(Press-News.org) A new software tool developed by Earlham Institute researchers will help bioinformaticians improve the quality and accuracy of their biological data, and avoid mis-assemblies. The fast, lightweight, user-friendly tool visualises genome assemblies and gene alignments from the latest next generation sequencing technologies.
Called Alvis, the new visualisation tool examines mappings between DNA sequence data and reference genome databases. This allows bioinformaticians to more easily analyse their data generated from common genomics tasks and formats by producing efficient, ready-made vector images.
First author and post-doctoral scientist at the Earlham Institute Dr Samuel Martin in the Leggett Group, said: "Typically, alignment tools output plain text files containing lists of alignment data. This is great for computer parsing and for being incorporated into a pipeline, but it can be difficult to interpret by humans.
"Visualisation of alignment data can help us to understand the problem at hand. As a new technology, several new alignment formats have been implemented by new tools that are specific to nanopore sequencing technology.
"We found that existing visualisation tools were not able to interpret these formats; Alvis can be used with all common alignment formats, and is easily extensible for future ones."
A key feature of the new command line tool is its unique ability to automatically highlight chimeric sequences - weak links in the DNA chain. This is where two sequences - from different parts of a genome or different species - are linked together by mistake to make one, affecting the data's accuracy.
Chimera sequences can be problematic for bioinformaticians when identifying specific DNA. The chimera formation can physically happen to the DNA molecules during either sequencing library preparation, during the sequencing process on some platforms, and by assembly tools when trying to piece together a genome.
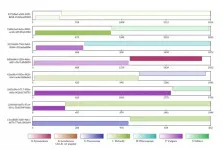
During the development of the tool, the team compared genome assemblies with and without using Alvis chimera detection. The vector image (example_contigalignment.pdf) produced shows an example output, where the intuitive tool tracks all reads it recognises as chimeras.
"Although chimeric sequences don't make up a large proportion of samples, they can have a significant effect, so we have to be careful that we have identified them during analysis," said Dr Martin.
"In the Alvis diagram example of chimera data, each rectangle across the page represents a read, and the coloured blocks inside them represent alignments. Most chimeras are easy to see because their alignments are different colours, meaning they map to different genomes. Others are more subtle because both alignments are to the same genome, but different regions."
The Alvis tool can pinpoint visualisation of only chimeric sequences for further inspection, and output numerical data describing the chimeras. This demonstrates that by applying the tool and then bioinformatically splitting the chimeras, the quality of the assemblies is significantly improved.
Accessed over 600 times since being made available at the beginning of March this year, Dr Martin, adds: "We hope that Alvis continues to be useful to other researchers working with, for example, nanopore sequencing; improving their understanding of their data by visualising alignments,''.
"Alignments are so fundamental to bioinformatics that it could be of use to anyone working with long read sequencing data, as well as alignments generated by sequencing data from short-read platforms. The diagrams that Alvis generates can be easily exported to directly use in publications, demonstrated in our study already."
The paper "Alvis: a tool for contig and read ALignment VISualisation and chimera detection" is published in BMC Bioinformatics.
INFORMATION:
One day in the near future dyes in electric motors might indicate when cable insulation is becoming brittle and the motor needs replacing. Scientists at Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg (MLU), together with ELANTAS, a division of the specialty chemicals group ALTANA, have developed a new process that enables the dyes to be directly integrated into the insulation. By changing colour, they reveal how much the insulating resin layer around the copper wires in the motor has degraded. The results were published in the journal "Advanced Materials".
Modern combustion engines have long had detectors that recognise, for example, when an oil change is needed, saving unnecessary inspections. Electric motors also show signs of wear. Inside, ...
Combining natural salt marsh habitats with conventional dikes may provide a more sustainable and cost-effective alternative for fully engineered flood protection. Researchers of the University of Groningen (UG) and the Royal Netherlands Institute for Sea Research (NIOZ) studied how salt marsh nature management can be optimized for coastal defence purposes. They found that grazing by both cattle and small herbivores such as geese and hare and artificial mowing can reduce salt marsh erosion, therefore contributing to nature-based coastal defence.
People around the world live in coastal areas that are ...
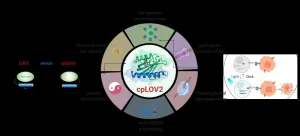
Recently, Prof. WANG Junfeng from the High Magnetic Field Laboratory of the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS), together with international scholars, developed a novel circular permutated light-oxygen-voltage 2 (LOV2) to expand the repertoire of genetically encoded photoswitches, which will accelerate the design of novel optogenetic devices. The result was published in Nature Chemical Biology.
LOV2 domain is a blue light-sensitive photoswitch. In a typical LOV2-based optogenetic device, an effector domain is fused after the C-terminal Jα helix of LOV2, intending to cage the effector via steric hindrance in the dark. On photostimulation, light-triggered unfolding of the Jα helix exposes the effector domain to restore its function. Crafting a LOV2-based ...
With the rise of the digital age, the amount of WiFi sources to transmit information wirelessly between devices has grown exponentially. This results in the widespread use of the 2.4GHz radio frequency that WiFi uses, with excess signals available to be tapped for alternative uses.
To harness this under-utilised source of energy, a research team from the National University of Singapore (NUS) and Japan's Tohoku University (TU) has developed a technology that uses tiny smart devices known as spin-torque oscillators (STOs) to harvest and convert wireless radio frequencies into energy ...
A new study may have uncovered why wall lizards have become the most successful reptile in the Mediterranean region. The results reveal how drastic changes in sea levels and climate 6 million years ago affected species formation in the area. The researchers believe they can now explain why the lizards became so diverse and widespread, something that has puzzled biologists since the 19th century. The study is published in Nature Communications.
The evolution of wall lizards offers clues on how major events in the Mediterranean climate and geology millions of years ago affected how species formed or became extinct, and also paved the way for biodiversity.
Wall lizards date back around 20 million years. However, ...
A University of Surrey project has revealed innovative methods that could dramatically improve the performance of future electrical vehicles (e-vehicles).
As part of the European Union's STEVE* project, Surrey has developed several pioneering approaches to torque vectoring in electric vehicles.
In e-vehicles with multiple motors, it is possible to deliver different amounts of drive power to each wheel. This benefits the vehicles' power consumption, safety and driveability. The process of calculating and optimising the precise amount of power needed while the vehicle ...
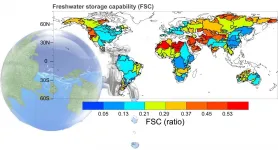
To support growing human and animal life, freshwater sources must continuously supply water. Freshwater from lakes, rivers, and underground is mainly recharged by rainfall. Ground reservoirs can store rainwater over time, depending on that location's storage capability. However, estimating freshwater storage capability (FSC) is still a challenge due to few observation opportunities and methods to measure and quantify FSC.
Prof. Xing Yuan and his Ph.D. student Enda Zhu, from the Institute of Atmospheric Physics at the Chinese Academy of Sciences, developed and applied a new metric that characterizes the "inertia" of water after rainfall. This method allows better ...
A research group at the University of Córdoba studied the molecular properties of the holm oak (Quercus ilex) in search of trees that are more resistant to drought and root rot.
One of the biggest problems affecting holm oaks is drought. The holm oak (Quercus ilex) boasts a high natural adaptability and resistance to inclement weather conditions in dry environments with high temperatures. However, drought is one of the main causes of mortality in holm oak plantations, with "drought stress" also an important factor contributing to root rot.
This is a multifactorial syndrome that causes the decay and death of holm oaks, consisting of a combination ...
Scientists have developed a mathematical model that predicts how the number and effects of bacterial mutations leading to drug resistance will influence the success of antibiotic treatments.
Their model, described today in the journal eLife, provides new insights on the emergence of drug resistance in clinical settings and hints at how to design novel treatment strategies that help avoid this resistance occurring.
Antibiotic resistance is a significant public health challenge, caused by changes in bacterial cells that allow them to survive drugs that ...
Researchers of Peter the Great St.Petersburg Polytechnic University (SPbPU) developed a new approach to determine the best electrode materials composition for Solid-state lithium-ion batteries. The results of the study were published in the first quartile journal Nanomaterials, MDPI. The Russian Science Foundation supports the project.
The development of miniature devices such as sensors and Internet of things (IoT) devices requires establishing small and complex power supplies with a high energy density. According to experts, traditional technologies for lithium-ion battery production reach their limits. It is difficult to reduce the size and control the shape of the power ...