Hepatitis C screening doubles when tests ordered ahead of time
2021-05-18
(Press-News.org) Twice as many eligible patients got screened for hepatitis C when it was already ordered for them compared to those who had to request it, according to a new study by researchers at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. Additionally, the patients in the study - whose average age was 63 - completed their screenings much more often when they were contacted via mail as opposed to electronic messaging. The study was published today in BMJ.
"We think that sending the lab order with outreach was so successful because it framed screening as the default," said the study's lead author, Shivan Mehta, MD, the associate chief innovation officer at Penn Medicine. "However, this strategy was also successful because it reduced effort and the number of steps to screen by both the patient and clinician."
More than 21,000 patients born between 1945 and 1965 - due to the high instances of hepatitis C but low screening rates in this population - were enrolled in the study. In Pennsylvania, where the study took place, state law requires health systems to offer screening to patients in this demographic. So the researchers decided this was a good venue to see if they could improve upon and rigorously evaluate something they were doing anyway.
Patients were chosen from participating primary care practices in the Philadelphia region and randomized into a number of groups to compare which resulted in higher screening rates: one examining whether pre-ordered screening tests were better than traditional outreach, another looking into mailed versus electronic communication, and the last trying out behavioral science-informed messaging. The study's active phase stretched 12 months from April 2019 until May 2020.
Mehta and his colleagues add more evidence to behavioral science's tenet that it's best to make the most beneficial choice the easiest. In the arm of the study where patients received a screening order in addition to the usual reminder letter, 43 percent of the patients completed their hepatitis C screening within four months; just 19 percent got screened if they only received the reminder letter with no lab order. This was what the researchers believed they'd find.
But the study had some unexpected findings. When the researchers compared the group of patients who received a mailed letter notification against a group who were notified via an online patient portal - like those many health systems use - the electronic method underperformed slightly, though not significantly. Roughly 18 percent of the patients mailed letters completed screening versus 14 percent of those who were contacted via a patient portal. There was a specifically pronounced divide when it came to Black patients in this phase of the study, as 11 percent fewer completed screenings if they were reminded via the patient portal.
"This was the biggest surprise for us. Many presume that most people are moving digital towards email, but for some populations, traditional letters might be best," Mehta said. "Additionally, the user experience of the secure messages also may have had to do with the lower response rate. Patients need to click on a link and remember their password, which may pose challenges."
Another slight surprise was the messages with content informed by behavioral science (such as "Join the majority of other patients who have been screened for Hepatitis C" or "Write down a date when you will get your screening done") did not make a difference in screening rates. A single percentage point separated the two groups of patients: roughly 15 percent of patients who were reached with traditional messaging were screened compared to about 14 percent of those from the behavioral science group.
"One of our hypotheses is that the behavioral-informed messages had a longer message, which may have been too much for patients," Mehta explained. "There is some evidence that shorter messages may be more effective. That may be the case in this situation."
Mehta said this study can inform clinical efforts beyond hepatitis C screening, assisting screenings and preventive care for other conditions.
Within hepatitis C, though, the researchers believe that the attachment of the order for screening was the greatest overall driver, so they hope to use that technique digitally, as well, to potentially boost those numbers. And screening recommendations are expanding to include all adults older than 18, which means there is a whole new population to reach.
INFORMATION:
This study was partially funded by a grant from the National Cancer Institute of the National Institutes of Health (K08CA234326).
Other authors on the study include Susan Day, Anne Norris, Jessica Sung, Catherine Reitz, Colin Wollack, Christopher Snider, Pamela Shaw, and David Asch, all of Penn.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-18
University of California scientists have discovered genetic data that will help food crops like tomatoes and rice survive longer, more intense periods of drought on our warming planet.
Over the course of the last decade, the research team sought to create a molecular atlas of crop roots, where plants first detect the effects of drought and other environmental threats. In so doing, they uncovered genes that scientists can use to protect the plants from these stresses.
Their work, published today in the journal Cell, achieved a high degree of understanding of the root functions because it combined genetic data from different cells of tomato roots grown both indoors and outside.
"Frequently, ...
2021-05-18
Bottom Line: The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommends that adults ages 45 to 75 be screened for colorectal cancer, lowering the age for screening that was previously 50 to 75. The USPSTF also recommends that clinicians selectively offer screening to adults 76 to 85 years of age. Colorectal cancer is the third leading cause of cancer death for both men and women in the United States. In 2016, 26% of eligible adults had never been screened and nearly one-third were not up to date with screening in 2018. The USPSTF routinely makes recommendations about the effectiveness of preventive care services and this statement replaces its 2016 recommendation.
To access the embargoed study: ...
2021-05-18
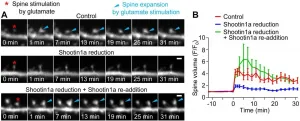
Ikoma, Japan - In neurons, changes in the size of dendritic spines - small cellular protrusions involved in synaptic transmission - are thought to be a key mechanism underlying learning and memory. However, the specific way in which these structural changes occur remains unknown. In a study published in Cell Reports, researchers from Nara Institute of Science and Technology (NAIST) have revealed that the binding of cell adhesion molecules with actin, via an important linker protein in the structural backbone of synapses, is vital for this process of structural plasticity.
Actin proteins make up an important part of a cell's structure, or cytoskeleton, and allow for dynamic changes in this structure by forming ...
2021-05-18
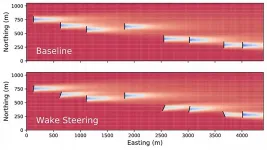
WASHINGTON, May 18, 2021 -- Wake steering is a strategy employed at wind power plants involving misaligning upstream turbines with the wind direction to deflect wakes away from downstream turbines, which consequently increases the net production of wind power at a plant.
In Journal of Renewable and Sustainable Energy, by AIP Publishing, researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy's National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) illustrate how wake steering can increase energy production for a large sampling of commercial land-based U.S. wind power plants.
While some plants showed less potential for wake steering due to unfavorable meteorological conditions or turbine layout, several wind power plants were ideal candidates ...
2021-05-18
What The Study Did: Telemedicine use grew rapidly during the COVID-19 pandemic but there was geographic variation in its use so researchers in this study examined the association of county-level telemedicine use with community factors among people with commercial or Medicare Advantage insurance.
Authors: Ateev Mehrotra, M.D., M.P.H., of Harvard Medical School in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.10330)
Editor's Note: The article includes funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and ...
2021-05-18
What The Study Did: Demographic information from 105 randomized clinical trials for primary open-angle glaucoma was combined to compare the rate of participation between individuals from racial/ethnic minority groups with white individuals.
Authors: Deepkumar G. Patel, D.D.S., M.P.H., of New York Ophthalmology Associates in Manhattan, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.8348)
Editor's Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media advisory: The full study is linked to this news release.
Embed ...
2021-05-18
Research to be published tomorrow in the journal Nature Communications is the first study to quantify the costs of storm damage caused by sea level rise driven specifically by human-induced climate change. Researchers from Stevens Institute of Technology, Climate Central, Rutgers University and other institutions found this self-inflicted damage to be $8.1 billion of Hurricane Sandy's damage and an additional 71,000 people and 36,000 homes exposed to Sandy's flooding.
Hurricane Sandy struck the northeast U.S. coast in 2012, causing widespread destruction estimated at ...
2021-05-18
BOSTON - Prompted by a recent alarming rise in cases of colorectal cancer in people younger than 50, an independent expert panel has recommended that individuals of average risk for the disease begin screening exams at 45 years of age instead of the traditional 50.
The guideline changes by the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF), published in the current issue of JAMA, updates its 2016 recommendations and aligns them with those of the American Cancer Society, which lowered the age for initiation of screening to 45 years in 2018.
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is one of the most preventable malignancies, owing to its long natural history of progression and the availability ...
2021-05-18
CLEVELAND - According to new study results, a team of researchers led by Cleveland Clinic's Thaddeus Stappenbeck, M.D., Ph.D., have found that a diet high in fat and sugar is associated with impaired intestinal immune cell function in mice. The findings, published in Cell Host & Microbe, provide novel insights into pathways linking obesity and disease-driving gut inflammation, and have implications for developing targets to treat inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) in patients.
Using data from more than 900 patients, the researchers found that elevated body mass index is associated with abnormal Paneth cells among patients with Crohn's disease and non-IBD patients.
Paneth cells are a type of anti-inflammatory immune cell found in ...
2021-05-18
Eating a Western diet impairs the immune system in the gut in ways that could increase risk of infection and inflammatory bowel disease, according to a study from researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis and Cleveland Clinic.
The study, in mice and people, showed that a diet high in sugar and fat causes damage to Paneth cells, immune cells in the gut that help keep inflammation in check. When Paneth cells aren't functioning properly, the gut immune system is excessively prone to inflammation, putting people at risk of inflammatory bowel disease and undermining effective control of disease-causing microbes. The findings, published May 18 in Cell Host & Microbe, open up new approaches to regulating gut immunity by restoring normal Paneth cell function.
"Inflammatory ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Hepatitis C screening doubles when tests ordered ahead of time