What are the effects of inappropriate prescriptions in older adults?
2021-05-19
(Press-News.org) Individuals are often prescribed increasing numbers of medications as they age, and while many of these prescriptions are justifiable, some may be inappropriate. A recent analysis published in the British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology examined the results of all studies investigating associations between potentially inappropriate prescribing--which includes prescribing medications that may not produce benefits relative to harm and not prescribing medications that are recommended--and outcomes of older adults.
Potentially inappropriate prescribing was significantly associated with a range of health-related and system-related outcomes, including functional decline, falls, and hospital admissions due to drug-related side effects.
"Several decision support tools for quality prescribing are available; however, our analysis highlights that medication-related harm due to inappropriate prescribing remains problematic," said lead author Alemayehu Mekonnen, PhD, of Deakin University, in Australia. "A comprehensive assessment of medication use, especially during care transitions such as at hospital discharge, is an important task to reduce medication-related harm and associated healthcare costs."
INFORMATION:
About Wiley
Wiley drives the world forward with research and education. Through publishing, platforms and services, we help students, researchers, universities, and corporations to achieve their goals in an ever-changing world. For more than 200 years, we have delivered consistent performance to all of our stakeholders. The Company's website can be accessed at http://www.wiley.com.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-19
By the end of the first year of the pandemic in metropolitan Stockholm, investigators estimate that one-fifth of adults in the region previously had COVID-19. The findings, which are published in the Journal of Internal Medicine, come from analyses of anti-viral antibody responses in healthy blood donors and pregnant women.
For the study, researchers examined blood from 2,600 blood donors and 2,500 pregnant women taken between March 14th 2020 and February 28th 2021. Blood donors and pregnant women had a similar rate of past infection, approaching 19% of the study group by the end of February 2021, shortly ...
2021-05-19
Monash University researchers have engineered new antimicrobial surfaces that can significantly reduce the formation of bacteria on medical instruments, such as urinary catheters, and reduce the risk of patient infection while in hospital.
This world-first study demonstrates the potential for 3D engineered surfaces in preventing the initial formation of microcolonies of Escherichiacoli (E.coli), Klebsiellapneumoniae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa - the three most common urinary tract bacterial infections (UTIs) associated with catheters.
The study team, led by Dr Victor Cadarso, from Monash University's Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering and the ...
2021-05-19
SALT LAKE CITY - A new study published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology reports findings on Huntsman at Home™, a cancer hospital-at-home model operated by Huntsman Cancer Institute (HCI) at the University of Utah (U of U). The study analyzed aspects of Huntsman at Home acute care--meaning a level of care that is generally provided in an inpatient hospital setting.
In the 30 days after study entry, Huntsman at Home participants had 55% fewer hospitalizations, 45% fewer emergency department visits, and shorter hospital stays by one day. They also had 47% lower health care costs during the same 30-day period ...
2021-05-19
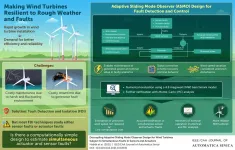
A key driver of energy research is the ever-growing demand for energy. Traditional fossil-fuel-based energy sources currently meet these demands and do it well, but they're non-renewable and cause major environmental pollution. In a world with looming climate and resource crises threats, researchers have turned to renewable sources of energy as sustainable alternatives. Among renewables, wind energy, in particular, has gained considerable attention due to its low cost. As Dr. Afef Fekih, Computer Engineer at the University of Louisiana, USA, with a specialization in wind turbine design, notes, "Wind energy has been described as 'the world's fastest-growing renewable energy source', seeing a 30% annual growth on ...
2021-05-19
A new survey study suggests that, for adolescents who received unplanned distance education due to the COVID-19 pandemic, experiencing one's own competence was linked to positive emotion, self-motivation to learn, and pro-learning behaviors. Feeling connected to others was also linked to positive emotion. Julia Holzer of the University of Vienna, Austria, and colleagues present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE.
The new research draws on a psychological theory known as self-determination theory, which outlines three basic psychological needs for well-being: autonomy, connection to others, and experiencing one's own competence. Previous research has provided much ...
2021-05-19
Americans who get their news from traditional sources (e.g.: TV, newspapers) are more likely to accept the COVID-19 vaccine than those who rely on social media.
INFORMATION:
Article Title: Examining the effect of information channel on COVID-19 vaccine acceptance
Funding: This research was with funding support from Jigsaw, Google. RPL, ES, JK, BH, and CMI received funding from Jigsaw to conduct this research. BG and TV are employed by Jigsaw/Google. Google, Inc. provided support in the form of salaries for authors, BG TV, but did not have any additional role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript. The specific roles of these authors are articulated in the 'author contribution'. The data ...
2021-05-19
Almost 1 in 4 COVID-19 patients have another bacterial, viral or fungal infection simultaneously or subsequently, with such patients experiencing worse disease outcomes.
INFORMATION:
Article Title: Prevalence and outcomes of co-infection and superinfection with SARS-CoV-2 and other pathogens: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Funding: NS received research support for this work from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases of the National Institutes of Health under Award Number DP2AI144244. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily ...
2021-05-19
Tsukuba, Japan - Autoimmune diseases occur when an individual's immune system fights their own body as if it was a foreign invader. However, in healthy people, these responses are prevented by a process known as immune tolerance. Many complex biological mechanisms maintain the necessary balance between immune activation and suppression to ensure immune tolerance does not prevent the body from effectively fighting pathogens.
In a new study published in PNAS, a group of researchers from the University of Tsukuba uncovered how the relationship between two receptors called DNAM-1 and TIGIT helps preserve the balance for optimal immune function. Both of these molecules have previously been studied ...
2021-05-19
Recently published in the scientific journal Brain Communications, a new study distinguished structural patterns between individuals with corpus callosum dysgenesis (CCD), a congenital condition that consists of the absence or incomplete development in the connecting structure between the two brain hemispheres. The research was carried out by the D'Or Institute for Research and Education (IDOR), the University of Pittsburgh, Oswaldo Cruz Foundation (Fiocruz), and the Federal University of Rio de Janeiro (UFRJ).
Investigating CCD is an arduous task for doctors and neuroscientists. There aren't many patients available for research, and the anatomical variability of brains with CCD creates a broad ...
2021-05-19
Philadelphia, May 18, 2021 - Many socioeconomically disadvantaged children face poor cognitive and mental health outcomes, and researchers are working to determine the specific factors that link childhood conditions to those poor outcomes, including how they might shape brain circuitry. In a new study, researchers have examined how "neighborhood disadvantage" can affect the developing brain, including the brain's connectivity between regions.
The study appears in Biological Psychiatry: Cognitive Neuroscience and Neuroimaging, published by Elsevier.
Sarah Whittle, PhD, and Divyangana Rakesh, lead authors of the study, studied existing brain scans from 7,618 children aged 9-10 collected as part of the Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] What are the effects of inappropriate prescriptions in older adults?