(Press-News.org) Irvine, Calif., May 17, 2021 -- Greenhouse gases and aerosol pollution emitted by human activities are responsible for increases in the frequency, intensity and duration of droughts around the world, according to researchers at the University of California, Irvine.
In a study published recently in Nature Communications, scientists in UCI's Department of Civil & Environmental Engineering showed that over the past century, the likelihood of stronger and more long-lasting dry spells grew in the Americas, the Mediterranean, western and southern Africa and eastern Asia.
"There has always been natural variability in drought events around the world, but our research shows the clear human influence on drying, specifically from anthropogenic aerosols, carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases," said lead author Felicia Chiang, who conducted the project as a UCI graduate student in civil & environmental engineering.
Chiang, who earned her Ph.D. in 2020 and is now a postdoctoral scholar at NASA's Goddard Institute for Space Studies in New York, said that her team's research demonstrated significant shifts in drought characteristics - frequency, duration and intensity - due to human influence, or what they call "anthropogenic forcing."
The researchers used the recently released Coupled Model Intercomparison Project Phase 6 platform to run climate simulations showing how the length and strength of droughts changes under various scenarios including "natural-only" and with the addition of greenhouse gas and aerosol emissions.
The modeling experiments under natural-only conditions did not show regional changes in drought characteristics from the late 19th to late 20th centuries, according to the study. But when the team accounted for anthropogenic greenhouse gas and aerosol contributions, statistically significant increases occurred in drought hotspots in southern Europe, Central and South America, western and southern Africa and eastern Asia.
The team found that in examining the anthropogenic forcings separately, greenhouse gases had a bigger impact in the Mediterranean, Central America, the Amazon and southern Africa, while anthropogenic aerosols played a larger role in Northern Hemisphere monsoonal and sub-arctic regions. Chiang said human-emitted aerosols are essentially particulate matter that are small enough to be suspended in the air. They can come from power plants, car exhaust and biomass burning (fires to clear land or to burn farm waste).
"Knowing where, how and why droughts have been worsening around the world is important, because these events directly and indirectly impact everything from wildlife habitats to agricultural production to our economy," said co-author Amir AghaKouchak, UCI professor of civil & environmental engineering and Earth system science. "Lengthy dry spells can even hamper the energy sector through disruptions to solar thermal, geothermal and hydropower generation."
Co-author Omid Mazdiyasni, who earned a Ph.D. in civil & environmental engineering at UCI in 2020 and is now a project scientist with the Los Angeles County Department of Public Works, said, "To make matters worse, droughts can be accompanied by heat waves, and high heat and low moisture can increase wildfire risk, which is already significant in the western United States."
Mazdiyasni said that while the research paints a gloomy picture of the unwanted impact of humans on the global environment, it points to a potential solution.
"If droughts over the past century have been worsened by human-sourced pollution, then there is a strong possibility that the problem can be mitigated by limiting those emissions," he said.
INFORMATION:
This study was supported by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Climate Program Office and relied on climate modeling software provided by the U.S. Department of Energy.
About the University of California, Irvine: Founded in 1965, UCI is the youngest member of the prestigious Association of American Universities and is ranked among the nation's top 10 public universities by U.S. News & World Report. The campus has produced three Nobel laureates and is known for its academic achievement, premier research, innovation and anteater mascot. Led by Chancellor Howard Gillman, UCI has more than 36,000 students and offers 224 degree programs. It's located in one of the world's safest and most economically vibrant communities and is Orange County's second-largest employer, contributing $7 billion annually to the local economy and $8 billion statewide. For more on UCI, visit http://www.uci.edu.
Media access: Radio programs/stations may, for a fee, use an on-campus ISDN line to interview UCI faculty and experts, subject to availability and university approval. For more UCI news, visit news.uci.edu. Additional resources for journalists may be found at communications.uci.edu/for-journalists.
DETROIT (May 17, 2021) - A national study on childhood asthma led by Henry Ford Health System has found that family history, race and sex are associated in different ways with higher rates of asthma in children.
In a study published in JAMA Pediatrics (hyperlink goes here), researchers found that children with at least one parent with a history of asthma had two to three times higher rates of asthma, mostly through age 4. They also reported that asthma rates in black children were much higher than white children during their preschool years, but the rates of incidence dropped in black children after age 9, while they increased for white children later in childhood.
"These findings help us ...
Archaeologists at Northern Arizona University are hoping a new technology they helped pioneer will change the way scientists study the broken pieces left behind by ancient societies.
The team from NAU's Department of Anthropology have succeeded in teaching computers to perform a complex task many scientists who study ancient societies have long dreamt of: rapidly and consistently sorting thousands of pottery designs into multiple stylistic categories. By using a form of machine learning known as Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), the archaeologists created a computerized method that roughly emulates the thought processes of the human mind in analyzing visual information. ...
The development of dementia, often from Alzheimer's disease, late in life is associated with abnormal blood levels of dozens of proteins up to five years earlier, according to a new study led by researchers at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health. Most of these proteins were not known to be linked to dementia before, suggesting new targets for prevention therapies.
The findings are based on new analyses of blood samples of over ten thousand middle-aged and elderly people--samples that were taken and stored during large-scale studies decades ago as part of an ongoing study. The researchers linked abnormal blood levels of 38 proteins to higher risks of developing Alzheimers within ...
May 16, 2021 -- In a study of low-income, urban youth in the U.S., researchers at Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health found that students exposed to Photovoice, an educational intervention, experienced greater improvements in STEM-capacity scores and environmental awareness scores compared to a group of youth who were not exposed to the activity. The results suggest that the Photovoice activities may be associated with improved learning outcomes. The study is published in the International Journal of Qualitative Methods.
"Our findings suggest that the Photovoice activities result in greater environmental awareness and may be associated with improved learning skills," said Nadav Sprague, doctoral fellow, ...
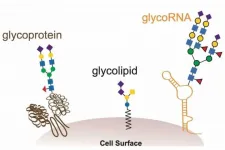
Stanford researchers have discovered a new kind of biomolecule that could play a significant role in the biology of all living things.
The novel biomolecule, dubbed glycoRNA, is a small ribbon of ribonucleic acid (RNA) with sugar molecules, called glycans, dangling from it. Up until now, the only kinds of similarly sugar-decorated biomolecules known to science were fats (lipids) and proteins. These glycolipids and glycoproteins appear ubiquitously in and on animal, plant and microbial cells, contributing to a wide range of processes essential for life.
The newfound glycoRNAs, neither ...
FRANKFURT. There are currently only a few synthetic agents that bind to and block the widespread membrane transport proteins, ATP-binding cassette transporters (ABC). Scientists at Goethe University and the University of Tokyo identified four of these macrocyclic peptides as models for a novel generation of active substances. They used methods for which the scientists involved are considered world leaders.
Thanks to deep sequencing, an extremely fast and efficient read-out procedure, the desired macrocyclic peptides could be filtered out of a "library" ...
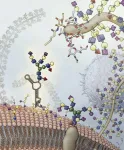
In a surprise find, scientists have discovered sugar-coated RNA molecules decorating the surface of cells.
These so-called "glycoRNAs" poke out from mammalian cells' outer membrane, where they can interact with other molecules. This discovery, reported May 17, 2021, in the journal Cell, upends the current understanding of how the cell handles RNAs and glycans.
"This was probably the biggest scientific shock of my life," says study author END ...
PULLMAN, Wash. -- Washington State University researchers have developed an innovative way to convert plastics to ingredients for jet fuel and other valuable products, making it easier and more cost effective to reuse plastics.
The researchers in their reaction were able to convert 90% of plastic to jet fuel and other valuable hydrocarbon products within an hour at moderate temperatures and to easily fine-tune the process to create the products that they want. Led by graduate student Chuhua Jia and Hongfei Lin, associate professor in the Gene and Linda Voiland School of Chemical Engineering and Bioengineering, they report on their work in the journal, ...
What The Study Did: Researchers assessed the feasibility of using positive behavior supports to promote the use of face coverings in school-aged children with autism spectrum disorders and/or attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) attending a summer program during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Authors: Benjamin Aaronson, Ph.D., of the University of Washington in Seattle, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.10281)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflicts of interest disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author ...
What The Study Did: Hospital discharge rates, hospitalization outcomes and demographic factors were examined among U.S. patients with ischemic stroke before and during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Authors: Adam de Havenon, M.D., of the University of Utah in Salt Lake City, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.10314)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest ...