the Rheological and Thermochemical Research Lab Richard Djimasbe, comments, "To obtain bitumen as a half-solid product from heavy oil, you have to extract light fractions, and the rest is non-oxidized bitumen. Because of the relatively low ratio of light fractions in heavy oil, it's a simple and cheap way of bitumen production. The method allows for rational use of both heavy oil and light oil."
Lab Head Mikhail Varfolomeev adds, "One of the priorities of our World-Level Research Center in Liquid Hydrocarbons is the use of heavy oils, which constitute the majority of reserves both in Russia and in the world. One of the most important parts of this is extraction and refining of heavy petroleum reserves. The paper makes steps in that direction."
Non-traditional reserves, such as heavy oil, natural bitumen, and shale oil, have been found in Canada, Venezuela, Brazil, Russia, Chad, Madagascar and many other countries.
The research team hopes that non-oxidized bitumen can become another popular product obtained from heavy oil in Russia.
"The researchers focused on the use of a specially packed oxidizing column to increase the contact surface between the feedstock and the injected compressed air in order to reduce production costs, followed by a comparison of oxidized and unoxidized bitumen obtained by steam distillation," says co-author, Junior Research Associate Ameen A. Al-Muntaser.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-13
Laura Riesenberg was visiting a local amusement park with three of her children when she suffered a massive heart attack.
"I was down for about 20 minutes and they defibrillated me twice on site, possibly three times," she says. "Obviously, I was unaware of it. I know from reading the reports what happened."
"I was extremely fortunate that someone found me within seconds of collapsing," says Riesenberg. "Had it happened anywhere else I wouldn't be talking to you right now. If I had been in the basement doing laundry, I would have been in trouble."
The 51-year-old Loveland, Ohio, resident ...
2021-05-13
Pregnant Aussie mums are being denied access to medications which treat severe nausea and vomiting by pharmacists and medical practitioners because of misleading labels and a lack of awareness about clinical guidelines.
A new study surveyed 249 Australian women who suffered from severe nausea and vomiting during pregnancy (NVP) or hyperemesis gravidarum (HG) and examined their experiences in accessing medications during pregnancy.
One in four women reported being denied medications for NVP/ HG at some stage during pregnancy. This most commonly involved the over-the-counter medicine doxylamine and interactions ...
2021-05-13
PHOENIX, Ariz. -- May 13, 2021 -- In the largest study of the associations between smoking and cardiovascular disease on cognitive function, researchers at the Translational Genomics Research Institute (TGen), an affiliate of City of Hope, found both impair the ability to learn and memorize; and that the effects of smoking are more pronounced among females, while males are more impaired by cardiovascular disease.
The results appear today in the journal Scientific Reports.
Previous attempts to quantify cognitive function among smokers and assess sex differences produced mixed results. The TGen researchers attribute this to the limited size of previous data sets. By ...
2021-05-13
College Park, Md. - Companies have often considered app adoption among their customers to have a positive impact on customer spending. According to new research from marketing professor P.K. Kannan at the University of Maryland's Robert H. Smith School of Business, higher app adoption among hotel chains could be linked to lower spending among lower-level loyalty customers, who are more likely to use apps to get the best deals.
Kannan worked with Xian Gu, an assistant professor of marketing at Indiana University, for the research, published as "The Dark Side of Mobile App Adoption: Examining the Impact on Customers' Multichannel ...
2021-05-13
When a piece of conducting material is heated up at one of its ends, a voltage difference can build up across the sample, which in turn can be converted into a current. This is the so-called Seebeck effect, the cornerstone of thermoelectric effects. In particular, the effect provides a route to creating work out of a temperature difference. Such thermoelectric engines do not have any movable part and are therefore convenient power sources in various applications, including propelling NASA's Mars rover Perseverance. The Seebeck effect is interesting for fundamental physics, too, as the magnitude and sign of the induced thermoelectric current is characteristic of the material and indicates ...
2021-05-13
A small drug molecule that appears to protect normal tissue from the damaging effects of radiation, may simultaneously be able to boost the cancer-killing effect of radiation therapy, according to a new study led by scientists at University of Iowa, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, and Galera Therapeutics, Inc.
The study, published online May 12 in Science Translational Medicine, suggests that the drug's dual effect is based on a fundamental difference between the ability of cancer cells and healthy cells to withstand the damaging effects of a highly reactive molecule called hydrogen peroxide, which is produced during the dismutation of superoxide.
The drug, known as Avasopasem manganese, is made by Galera Therapeutics. ...
2021-05-13
The stock market is a staple of business news, but it is unclear how meaningful stock prices are to the larger economy. Do changes in stock prices directly affect shorter-term consumption, or are they just leading indicators for subsequent economic activity? The U.S. Federal Reserve, for its part, usually seems to act as if stock-based wealth does help drive spending and employment. But is this correct?
A new study co-authored by an MIT economist brings data to the discussion and finds that increased stock market wealth has moderate but clear economic effects. After looking at the U.S. on a county-by-county basis, the study finds that after large market ...
2021-05-13
Sydney, Australia; New York City, USA (May 13, 2021)--In a collaborative report published today in Cell, scientists from Sydney and New York describe the critical worldwide need to improve the diversity of cells used in medical research. Currently, 95% of all human cell lines used in research are of European descent. The authors provide actionable steps that researchers and the biomedical community can take to promote more inclusivity in preclinical and basic science research.
The commentary, "Ancestry Matters: Building inclusivity into preclinical study design," is co-authored by Sophie Zaaijer, PhD, who co-founded FIND Genomics (findgen.bio), a company that aims to improve reproducible ...
2021-05-13
The once-abundant California condor briefly went extinct in the wild, with only 22 individuals living in captivity by 1982. Today, 300 condors live freely in the wild and another 200 are in captivity. But, despite the condor's struggles, a new study of the California condor genome reported in the journal Current Biology on May 13 has found a surprising amount of genetic diversity.
The study is the first to begin quantifying diversity across the entire California condor genome, which offers researchers needed baseline information to inform future research and conservation of this iconic species, ...
2021-05-13
New York, NY (May 13, 2021)-- Artificial food colorants can cause disease when the immune system has become dysregulated, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai researchers report. The study, published in Cell Metabolism in May, was the first to show this phenomenon.
The study, conducted in mice, found that the mice developed colitis when they consumed food with the artificial food colorants FD&C Red 40 and Yellow 6 when a specific component of their immune system, known as cytokine IL-23, was dysregulated. While it remains unclear whether food colorants have similar effects in humans, researchers plan to investigate exactly how cytokine IL-23 promotes the development of colitis after food colorant exposure.
Colitis is a form of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and cytokine ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Tests of bitumen pave way to rational approaches in road building
A research conducted by Kazan Federal University was published in Scientific Reports