Scientists shed light on the mechanism of photoactivation of the orange carotenoid protein
Biochemists from the Federal Research Centre of Biotechnology RAS and their international colleagues have deciphered an activation mechanism of the Orange Carotenoid Protein (OCP)
2021-05-17
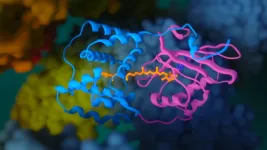
(Press-News.org) Exposure to light is compulsory for photosynthetic organisms for the conversion of inorganic compounds into organic ones. However, if there is too much solar energy, the photosystems and other cell components could be damaged. Thanks to special protective proteins, the overexcitation is converted into heat - in the process called non-photochemical quenching. The object of the published study, OCP, was one of such defenders. It was first isolated in 1981 from representatives of the ancient group of photosynthetic bacteria, ?yanobacteria. OCP comprises two domains forming a cavity, in which a carotenoid pigment is embedded.
"When light is absorbed by the carotenoid molecule, OCP can change from an inactive orange to an active red form. This process is multi-stage and follows a complex hierarchy of events. We showed the asynchrony of these changes in previous work, but the mechanism of the very first stage of OCP activation, associated with the breakage of hydrogen bonds between the carotenoid and the protein, remained unsolved," - says Dr. Eugene Maksimov, Senior Researcher of the Federal Research Centre of Biotechnology of RAS.
Scientists conducted a comprehensive study using methods of structural biology, biochemistry, spectroscopy, and quantum chemistry. Researchers from the Federal Research Centre for Biotechnology, Russian Academy of Sciences, have created a "super orange" version of OCP with unique spectral and structural properties and determined its crystal structure with the highest spatial resolution among all OCP-related proteins.
The analysis of the obtained data revealed that a charge separation reaction could occur along the hydrogen bond between the carotenoid molecule and one of the amino acid residues of the protein as a result of the absorption of a photon in OCP. In darkness, this hydrogen bond stabilizes the orange OCP state, but upon illumination, it breaks quickly due to the redistribution of the electron density in the carotenoid molecule. As a result, the protein becomes a dipole, which leads to a change in its entire structure. This photochemical reaction has been described for carotenoids for the first time.
"Our discovery will allow controlling the process of OCP activation and its spectral properties. Consequently, this can lead to the creation of new light-controlled systems and "smart" biocompatible materials based on photoactive proteins for optogenetics and functional imaging," - says Dr. Nikolai Sluchanko, Leading Researcher of the Federal Research Center of Biotechnology of RAS.
INFORMATION:
The work was carried out jointly with colleagues from the Faculty of Biology of Lomonosov Moscow State University, Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology, Semenov Federal Research Center of Chemical Physics RAS, Shemyakin and Yu.A. Ovchinnikov Institute of Bioorganic Chemistry RAS, Russian Academy of Sciences, and from scientific institutions of Germany and Czech Republic.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-17
For much of the nation's food supply, removing unsafe products off of store shelves can take up to 10 months, according to news reports -- even when people are getting sick.
The growing complexity and scope of modern supply chains result in painfully slow product recalls, even when consumer well-being is at stake. For example, in 2009, salmonella-tainted peanuts killed nine people and sickened more than 700 in 46 states, and the resulting nationwide recall cost peanut farmers, their wholesale customers and retailers more than $1 billion in lost production ...
2021-05-17
Viruses attack the body by sending their genetic code -- DNA and RNA -- into cells and multiplying. A promising class of therapeutics that uses synthetic nucleic acids to target and shut down specific, harmful genes and prevent viruses from spreading is gaining steam.
However, only a handful of siRNA, or other RNA interference-based therapeutics have been approved. One of the main problems is getting the siRNA into the body and guiding it to the target.
Chemical engineering researchers in the Cockrell School of Engineering aim to solve that problem, while improving the targeting effectiveness of siRNA. In a new paper in the Journal of Controlled Release, the researchers created several different types of nanoparticles and analyzed them for the ability to deliver and protect siRNA from ...
2021-05-17
May 17, 2021 - Amid the rising toll of opioid overdoses and deaths in the U.S., several states are considering laws enabling civil commitment for involuntary treatment of patients with substance use disorders (SUDs). Most addiction medicine physicians support civil commitment for SUD treatment - but others strongly oppose this approach, reports a survey study in Journal of Addiction Medicine, the official journal of the American Society of Addiction Medicine (ASAM). The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
"Civil commitment has emerged as a sometimes compelling yet controversial policy option," according to the new study, led by Abhishek Jain, MD. At the time of ...
2021-05-17
Some 16 million Americans are believed to have alcohol use disorder, and an estimated 93,000 people in the U.S. die from alcohol-related causes each year. Both of those numbers are expected to grow as a result of heavier drinking during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Yet, in a new study involving data from more than 200,000 people with and without alcohol problems, researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis found that although the vast majority of those with alcohol use disorder see their doctors regularly for a range of issues, fewer than one in 10 ever get treatment for drinking.
The findings are published in the June issue of the journal Alcoholism: Clinical & Experimental Research.
Analyzing data gathered from 2015 through 2019 via the National ...
2021-05-17
In a world that's changing fast, the Long Term Ecological Research (LTER) Network can seem almost an anachronism. Yet the patience and persistence that have generated 40 years of careful, reliable science about the Earth's changing ecosystems may prove to be just what's needed in this rapidly shifting world. We can't wait for a crystal ball -- and we don't have to. By harnessing decades of rich data, scientists are beginning to forecast future conditions and plan ways to manage, mitigate, or adapt to likely changes in ecosystems that will impact human economies, health and wellbeing.
The National Science Foundation established the LTER Network more than 40 years ago to provide an alternative to funding models that favored constant innovation over continuity. The model has proven to be extraordinarily ...
2021-05-17
An international study has found that four out of five women in prison in Scotland have a history of head injury, mostly sustained through domestic violence. Published recently in The Lancet, researchers, including SFU psychology graduate student Hira Aslam, say the study has important implications for the female prison population more broadly and could help to inform mental health and criminal justice policy development.
"The findings are incredibly sobering," says Aslam. "While we anticipated that the incidence of head injuries among women who are involved in the criminal justice system would be high, these estimates exceeded our expectations."
Researchers also found that violent criminal behaviour was three times more likely among women who had a history of significant head injury, ...
2021-05-17
ATS 2021, New York, NY - Air quality standards recommended by the American Thoracic Society (ATS) have the potential to prevent more illness and death than standards adopted by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), according to research presented at the ATS 2021 International Conference.
Laura Gladson, MS, a research scholar with the Air Quality Program at the Marron Institute of Urban Management, New York University (NYU) and colleagues from NYU and the ATS assessed differences between the potential public health protections provided by EPA air quality standards and the more stringent standards proposed by the ATS. Comparing real-world ...
2021-05-17
Two components of imagination -- constructing and evaluating imagined scenarios -- rely on separate subnetworks in the default mode network, according to research recently published in JNeurosci.
Even when you aren't doing anything, your brain is hard at work. The default mode network (DMN) activates during the brain's resting state and has been linked to daydreaming, planning, and imagining the future. In previous studies, scientists noticed the DMN could be divided into two subnetworks, ventral and dorsal, but their different roles were debated.
Lee et al. used fMRI to measure participants' brain activity while they imagined scenarios listed on prompts, like "Imagine you win the lottery." The scenarios ...
2021-05-17
KINGSTON, R.I. - May 17, 2021 - An article recently published in the prestigious journal Nature Communications, written by University of Rhode Island END ...
2021-05-17
Clinicians and surgeons are increasingly using medical devices based on artificial intelligence. These AI devices, which rely on data-driven algorithms to inform health care decisions, presently aid in diagnosing cancers, heart conditions and diseases of the eye, with many more applications on the way.
Given this surge in AI, two Stanford University faculty members are calling for efforts to ensure that this technology does not exacerbate existing heath care disparities.
In a new perspective paper, Stanford faculty discuss sex, gender and race bias in medicine and how these biases could be perpetuated by AI devices. The authors suggest several short- and long-term approaches to prevent AI-related ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Scientists shed light on the mechanism of photoactivation of the orange carotenoid protein
Biochemists from the Federal Research Centre of Biotechnology RAS and their international colleagues have deciphered an activation mechanism of the Orange Carotenoid Protein (OCP)