(Press-News.org) Philadelphia, May 18, 2021 - Many socioeconomically disadvantaged children face poor cognitive and mental health outcomes, and researchers are working to determine the specific factors that link childhood conditions to those poor outcomes, including how they might shape brain circuitry. In a new study, researchers have examined how "neighborhood disadvantage" can affect the developing brain, including the brain's connectivity between regions.
The study appears in Biological Psychiatry: Cognitive Neuroscience and Neuroimaging, published by Elsevier.
Sarah Whittle, PhD, and Divyangana Rakesh, lead authors of the study, studied existing brain scans from 7,618 children aged 9-10 collected as part of the Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development (ABCD) Study. Previous studies have identified differences in some brain regions in disadvantaged children, but the current study used magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to measure functional connectivity, or how well different regions of the brain are connected with one another, at rest.
Rather than considering a single measure of status such as household income, the new study classified children according to neighborhood disadvantage, which encompasses multiple risk factors such as pollution, crime, and access to lower-quality education and healthcare.
Dr. Whittle said the purpose of the study was to "inform us of the mechanisms through which disadvantage impacts children's development and functioning." The team also wanted to investigate the role of factors such as positive home and school environments that may help reduce the harmful effects of disadvantage.
Analysis of the brain scans revealed that, in children with higher scores reflecting greater disadvantage, functional connectivity was reduced both between and within several brain networks.
"Our findings suggest that growing up in a disadvantaged neighborhood indeed impacts the brain. Importantly, however, findings suggest that providing children with better home and school environments where they feel supported, receive positive feedback, and have opportunities to engage in different activities, can offset some of the negative effects of neighborhood disadvantage on children's brain development," Ms. Rakesh said.
The findings have policy implications in the context of designing interventions and policies targeted at youth and families exposed to disadvantage; they suggest a need to shift attention from a sole focus on family-level factors to community-level research and policies.
Cameron Carter, MD, Editor of Biological Psychiatry: Cognitive Neuroscience and Neuroimaging, said of the study, "These remarkable results show that improvements in the home and school environments can mitigate against the otherwise deleterious effects of growing up in a disadvantaged setting, providing a powerful message for the importance of public policies that provide more support at home and at school."
INFORMATION:
Notes for editors
The article is "Associations between neighborhood disadvantage, resting-state functional connectivity, and behavior in the Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development (ABCD) Study: Moderating role of positive family and school environments," by Divyangana Rakesh, Caio Seguin, Andrew Zalensky, Vanessa Cropley, Sarah Whittle (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpsc.2021.03.008). It appears as an Article in Press in Biological Psychiatry: Cognitive Neuroscience and Neuroimaging, published by Elsevier.
Copies of this paper are available to credentialed journalists upon request; please contact Rhiannon Bugno at BPCNNI@sobp.org or +1 254 522 9700. Journalists wishing to interview the authors may contact Divyangana Rakesh at rakeshd@student.unimelb.edu.au or +61 4 7878 2088, or Sarah Whittle at +61 402 597 590 or swhittle@unimelb.edu.au.
The authors' affiliations and disclosures of financial and conflicts of interests are available in the article.
Cameron S. Carter, MD, is Professor of Psychiatry and Psychology and Director of the Center for Neuroscience at the University of California, Davis. His disclosures of financial and conflicts of interests are available here.
About Biological Psychiatry: Cognitive Neuroscience and Neuroimaging
Biological Psychiatry: Cognitive Neuroscience and Neuroimaging is an official journal of the Society of Biological Psychiatry, whose purpose is to promote excellence in scientific research and education in fields that investigate the nature, causes, mechanisms and treatments of disorders of thought, emotion, or behavior. In accord with this mission, this peer-reviewed, rapid-publication, international journal focuses on studies using the tools and constructs of cognitive neuroscience, including the full range of non-invasive neuroimaging and human extra- and intracranial physiological recording methodologies. It publishes both basic and clinical studies, including those that incorporate genetic data, pharmacological challenges, and computational modeling approaches. The 2019 Impact Factor score for Biological Psychiatry: Cognitive Neuroscience and Neuroimaging is 5.335. http://www.sobp.org/bpcnni
About Elsevier
As a global leader in information and analytics, Elsevier helps researchers and healthcare professionals advance science and improve health outcomes for the benefit of society. We do this by facilitating insights and critical decision-making for customers across the global research and health ecosystems.
In everything we publish, we uphold the highest standards of quality and integrity. We bring that same rigor to our information analytics solutions for researchers, health professionals, institutions and funders.
Elsevier employs 8,100 people worldwide. We have supported the work of our research and health partners for more than 140 years. Growing from our roots in publishing, we offer knowledge and valuable analytics that help our users make breakthroughs and drive societal progress. Digital solutions such as ScienceDirect, Scopus, SciVal, ClinicalKey and Sherpath support strategic research management, R&D performance, clinical decision support, and health education. Researchers and healthcare professionals rely on our 2,500+ digitized journals, including The Lancet and Cell, our 40,000 eBook titles; and our iconic reference works, such as Gray's Anatomy. With the Elsevier Foundation and our external Inclusion & Diversity Advisory Board, we work in partnership with diverse stakeholders to advance inclusion and diversity in science, research and healthcare in developing countries and around the world.
Elsevier is part of RELX, a global provider of information-based analytics and decision tools for professional and business customers. http://www.elsevier.com
Media contact
Rhiannon Bugno, Editorial Office
Biological Psychiatry: Cognitive Neuroscience and Neuroimaging
+1 254 522 9700
BPCNNI@sobp.org
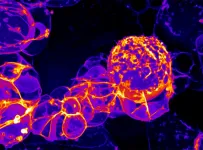
EUGENE, Ore. -- May 19, 2021 -- High-resolution imaging of fruit flies at the University of Oregon has captured mechanical motions that stem cells use to make neurons, the cells that make up the brain.
These motions coordinate cell division with differentiation, where newly born cells become neurons. Differentiation is essential for building the brain circuitry in complex organisms that underlies human cognition and emotions, said Ken Prehoda, a professor in the UO's Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry.
Prehoda was principal investigator of a project published online May 18 in the journal ...
Researchers at UVA Cancer Center have unveiled important new insights into how hormones known as androgens act on our cells - and the discovery could boost efforts to develop better treatments for prostate, ovarian and breast cancers.
The findings shed light on how androgens interact with their receptors inside cells to affect gene activity. This process is important in both healthy cells and certain cancers. Hormone therapy for prostate cancer, for example, aims to reduce the amount of androgen in the body, or to stop it from fueling the cancer cells. However, ...
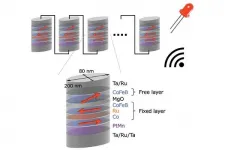
Researchers at the National University of Singapore (NUS) and Tohoku University have demonstrated that an array of electrically connected spintronic devices can harvest a 2.4 GHz wireless signal, which can be used to power and charge small electronic devices and sensors.
The researchers from NUS and Tohoku University have successfully synchronized the four electrically connected magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ), for the signal transmission at 2.4 GHz. Furthermore, the eight MTJs array was integrated with the conventional battery-free electronics to harvest a wireless signal of 2.4 GHz to a DC signal, which is used to power light emitting ...
In a world hungry for cheaper, more efficient renewable energy, Australian researchers have served up a treat.
Work led by the ARC Centre of Excellence in Exciton Science has shown that the two-dimensional (2D) thin films used in some perovskite solar cells closely resemble a sandwich. Perovskite is an exciting material at the forefront of solar energy research and design.
Previously, scientists thought these 2D perovskite films had a 'gradient' structure, in which certain components were found deep in the material, with other complementary elements only located nearer to the surface, like topping on a cracker.
However, in a paper published ...
Nearly a quarter of pregnant women say they've been around secondhand smoke - in their homes, at work, around a friend or relative - which, according to new research, is linked to epigenetic changes - meaning changes to how genes are regulated rather than changes to the genetic code itself - in babies that could raise the risk of developmental disorders and cancer.
The study, published today in Environmental Health Perspectives by researchers at Virginia Commonwealth University Massey Cancer Center, is the first to connect secondhand smoke during pregnancy with epigenetic modifications to disease-related genes, measured at birth, which supports the idea that many adult ...
While a pint-sized snorer may seem adorable tucked up in bed, studies shows that children with sleep disordered breathing are likely to show aggressive and hyperactive behaviours during the day.
The recommended treatment is an adenotonsillectomy - the removal of adenoid and tonsils - not only to fix the snore, but also the behaviour.
Yet according to new research from the University of South Australia, while the surgery can cure a child's snoring it doesn't change their behaviour, despite common misconceptions by parents and doctors alike.
Conducted in partnership with the University ...
The nerve cells, also called neurons, in our brain control all the basic processes of our body. For this reason, there are different types of neurons distributed over specific regions of the brain. Researchers at the Max Planck Institute for Metabolic Research and the CECAD Cluster of Excellence in Aging Research of the University of Cologne have developed an approach that allows them to show that neurons that are supposedly the same are actually very different: they not only sense different hormones for the body's energy state, but also have a different influence on food intake. This can have a direct effect on our metabolism, for example by differentially restraining our appetite.
The brain processes our sensory perceptions, controls our behaviour and stores ...
Traditionally, an infection is thought to happen when microbes - bacteria, fungi, or viruses - enter and multiply in the body, and its severity is associated with how prevalent the microbes are in the body.
Now, an international research team led by Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore) has proposed a new way of understanding infections. Their study of close to 400 respiratory samples from patients with bronchiectasis, a chronic lung condition, has shown that microbes in the body exist as a network, and that an infection's severity could be a result of interactions between these microbes.
Through statistical modelling ...
Among the large cast of microbiome players, bacteria have long been hogging the spotlight. But the single-celled organisms known as protists are finally getting the starring role they deserve.
A group of scientists who study the interactions between plants and microbes have released a new study detailing the dynamic relationships between soil-dwelling protists and developing plants, demonstrating that soil protists respond to plant signals much like bacteria do.
An enormous variety and diversity of microbes live in soil, and studying how these organisms interact with each ...
For young plants, timing is just about everything. Now, scientists have found that herbivores, animals that consume plants, have a lot to say about evolution at this vulnerable life stage.
Once a plant seedling breaches the soil surface and begins to grow, a broad range of factors will determine whether it thrives or perishes.
Scientists have long perceived that natural selection favors early rising seeds. Seedlings that emerge early in the growing season should have a competitive advantage in monopolizing precious soil resources. Early growth also should mean more access to light, since early growers can block sunlight for seedlings that emerge later in the season.
Despite plenty of proof that germinating early is highly advantageous, many plants germinate ...