(Press-News.org) An innovative cardiac rehabilitation intervention started earlier and more custom-tailored to the individual improved physical function, frailty, quality-of-life, and depression in hospitalized heart failure patients, compared to traditional rehabilitation programs. Supported by the National Institute on Aging (NIA), part of the National institutes of Health, these new study results were published May 16 in the New England Journal of Medicine and also presented at the American College of Cardiology's 70th Annual Scientific Session.
"Designing earlier and more personalized individual-specific approaches to heart failure rehab shows great promise for improving outcomes for this common but complex condition that is one of the leading causes of hospitalization for older adults," said NIA Director Richard J. Hodes, M.D. "These results mark encouraging progress on a path to better overall quality of life and physical function for the millions of older Americans who develop heart failure each year."
For this new study, a research team led by Dalane W. Kitzman, M.D., professor of cardiovascular medicine and geriatrics/gerontology at Wake Forest School of Medicine, Winston-Salem, North Carolina, followed 349 END
Tailored, earlier heart failure rehab has physical, emotional benefits for patients
NIH-funded clinical trial improved frailty, depression and overall quality of life
2021-05-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Novel monoclonal antibody can substantially lower triglycerides in patients with acute pancreatitis
2021-05-16
The investigational drug evinacumab reduced triglycerides in patients with severe hypertriglyceridemia (sHTG) and a history of hospitalizations for acute pancreatitis in a phase 2 global study led by Mount Sinai. The fully human monoclonal antibody produced sustained reductions in triglyceride levels of up to 82 percent, depending on the patient's genotype, while also lowering the risk of recurrent acute pancreatitis. The results of the study will be presented as a late-breaking clinical trial at the American College of Cardiology (ACC) Annual Scientific Session, on May 16.
"Evinacumab has the potential to not only lower triglycerides, but the risk of acute pancreatitis, quality of life, and the risk of cardiovascular events in ...
Simple surgery prevents strokes in heart patients
2021-05-15
Hamilton, ON (May 15, 2021) - A simple surgery saves patients with heart arrhythmia from often-lethal strokes, says a large international study led by McMaster University.
Researchers found that removing the left atrial appendage -- an unused, finger-like tissue that can trap blood in the heart chamber and increase the risk of clots -- cuts the risk of strokes by more than one-third in patients with atrial fibrillation.
Even better, the reduced clotting risk comes on top of any other benefits conferred by blood-thinner medications patients with this condition are usually prescribed.
"If you have atrial fibrillation and are undergoing heart surgery, the surgeon should be removing your left atrial appendage, because it is a set-up for forming clots. Our trial has shown ...
Rutgers reports first instance of COVID-19 triggering recurrent blood clots in arms
2021-05-15
Researchers at Rutgers Robert Wood Johnson Medical School are reporting the first instance of COVID-19 triggering a rare recurrence of potentially serious blood clots in people's arms.
The discovery, published in the journal Viruses, improves the understanding of how inflammation caused by COVID-19 can lead to upper extremity blood clots and how best to treat them. The case study is part of a larger Rutgers study of 1,000 hospitalized patients diagnosed with COVID-19 who were admitted and discharged between March and May 2020.
While there have been reports of lower extremity deep vein thrombosis following COVID-19, ...
New technology enables rapid sequencing of entire genomes of plant pathogens
2021-05-14
Next-generation sequencing technology has made it easier than ever for quick diagnosis of plant diseases. "It's really exciting to see how sequencing technologies have evolved and how this new technology facilitates sequencing of entire genomes in such a short amount of time," said Yazmín Rivera, a plant pathologist with the United States Department of Agriculture's Plant Protection and Quarantine program, who recently published a research paper on the efficacy of Oxford Nanopore Technologies protocols.
"We wanted to provide an unbiased assessment of the technology and protocols available for long read sequencing," Rivera explained. Along with other plant pathologists, Rivera used the company's protocols to prepare RNA and DNA libraries from virus-infected plant material ...
People at high genetic risk for colorectal cancer benefit more from lifestyle changes
2021-05-14
People with a high polygenic risk score for colorectal cancer could benefit more at preventing the disease by leading healthy lifestyles than those at lower genetic risk, according to a study by Vanderbilt researchers published in the April issue of The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition.
Analyzing data from participants in the UK Biobank, the researchers estimated that maintaining a healthy lifestyle was associated with a nearly 40% reduction in colorectal cancer risk among those with a high genetic risk of developing the disease. The percentage dropped to only about 25% among people at ...
Compound may prevent risk of a form of arrhythmia from common medications
2021-05-14
Dozens of commonly used drugs, including antibiotics, antinausea and anticancer medications, have a potential side effect of lengthening the electrical event that triggers contraction, creating an irregular heartbeat, or cardiac arrhythmia called acquired Long QT syndrome. While safe in their current dosages, some of these drugs may have a more therapeutic benefit at higher doses, but are limited by the risk of arrhythmia.
Through both computational and experimental validation, a multi-institutional team of researchers has identified a compound that prevents the lengthening of the heart's electrical event, or action potential, resulting in a major step toward safer use and expanded therapeutic efficacy of these ...
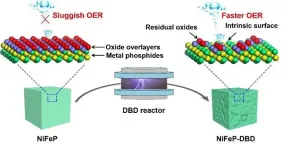
Etching process enhances the extraction of hydrogen during water electrolysis
2021-05-14
Extracting hydrogen from water through electrolysis offers a promising route for increasing the production of hydrogen, a clean and environmentally friendly fuel. But one major challenge of water electrolysis is the sluggish reaction of oxygen at the anode, known as the oxygen evolution reaction (OER).
A collaboration between researchers at Hunan University and Shenzhen University in China, has led to a discovery that promises to improve the OER process. In their recent paper, published in the KeAi journal Green Energy & Environment, they report that etching - or, in other words, chemically removing - the oxide overlayers that form on the surface of the metal phosphide electrocatalysts regularly used in electrolysis, can increase ...
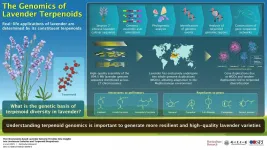
Terpen-tales: The mystery behind the unique fragrance of the lovely lavender
2021-05-14
Even the mention of lavender evokes the distinct fragrance of the flower. This beautiful flower has been used to make perfumes and essential oils since time immemorial. The aesthetics of the flower have captured the imagination of hundreds, worldwide. So, what makes this flower so special? What are the "magical" compounds that gives it its unique fragrance? What is the genetic basis of these compounds? These questions have long puzzled scientists.
To find out the answers, a group of scientists from China have sequenced the genome of lavender, which is known in the scientific world as Lavandula angustifolia. The team headed by Dr. Lei Shi, Professor at the Key Laboratory of Plant Resources and Beijing Botanical Garden, Institute of Botany, Chinese ...
Cataloging breast cells to find cancer origins
2021-05-14
What if you could predict which cells might become cancerous? Breast tissue changes dramatically throughout a woman's life, so finding markers for sudden changes that can lead to cancer is especially difficult. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) Associate Professor Camila dos Santos and her team identified and cataloged thousands of normal human and mouse breast cell types. The new catalog redefines healthy breast tissue so that when something goes awry, scientists can pinpoint its origin.
Any breast cell could become cancerous. Dos Santos says:
"To understand breast cancer risk, you have to understand normal breast cells first, so when we think about preventive and even targeting therapies, ...
Heart attack recovery aided by injecting heart muscle cells that overexpress cyclin D2
2021-05-14
BIRMINGHAM, Ala. - In a large-animal study, researchers have shown that heart attack recovery is aided by injection of heart muscle cells derived from human induced pluripotent stem cell line, or hiPSCs, that overexpress cyclin D2. This research, published in the journal Circulation, used a pig model of heart attacks, which more closely resembles the human heart in size and physiology, and thus has higher clinical relevance to human disease, compared to studies in mice.
An enduring challenge for bioengineering researchers is the failure of the heart to regenerate muscle tissue after a heart attack has killed part of its muscle wall. That dead tissue can strain the surrounding muscle, leading to a lethal heart enlargement.
Heart experts thus have sought to create new tissue -- applying ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Exercise and nutritional drinks can reduce the need for care in dementia
Michelson Medical Research Foundation awards $750,000 to rising immunology leaders
SfN announces Early Career Policy Ambassadors Class of 2026
Spiritual practices strongly associated with reduced risk for hazardous alcohol and drug use
Novel vaccine protects against C. diff disease and recurrence
An “electrical” circadian clock balances growth between shoots and roots
Largest study of rare skin cancer in Mexican patients shows its more complex than previously thought
Colonists dredged away Sydney’s natural oyster reefs. Now science knows how best to restore them.
Joint and independent associations of gestational diabetes and depression with childhood obesity
Spirituality and harmful or hazardous alcohol and other drug use
New plastic material could solve energy storage challenge, researchers report
Mapping protein production in brain cells yields new insights for brain disease
Exposing a hidden anchor for HIV replication
Can Europe be climate-neutral by 2050? New monitor tracks the pace of the energy transition
Major heart attack study reveals ‘survival paradox’: Frail men at higher risk of death than women despite better treatment
Medicare patients get different stroke care depending on plan, analysis reveals
Polyploidy-induced senescence may drive aging, tissue repair, and cancer risk
Study shows that treating patients with lifestyle medicine may help reduce clinician burnout
Experimental and numerical framework for acoustic streaming prediction in mid-air phased arrays
Ancestral motif enables broad DNA binding by NIN, a master regulator of rhizobial symbiosis
Macrophage immune cells need constant reminders to retain memories of prior infections
Ultra-endurance running may accelerate aging and breakdown of red blood cells
Ancient mind-body practice proven to lower blood pressure in clinical trial
SwRI to create advanced Product Lifecycle Management system for the Air Force
Natural selection operates on multiple levels, comprehensive review of scientific studies shows
Developing a national research program on liquid metals for fusion
AI-powered ECG could help guide lifelong heart monitoring for patients with repaired tetralogy of fallot
Global shark bites return to average in 2025, with a smaller proportion in the United States
Millions are unaware of heart risks that don’t start in the heart
What freezing plants in blocks of ice can tell us about the future of Svalbard’s plant communities
[Press-News.org] Tailored, earlier heart failure rehab has physical, emotional benefits for patientsNIH-funded clinical trial improved frailty, depression and overall quality of life