How COVID-19 survival improved in UK hospitals during first wave
2021-05-17
(Press-News.org) The likelihood of people surviving COVID-19 in UK hospitals has been improving over time, a new study has found.
Research published in The Lancet Respiratory Medicine by the ISARIC Coronavirus Clinical Characterisation Consortium found that in-hospital mortality declined from 32% at the start of the first wave (Mar-Apr 2020) to 16% at the end of the first wave (Jun-Jul 2020).
In their study of 63,972 adults admitted to 247 UK hospitals the researchers found reductions in mortality were observed in all age groups, in all ethnic groups, for both sexes, and in patients with and without comorbidities. This improvement was found to be associated with adoption of steroids as a newly proven treatment and improvements in respiratory support and critical care use, in part reflecting improved clinical knowledge.
Dr Annemarie Docherty, Senior Clinical Lecturer at the University of Edinburgh and a Consultant in Intensive Care Medicine, said: "The risk of death for people admitted to hospital with covid-19 was extremely high at around one in three at the beginning of the first wave, and consistently improved over subsequent months. Part of this improvement can be explained by differences in the people who were admitted to hospital, and how sick they were. Further reduction in the risk of death can be explained by improvements in care of covid-19 patients with treatments such as dexamethasone and better use of advanced respiratory support."
Professor Calum Semple, Professor of Child Health and Outbreak Medicine at the University of Liverpool and Co-Lead of ISARIC4C, said: "This is good news in a week where there is some anxiety about how new variants will impact upon the roadmap out of lock down. We now understand better how changes in patient characteristics and improvement in medical care have led to improved survival in UK hospitals. The discovery of what works and as importantly what does not work was only possible because of prepared research capacity that was put in place by the investigators collaborating at Universities of Liverpool, Edinburgh, Imperial College, and Oxford with NIHR support."
Professor Chris Whitty, Chief Medical Officer and co-lead of the National Institute for Health Research, said: "This National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) supported research provides evidence that frontline clinicians and healthcare professionals learnt and adapted to COVID-19 to improve patient care. Many of those healthcare professionals also facilitated research into treatments, such as dexamethasone, which was vital to the improvement in mortality described in this paper. These improvements are testament to the hard work of many."
The work is the latest result from ISARIC - a global network of clinicians and scientists who have been preparing to prevent disease and death from severe outbreaks since 2012 in readiness for a pandemic such as this. The ISARIC4C study is led by researchers from Liverpool, Edinburgh and Imperial College London and is principally funded by grants from the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) and UK Medical Research Council.
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-17
A group of Brazilian and Portuguese researchers observed a correlation between the presence of lead in the organism and a microRNA (miRNA) that could be associated with the mechanisms that regulate DNA methylation, a physiological process required to control gene expression and ensure that genes function properly.
The alterations were detected in blood cells from workers in automotive battery plants, which use lead as a raw material. Curiously, lead levels in blood samples from 85 volunteers – averaging 20 micrograms per deciliter of blood (20 μg/dl) – were lower than the acceptable ceiling defined in Brazilian law (60 μg/dl).
The study was supported by FAPESP and ...
2021-05-17
A long noncoding RNA whose function was previously unknown turns out to play an important role in promoting the body's immune response against cancer and holds promise for enhancing the efficacy of anti-cancer immunotherapy.
That's according to new findings reported in Nature Cell Biology by researchers at the University of Michigan Rogel Cancer Center.
The group dubbed the RNA they identified LIMIT -- for long noncoding RNA inducing major histocompatibility complex class I and immunogenicity of tumor.
"LIMIT is easy to remember, but really it does the opposite. It stimulates immune functions against cancer," says senior study author Weiping Zou, M.D., Ph.D., the Charles B. de Nancrede Professor of Pathology, Immunology, Biology, and Surgery at U-M.
Only a small part of the human ...
2021-05-17
Researchers at the University of California, Davis, have found a link between traffic-related air pollution and an increased risk for age-related dementia, including Alzheimer's disease. Their study, based on rodent models, corroborates previous epidemiological evidence showing this association.
Alzheimer's disease is the most common cause of age-related dementia and the sixth leading cause of death in the United States. More than 5 million Americans currently live with Alzheimer's disease -- a number that is expected to triple by 2050 as the population ages. ...
2021-05-17
In patients receiving therapeutic hypothermia after suffering out-of-hospital cardiac arrest, those who were cooled below 31 degrees Celsius (about 88 degrees Fahrenheit) for 24 hours showed no difference in terms of death or poor neurological outcomes at six months compared with patients receiving guideline-recommended cooling of 34 C (about 93 F). These findings are part of a study presented at the American College of Cardiology's 70th Annual Scientific Session.
Therapeutic hypothermia is a procedure in which a person's body is cooled far below normal body temperature. It has been shown to improve survival and reduce brain damage in people who have been resuscitated but remain comatose after suffering cardiac arrest (when the heart stops ...
2021-05-17
Sperm are generally viewed as having just one action in reproduction - to fertilise the female's egg - but studies at the University of Adelaide are overturning that view.
Published in Nature Research journal Communications Biology, new research shows that sperm also deliver signals directly to the female reproductive tissues to increase the chances of conception.
Robinson Research Institute's Professor Sarah Robertson, who led the project, said: "This research is the first to show that the female immune response is persuaded by signals in sperm to allow the male partner ...
2021-05-17
Marilyn Monroe famously sang that diamonds are a girl's best friend, but they are also very popular with quantum scientists - with two new research breakthroughs poised to accelerate the development of synthetic diamond-based quantum technology, improve scalability, and dramatically reduce manufacturing costs.
While silicon is traditionally used for computer and mobile phone hardware, diamond has unique properties that make it particularly useful as a base for emerging quantum technologies such as quantum supercomputers, secure communications and sensors.
However there are two key problems; cost, and difficulty in fabricating the single crystal diamond layer, which is smaller ...
2021-05-17
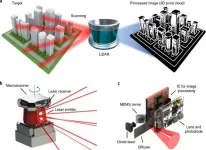
The nanophotonics-based LiDAR technology developed by a POSTECH research team was presented as an invited paper in Nature Nanotechnology, the leading academic journal in the field of nanoscience and nanoengineering.
In this paper, a POSTECH research team (led by Professor Junsuk Rho of the departments of mechanical engineering and chemical engineering, postdoctoral researcher Dr. Inki Kim of the Department of Mechanical Engineering, and Ph.D. candidate Jaehyuck Jang of the Department of Chemical Engineering) in cooperation with the French National Science Institute (CNRS-CRHEA) focused on the LiDAR device developed through studying the metamaterials based ultralight nanophotonics.
In addition, the paper ...
2021-05-17
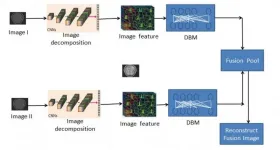
Image fusion is a process that can enhance the clinical value of medical images, improving the accuracy of medical diagnoses and the quality of patient care.
Researchers at the College of Data Science Software Engineering at China's Qingdao University, have developed a new 'multi-modal' image fusion method based on supervised deep learning that enhances image clarity, reduces redundant image features and supports batch processing. Their END ...
2021-05-17
ATS 2021, New York, NY - The COVID-19 pandemic has, and will continue to have, a tremendous impact on ICU nurses' mental health and willingness to continue in the critical care work force, according to research presented at the ATS 2021 International Conference.
Jill Guttormson, PhD, RN, associate dean for Academic Affairs and associate professor, College of Nursing, Marquette University, and colleagues sought to describe the impact of COVID-19 on ICU nurses through a survey using valid and reliable measures of burnout, moral distress, depression, anxiety, and posttraumatic stress symptoms.
The researchers recruited a national sample of nurses who have worked in the ICU during the COVID-19 pandemic between October and ...
2021-05-17
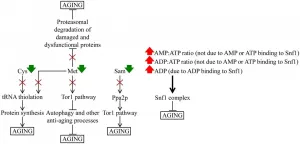
The cover for issue 7 of Oncotarget features Figure 14, "A hypothetical model of how a specific remodeling of cellular metabolism by CR slows down yeast chronological aging," published in "Caloric restriction creates a metabolic pattern of chronological aging delay that in budding yeast differs from the metabolic design established by two other geroprotectors" by Mohammad, et al. which reported that caloric restriction and the tor1Δ mutation are robust geroprotectors in yeast and other eukaryotes.
The authors demonstrate that caloric restriction generates a unique metabolic pattern.
Unlike the tor1Δ mutation or lithocholic acid, it slows down the metabolic pathway ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] How COVID-19 survival improved in UK hospitals during first wave