Colonization of the Antilles by South American fauna: Giant sunken islands as a passageway
2021-05-18
(Press-News.org) Fossils of land animals from South America have been found in the Antilles, but how did these animals get there? According to scientists from the CNRS, l'Université des Antilles, l'Université de Montpellier and d'Université Côte d'Azur, land emerged in this region and then disappeared beneath the waves for millions of years, explaining how some species were able to migrate to the Antilles. This study will be published in June 2021 issue in Earth-Science Reviews.
Fossils of land animals from the Antilles, including mammals and amphibians, have their closest relatives in South America. The crossing of the Caribbean Sea from South America was therefore possible, but how?
As swimming across the continent must be ruled out, given that several hundred kilometres separate the South American continent from the Antilles, the dispersal of this fauna has been attributed either to natural rafts coming out of the continent's flooded rivers, or to the existence of land bridges that are now submerged.
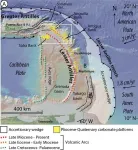
A scientific project involving geologists, palaeontologists and geophysicists1 is now solving some of the mysteries related to these terrestrial species in the Antilles. The researchers have reconstructed the geography of the northern Lesser Antilles over the last 40 million years and have shown that the movements of the tectonic plates at the junction between the Lesser Antilles, the Greater Antilles and the Aves Ridge (an underwater mountain), have several times given birth to archipelagos and islands quite close to each other, which were then swallowed up in the course of time.
In addition to tectonic movements, the glacial-interglacial cycles for 1.5 million years (Quaternary) have favoured the appearance and disappearance of archipelagos. Indeed, during these cycles, the sea level decreases or increases according to the storage of water in the ice caps or their melting (the duration of these cycles is about 100,000 years). The formation of these archipelagos could thus have favoured terrestrial connections between the Aves Ridge, the Greater Antilles and the Lesser Antilles.
Scientists will now extend their studies southward, between Guadeloupe and South America, to reconstruct the past geography of the entire Caribbean Plate, in order to define more precisely the nature of the terrestrial species' dispersal paths between the Americas.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-18
Urban megaprojects tend to be the antithesis of good urban planning. They have a negative impact on local water systems, deprive local communities of water-related human rights, and their funders and sponsors have little accountability for their impact.
These are the findings of the University of Adelaide's Dr Scott Hawken from the School of Architecture and Built Environment who led a review of the impact of urban megaprojects on water justice in South East Asia.
"Urban megaprojects have severe implications for environmental processes," said Dr Hawken.
"They have a major impact on hydrological systems and during all phases of development affect water security and human ...
2021-05-18
China's Large High Altitude Air Shower Observatory (LHAASO)--one of the country's key national science and technology infrastructure facilities--has found a dozen ultra-high-energy (UHE) cosmic accelerators within the Milky Way. It has also detected photons with energies exceeding 1 peta-electron-volt (quadrillion electron-volts or PeV), including one at 1.4 PeV. The latter is the highest energy photon ever observed.
These findings overturn the traditional understanding of the Milky Way and open up an era of UHE gamma astronomy. These observations will prompt people to rethink the mechanism by which high-energy particles are generated and propagated in the Milky Way, and will encourage people to explore more deeply violent celestial phenomena and their physical processes ...
2021-05-18
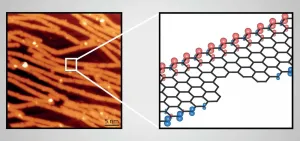
Graphene nanoribbons (GNRs), narrow strips of single-layer graphene, have interesting physical, electrical, thermal, and optical properties because of the interplay between their crystal and electronic structures. These novel characteristics have pushed them to the forefront in the search for ways to advance next-generation nanotechnologies.
While bottom-up fabrication techniques now allow the synthesis of a broad range of graphene nanoribbons that feature well-defined edge geometries, widths, and heteroatom incorporations, the question of whether or not structural disorder is present in these atomically precise GNRs, and to what extent, is still subject to debate. The answer to ...
2021-05-18
Manufactured in a new process based on crystalline materials, these low-loss mirrors promise to open up completely new application areas, for example in optical respiratory gas analysis for early cancer detection or the detection of greenhouse gases. This work will be published in the current issue of the journal Optica.
In 2016 researchers at the LIGO laser interferometer succeeded in the first direct observation of gravitational waves, which had originally been predicted by Albert Einstein in 1916. A significant contribution to the observation of this wave-like propagation of disturbances in space-time, which was rewarded with the Nobel Prize a year later, was provided by the laser mirrors of the kilometer-long interferometer assembly. ...
2021-05-18
Spintronics is an emerging technology for manufacturing electronic devices that take advantage of electron spin and its associated magnetic properties, instead of using the electrical charge of an electron, to carry information. Antiferromagnetic materials are attracting attention in spintronics, with the expectation of spin operations with higher stability. Unlike ferromagnetic materials, in which atoms align along the same direction like in the typical refrigerator magnets, magnetic atoms inside antiferromagnets have antiparallel spin alignments that cancel out the net magnetization.
Scientists have worked on controlling the alignment of magnetic atoms within antiferromagnetic ...
2021-05-18
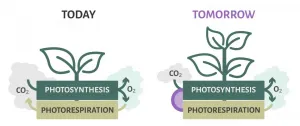
In today's plants, photorespiration dissipates some of the energy produced by photosynthesis and releases CO2. It begins when the enzyme RuBisCO acts on oxygen instead of carbon dioxide and creates toxic side-products requiring costly recycling reactions. The detoxification process uses up fixed carbon and wastes energy, thus strongly limiting agricultural productivity.
Scientists generally pursue two approaches to minimizes the deleterious effects of photorespiration: mimic the carbon concentrating mechanism of C4 plants or introduce new metabolic pathways to bypass the photorespiration.
Researchers led by Andreas Weber from Heinrich ...
2021-05-18
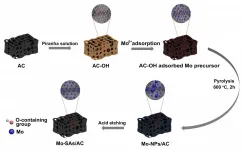
In a recent research, researchers led by Prof. ZHANG Haimin from the Institute of Solid State Physics of the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS) realized the synthesis of Mo single atoms anchored on activated carbon (Mo-SAs/AC) by the formed Mo-Ox bonds. The result was published on Chemical Communications.
According to the researchers, this new oxygen-coordinated molybdenum single atom catalyst was proved efficient to electrosynthesis of ammonia. The O-coordinated environment in this study, different from N-coordinated environment reported before, provided the sites to anchor Mo single atoms and form Mo-Ox sites, which could be used as the active centers for the adsorption and activation of N2, resulting in high ...
2021-05-18
A new software tool developed by Earlham Institute researchers will help bioinformaticians improve the quality and accuracy of their biological data, and avoid mis-assemblies. The fast, lightweight, user-friendly tool visualises genome assemblies and gene alignments from the latest next generation sequencing technologies.
Called Alvis, the new visualisation tool examines mappings between DNA sequence data and reference genome databases. This allows bioinformaticians to more easily analyse their data generated from common genomics tasks and formats by producing efficient, ready-made vector images.
First author and post-doctoral scientist at the Earlham Institute Dr Samuel Martin in the Leggett Group, said: "Typically, alignment tools output plain ...
2021-05-18
One day in the near future dyes in electric motors might indicate when cable insulation is becoming brittle and the motor needs replacing. Scientists at Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg (MLU), together with ELANTAS, a division of the specialty chemicals group ALTANA, have developed a new process that enables the dyes to be directly integrated into the insulation. By changing colour, they reveal how much the insulating resin layer around the copper wires in the motor has degraded. The results were published in the journal "Advanced Materials".
Modern combustion engines have long had detectors that recognise, for example, when an oil change is needed, saving unnecessary inspections. Electric motors also show signs of wear. Inside, ...
2021-05-18
Combining natural salt marsh habitats with conventional dikes may provide a more sustainable and cost-effective alternative for fully engineered flood protection. Researchers of the University of Groningen (UG) and the Royal Netherlands Institute for Sea Research (NIOZ) studied how salt marsh nature management can be optimized for coastal defence purposes. They found that grazing by both cattle and small herbivores such as geese and hare and artificial mowing can reduce salt marsh erosion, therefore contributing to nature-based coastal defence.
People around the world live in coastal areas that are ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Colonization of the Antilles by South American fauna: Giant sunken islands as a passageway