Music may benefit older adults with cognitive impairment
2021-05-19
(Press-News.org) Active music-making can provide cognitive benefits to older adults with mild cognitive impairment or dementia, according to an analysis of all relevant studies. The analysis, which is published in the Journal of the American Geriatrics Society, also found that music may help improve their quality of life and mood.
The analysis included nine studies with a total of 495 participants. The authors noted that music-based interventions could potentially provide millions of older adults with critical support for their cognitive, emotional, and social well-being.
"We are excited to see these results because participating in music, like singing in a choir or playing in a drum circle, is a safe, engaging activity that our research demonstrates can support cognition at a critical time for older adults facing cognitive decline," said lead author Jennie L. Dorris, MM, of the University of Pittsburgh.
INFORMATION:
About Wiley
Wiley drives the world forward with research and education. Through publishing, platforms and services, we help students, researchers, universities, and corporations to achieve their goals in an ever-changing world. For more than 200 years, we have delivered consistent performance to all of our stakeholders. The Company's website can be accessed at http://www.wiley.com.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-19
Brazil is the world leader in sweet orange production, but citrus cultivation in the region faces constant threats concerning the availability of water and the outbreak of diseases. New research published in the Journal of Applied Microbiology indicates that a fatty acid called hexanoic acid may help protect against one such problem: citrus canker, a bacterial infection that causes brownish eruptive lesions on the leaves, stems, and fruit of citrus trees.
Hexanoic acid might be a suitable substitute for chemicals used to protect citrus from bacterial infections. Investigators examined several ...
2021-05-19
Little is known concerning environmental contaminants in predators at the top of a food chain. A study published in Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry has demonstrated that new types of brominated flame retardants accumulate in the tissues of killer whales near Norway and are also passed on to nursing offspring.
Investigators also detected man-made chemicals called perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in the tissues of adult killer whales. Thresholds for health effects of PFAS in marine mammals are not established, but the chemical has been linked to reproductive and endocrine effects in wildlife. In addition, polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), which have long been banned, were detected in the blubber of 7 of the 8 killer whales in the study at levels that exceeded the ...
2021-05-19
Skoltech researchers and their colleagues from China and Germany have presented a new search algorithm for single-atom-alloy catalysts (SAACs) that found more than 200 yet unreported candidates. Their work provides a recipe for finding best SAACs for various applications. The paper was published in the journal END ...
2021-05-19
Scientists have successfully treated flies displaying behavioural problems linked to newly discovered schizophrenia-associated genes in humans, using common anti-psychotics.
Schizophrenia is a severe long-term mental health condition that is historically poorly understood and treated. It is relatively common, affecting one to two per cent of the population, and is known to be up to 80 per cent genetic in origin.
Recent advances in sequencing genomes of people with schizophrenia have identified a list of novel genes and mutations associated with the disease. Many ...
2021-05-19
NEW YORK, NY (May 19, 2021)--A new study from Columbia University and an international team of researchers identifies multiple ways to achieve the same health benefits from exercise--as long as the exercise "cocktail" includes plenty of light physical activity.
"For decades, we've been telling people that the way to stay healthy is to get at least 30 minutes of exercise five days a week," says Keith Diaz, PhD, assistant professor of behavioral medicine and director of the exercise testing laboratory at the Center for Behavioral Cardiovascular Health at Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons.
"But even if you're one of the few adults who can stick to this advice, 30 minutes represents ...
2021-05-19
The work was conducted under the auspices of the Russian Science Foundation; the project "Synthesis and research of a new class of nanocomposite ceramics with degenerate dielectric constant for optoplasmonic applications" is headed by Professor Sergey Kharintsev (KFU's Institute of Physics).
Professor Kharintsev, the first co-author, comments, "Under the influence of light, collective oscillations of electrons can be excited in metallic nanostructures, and as a result the electric field in the vicinity of the nanostructures strongly increases. The field of physics that studies the effects of generation and propagation of such electromagnetic excitations is ...
2021-05-19
Computed tomography -- CT scanning -- which combines a series of X-ray images taken from different angles around an organism and uses computer processing to create cross-sectional images of its bones, is providing new insight into an old initiative to characterize fishes in Africa's Lake Malawi.
The process, demonstrated in a new study using the high-resolution X-ray computer system in Penn State's Center for Quantitative X-Ray Imaging, is important because it will lead to the identification and management of more of the fish species in Africa's second largest lake, according to lead researcher Jay Stauffer Jr., distinguished professor of ichthyology in the College of Agricultural Sciences.
"Before they can effectively ...
2021-05-19
"I think you're on mute." This was the most-used phrase of 2020, according to Human Resources Online. Emblazoned on T-shirts and embossed on coffee-mugs, we used the meme to make fun of ourselves while learning video-conferencing tools like Zoom and Microsoft's Teams.
But for the more than 7 million Americans who suffer from vocal disorders, not being heard is a serious matter. Many people who have normal speaking skills have great difficulty communicating when their voice box, the larynx, fails. This can occur if the vocal cords, the two bands of smooth muscle tissue in the larynx, suffer damage from an accident, surgical procedure, viral infection or cancer.
There is no replacement for the ...
2021-05-19
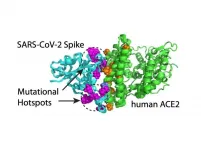
SARS-CoV-2 has evolved to acquire mutations on the spike protein--the part of the virus that protrudes from its surface and latches onto cells to infect them--that enhance the coronavirus' ability to bind to human cells or evade antibodies. A new study from the Centers for Genomics and Systems Biology at New York University and NYU Abu Dhabi uses computational modeling to assess the biological significance of spike protein mutations, uncovering versions of the virus that bind more tightly or resist antibodies and offering a promising public health surveillance tool.
The study, which appears in the Journal of Molecular Biology, also suggests that these mutations on the spike protein are a key ...
2021-05-19
Press release - ESE statement: COVID-19 and endocrine and metabolic diseases. An updated statement from the European Society of Endocrinology
New expert statement confirms strong links between our hormones and COVID-19
The endocrine system is strongly involved in SARS-Cov-2 infection - so much so that evidence of an "endocrine phenotype" of COVID-19 has emerged, according to a statement by the European Society of Endocrinology (ESE) published in the journal Endocrine in April 2021. Leading endocrinology researchers looked into the evidence that has accumulated over the past year since the pandemic emerged, and consistently found evidence ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Music may benefit older adults with cognitive impairment