INFORMATION:
Ancient Australian Aboriginal memory tool superior to 'memory palace' learning
Study of medical studies reveals ancient aboriginal memory technique superior
2021-05-18
(Press-News.org) Australian scientists have compared an ancient Greek technique of memorising data to an even older technique from Aboriginal culture, using students in a rural medical school.
The study found that students using a technique called memory palace in which students memorised facts by placinthem into a memory blueprint of the childhood home, allowing them to revisit certain rooms to recapture that data. Another group of students were taught a technique developed by Australian Aboriginal people over more than 50,000 years of living in a custodial relationship with the Australian land.
The students who used the Aboriginal method of remembering had a significantly improved retention of facts compared to the control and the "memory palace" group.
The study led by Dr David Reser, from the Monash University School of Rural Health and Dr Tyson Yunkaporta, from Deakin University's NIKERI Institute, has just been published in PLOS One.
Medical students, and doctors, need to retain large amounts of information from anatomy to diseases and medications.
Because one of the main stressors for medical students is the amount of information they have to rote learn, we decided to see if we can teach them alternate, and better, ways to memorise data," Dr Reser said.
The memory palace technique dates back to the early Greeks and was further utilised by Jesuit priests. Handwritten books were scarce and valuable, and one reading would have to last a person's lifetime, so ways to remember the contents were developed.
In Aboriginal culture, which relies on oral history, important facts like navigation, food sources, tool use and inter and intra tribal political relationships are important for survival. Aboriginal methods of memorising also used the idea of attaching facts to the landscape, but with added stories which describe the facts and the placement to facilitate recall.
Working with Dr Yunkaporta, formerly at the Monash School of Rural Health, the research team randomly divided 76 medical students attending Monash's Churchill Campus, in rural Victoria, into three groups. The students were given 30 minutes of training in the memory palace, Aboriginal techniques, or were in a control group who watched a video rather than undergo training. The students were then asked to memorize 20 common butterfly names (to dissociate from medical curriculum).
They were then tested on their recalls at 10 minutes and then 30 minutes after using their assigned techniques to memorize the list.
The researchers found the students who used the Aboriginal technique for remembering ie a narrative plus locations from around the campus were almost three times more likely to correctly remember the entire list than they were prior to training (odds ratio: 2.8). The students using the memory palace technique were about twice as likely to get a perfect score after training (2.1), while the control group improved by about 50% (1.5) over their pre-training performance.
Importantly a qualitative survey found the students using the Aboriginal technique found it more enjoyable, "both as a way to remember facts but also as a way to learn more about Aboriginal culture," Dr Reser said.
Dr Reser said the Monash School of Rural Health is considering incorporating these memory tools into the medical curriculum once teaching returns to a post-COVID normal. "This year we hope to offer this to students as a way to not only facilitate their learning but to reduce the stress associated with a course that requires a lot of rote learning,"he said.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Bone marrow disorder nearly 10-times more common in those with venom allergy
2021-05-18
Researchers at Michigan Medicine found that people with venom allergies are much more likely to suffer mastocytosis, a bone marrow disorder that causes higher risk of fatal reactions.
The team of allergists examined approximately 27 million United States patients through an insurance database - easily becoming the nation's largest study of allergies to bee and wasp stings, or hymenoptera venom. The results, published in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, revealed mastocytosis in fewer than 0.1% of venom allergy patients - still near 10 times higher than those without allergies.
"Even though there is mounting interest, mast cell diseases are quite understudied; ...
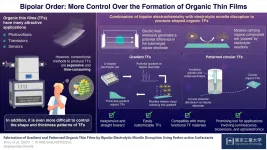
Bipolar order: A straightforward technique to have more control over organic thin films
2021-05-18
Modern and emerging applications in various fields have found creative uses for organic thin films (TFs); some prominent examples include sensors, photovoltaic systems, transistors, and optoelectronics. However, the methods currently available for producing TFs, such as chemical vapor deposition, are expensive and time-consuming, and often require highly controlled conditions. As one would expect, making TFs with specific shapes or thickness distributions is even more challenging. Because unlocking this customizability could spur advances in many sophisticated applications, researchers are actively exploring new approaches for ...
What happens in the brain when we imagine the future?
2021-05-18
In quiet moments, the brain likes to wander—to the events of tomorrow, an unpaid bill, an upcoming vacation.
Despite little external stimulation in these instances, a part of the brain called the default mode network (DMN) is hard at work. "These regions seem to be active when people aren't asked to do anything in particular, as opposed to being asked to do something cognitively," says Penn neuroscientist Joseph Kable.
Though the field has long suspected that this neural network plays a role in imagining the future, precisely how it works hadn't been fully understood. Now, research from Kable and two former graduate students in his lab, Trishala Parthasarathi, associate director of scientific services at OrtleyBio, and Sangil Lee, a postdoc at University of California, ...
San Diego Zoo Wildlife Alliance study finds topography is key factor in where Andean bears mothers make their dens
2021-05-18
SAN DIEGO (May TK, 2021) - Compared to most other bear species, very little is known about how female Andean bears choose where they give birth to cubs. As a critical component of the reproductive cycle, birthing dens are essential to the survival of South America's only bear species, listed as Vulnerable on the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species.
A new study led by Russ Van Horn, Ph.D., published April in the journal Ursus, takes the most detailed look yet at the dens of this species. Van Horn, a population sustainability scientist, leads San Diego Zoo Wildlife Alliance's Andean bear conservation program. He was joined by colleagues from the University of British Columbia's Department of Forest ...
Study shows racial differences in personal care product use, may lead to health inequities
2021-05-18
A large survey of women in California shows significant racial and ethnic differences in the types of personal care products women use on a daily basis. Because many personal care products contain endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs) like parabens and phthalates that interfere with the body's hormones, the findings could shed light on how different products influence women's exposures to harmful chemicals that contribute to health inequities.
The study appears in the Journal of Exposure Science & Environmental Epidemiology as part of a special issue focused on health equity. ...
New model for infectious disease could better predict future pandemics
2021-05-18
In the midst of a devastating global pandemic of wildlife origin and with future spillovers imminent as humans continue to come into closer contact with wildlife, infectious-disease models that consider the full ecological and anthropological contexts of disease transmission are critical to the health of all life. Existing models are limited in their ability to predict disease emergence, since they rarely consider the dynamics of the hosts and ecosystems from which pandemics emerge.
Published May 17 in Nature Ecology and Evolution, Smithsonian scientists and partners provide a framework for a new approach to modeling infectious diseases. It adapts established methods developed to study the planet's natural systems, including ...
Salk scientists reveal role of genetic switch in pigmentation and melanoma
2021-05-18
LA JOLLA--(MAY 18, 2021) Despite only accounting for about 1 percent of skin cancers, melanoma causes the majority of skin cancer-related deaths. While treatments for this serious disease do exist, these drugs can vary in effectiveness depending on the individual.
A Salk study published on May 18, 2021, in the journal Cell Reports reveals new insights about a protein called CRTC3, a genetic switch that could potentially be targeted to develop new treatments for melanoma by keeping the switch turned off.
"We've been able to correlate the activity of this genetic switch to melanin production and cancer," says Salk study ...
Study finds potential causality between blood clot factors and migraine with aura
2021-05-18
Nearly 15 percent of the U.S. population experiences migraine. One subtype of migraine that is not well understood is migraine with aura (MA). Individuals who experience MA often see flashing lights, blind spots, or jagged lines in their visual field prior to onset of their migraine headaches. Individuals who experience MA also face a heightened risk of stroke and cardiovascular disease, although scientists continue to explore why this correlation exists. In a new study from Brigham and Women's Hospital, researchers used a technique in genetic analysis termed Mendelian randomization to examine 12 coagulation measures, uncovering four that are associated ...
Novel simulation method predicts blood flow conditions behind von Willebrand disease
2021-05-18
For the first time, researchers can quantitatively predict blood flow conditions that likely cause pathological behavior of the human blood protein von Willebrand factor (vWF). Predictions from this new method of simulation, developed at Lehigh University, can be used to optimize the design of the mechanical pumps known as left ventricular assist devices used in heart failure patients. The method also has the potential to improve diagnosis and treatment of von Willebrand disease, the most common inherited bleeding disorder in the U.S., according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The article, "Predicting pathological von Willebrand factor unraveling in elongational flow," appears ...
Ancient horse DNA reveals gene flow between Eurasian and North American horses
2021-05-18
A new study of ancient DNA from horse fossils found in North America and Eurasia shows that horse populations on the two continents remained connected through the Bering Land Bridge, moving back and forth and interbreeding multiple times over hundreds of thousands of years.
The new findings demonstrate the genetic continuity between the horses that died out in North America at the end of the last ice age and the horses that were eventually domesticated in Eurasia and later reintroduced to North America by Europeans. The study has been accepted for publication in the journal Molecular Ecology and is currently available ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
[Press-News.org] Ancient Australian Aboriginal memory tool superior to 'memory palace' learningStudy of medical studies reveals ancient aboriginal memory technique superior