Alzheimer protein APP regulates learning and social behavior in the healthy brain
Beyond plaques: Heidelberg scientists unravel the natural functions of the APP protein family
2021-05-19
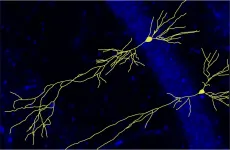
(Press-News.org) While the APP protein is well-known for its key role in Alzheimer's disease, its contribution to healthy brain function, by contrast, has remained largely unknown until now. Recently, an international research team, led by molecular biologist Prof. Dr Ulrike Müller from Heidelberg University, gained new insights on the physiological functions of the APP protein family by using a mouse model lacking APP. The absence of APP during brain development was shown to result in the malformation of important brain regions implicated in learning and memory. Consequently, these mice were severely impaired in their learning abilities and exhibited autistic-like behaviour.
Alzheimer's disease is triggered by insoluble protein deposits in the brain, which aggregate around nerve cells to form plaques. These plaques consist mainly of small β-amyloid peptides (Aβ), which are a cleavage product of the amyloid precursor protein (APP). Aβ peptides inflict damage on nerve cells and ultimately lead them to their death. While the detrimental effect of Aβ peptides on neurons has been recognised for many years, little is known about the natural physiological functions of APP. According to the researchers, this non-pathological perspective is worthy of investigation considering the fact that APP, as well as two other closely-related proteins, is produced by most nerve cells in the brain - particularly in critical regions for learning and memory formation.
To investigate the role of the APP protein family in the development and functionality of the nervous system, Prof. Müller's research group used mice as a model organism, which had been genetically engineered to block the production of all APP family proteins. Close examination of their brains revealed that the loss of APP during brain development led to malformations in the layered structure of the hippocampus - an essential brain region for memory formation. "We observed that the absence of APP led to impaired neuronal wiring and a decrease in the number of synaptic connections. It also greatly reduced communication between nerve cells and severely affected the animal's performance in behaviour tests that assess learning," says Ulrike Müller, who heads the department of Functional Genomics at the Institute of Pharmacy and Molecular Biotechnology of Heidelberg University.
According to Prof. Müller, the team was surprised to discover that these disruptions in brain development also gave rise to behavioural changes that resembled those occurring in autism spectrum disorder. The mice displayed the characteristic recurring movement patterns and lack of interest in social interactions with other mice. "Our findings suggest that the APP family plays a crucial role in the normal development of the nervous system, learning, memory formation and social communication," explains the scientist. "In the future, these understandings may aid the development of novel therapeutics for Alzheimer's disease."
INFORMATION:
Funded by the German Research Foundation, this study was an international collaborative effort involving the research team based in Heidelberg as well as scientists from Technische Universität Braunschweig, the University of Mainz, and the University of Zurich (Switzerland). The results were published in "The EMBO Journal".
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-19
In an article published in the International Journal of Mental Health Nursing, experts stress that the COVID-19 pandemic presents the "perfect storm" for family violence, where a set of rare circumstances have combined to aggravate intimate partner violence, domestic abuse, domestic violence, and child abuse.
Factors during the pandemic that have come together to contribute to family violence may include increased stress and trauma, economic hardship, imposed isolation, and decreased access to community and faith-based support.
The authors note that public health officials and mental health professionals need to be aware of the impact of disasters on family violence, and they should strive to identify those at risk and provide ...
2021-05-19
Individuals are often prescribed increasing numbers of medications as they age, and while many of these prescriptions are justifiable, some may be inappropriate. A recent analysis published in the British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology examined the results of all studies investigating associations between potentially inappropriate prescribing--which includes prescribing medications that may not produce benefits relative to harm and not prescribing medications that are recommended--and outcomes of older adults.
Potentially inappropriate prescribing was significantly associated with a range of health-related and system-related outcomes, including functional decline, falls, ...
2021-05-19
By the end of the first year of the pandemic in metropolitan Stockholm, investigators estimate that one-fifth of adults in the region previously had COVID-19. The findings, which are published in the Journal of Internal Medicine, come from analyses of anti-viral antibody responses in healthy blood donors and pregnant women.
For the study, researchers examined blood from 2,600 blood donors and 2,500 pregnant women taken between March 14th 2020 and February 28th 2021. Blood donors and pregnant women had a similar rate of past infection, approaching 19% of the study group by the end of February 2021, shortly ...
2021-05-19
Monash University researchers have engineered new antimicrobial surfaces that can significantly reduce the formation of bacteria on medical instruments, such as urinary catheters, and reduce the risk of patient infection while in hospital.
This world-first study demonstrates the potential for 3D engineered surfaces in preventing the initial formation of microcolonies of Escherichiacoli (E.coli), Klebsiellapneumoniae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa - the three most common urinary tract bacterial infections (UTIs) associated with catheters.
The study team, led by Dr Victor Cadarso, from Monash University's Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering and the ...
2021-05-19
SALT LAKE CITY - A new study published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology reports findings on Huntsman at Home™, a cancer hospital-at-home model operated by Huntsman Cancer Institute (HCI) at the University of Utah (U of U). The study analyzed aspects of Huntsman at Home acute care--meaning a level of care that is generally provided in an inpatient hospital setting.
In the 30 days after study entry, Huntsman at Home participants had 55% fewer hospitalizations, 45% fewer emergency department visits, and shorter hospital stays by one day. They also had 47% lower health care costs during the same 30-day period ...
2021-05-19
A key driver of energy research is the ever-growing demand for energy. Traditional fossil-fuel-based energy sources currently meet these demands and do it well, but they're non-renewable and cause major environmental pollution. In a world with looming climate and resource crises threats, researchers have turned to renewable sources of energy as sustainable alternatives. Among renewables, wind energy, in particular, has gained considerable attention due to its low cost. As Dr. Afef Fekih, Computer Engineer at the University of Louisiana, USA, with a specialization in wind turbine design, notes, "Wind energy has been described as 'the world's fastest-growing renewable energy source', seeing a 30% annual growth on ...
2021-05-19
A new survey study suggests that, for adolescents who received unplanned distance education due to the COVID-19 pandemic, experiencing one's own competence was linked to positive emotion, self-motivation to learn, and pro-learning behaviors. Feeling connected to others was also linked to positive emotion. Julia Holzer of the University of Vienna, Austria, and colleagues present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE.
The new research draws on a psychological theory known as self-determination theory, which outlines three basic psychological needs for well-being: autonomy, connection to others, and experiencing one's own competence. Previous research has provided much ...
2021-05-19
Americans who get their news from traditional sources (e.g.: TV, newspapers) are more likely to accept the COVID-19 vaccine than those who rely on social media.
INFORMATION:
Article Title: Examining the effect of information channel on COVID-19 vaccine acceptance
Funding: This research was with funding support from Jigsaw, Google. RPL, ES, JK, BH, and CMI received funding from Jigsaw to conduct this research. BG and TV are employed by Jigsaw/Google. Google, Inc. provided support in the form of salaries for authors, BG TV, but did not have any additional role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript. The specific roles of these authors are articulated in the 'author contribution'. The data ...
2021-05-19
Almost 1 in 4 COVID-19 patients have another bacterial, viral or fungal infection simultaneously or subsequently, with such patients experiencing worse disease outcomes.
INFORMATION:
Article Title: Prevalence and outcomes of co-infection and superinfection with SARS-CoV-2 and other pathogens: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Funding: NS received research support for this work from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases of the National Institutes of Health under Award Number DP2AI144244. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily ...
2021-05-19
Tsukuba, Japan - Autoimmune diseases occur when an individual's immune system fights their own body as if it was a foreign invader. However, in healthy people, these responses are prevented by a process known as immune tolerance. Many complex biological mechanisms maintain the necessary balance between immune activation and suppression to ensure immune tolerance does not prevent the body from effectively fighting pathogens.
In a new study published in PNAS, a group of researchers from the University of Tsukuba uncovered how the relationship between two receptors called DNAM-1 and TIGIT helps preserve the balance for optimal immune function. Both of these molecules have previously been studied ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Alzheimer protein APP regulates learning and social behavior in the healthy brain
Beyond plaques: Heidelberg scientists unravel the natural functions of the APP protein family