IBS patients' symptoms improved under COVID-19 lockdown orders
Unexpected reduction in symptoms may result from lower stress and more control over diet at home
2021-05-23
(Press-News.org) Bethesda, MD (May 23, 2021) -- Patients' irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) symptoms unexpectedly improved when they were under COVID-19 stay-at-home orders, reaffirming the gut-brain connection in functional gastrointestinal disorders, according to research that was selected for presentation at Digestive Disease Week® (DDW) 2021.
"One of our main hypotheses was that these patients were going to be worse because of pressure and stress due to COVID-19," said Juan Pablo Stefanolo, MD, a lead author on the study and a physician with the Neurogastroenterology and Motility section, Hospital de Clínicas José de San Martín, Buenos Aires University, Argentina. "We think the results have something to do with people staying at home. They were not exposed to outside stress, and at home they were able to avoid food triggers."
Pandemic lockdown orders in Argentina created a unique opportunity for researchers to study the impact of pandemic stressors and reduced social interaction on 129 IBS patients whose pre-pandemic data had already been collected through an earlier research project. The patients were re-assessed during the lockdown with the same online survey that included multiple validated measures of IBS severity, anxiety and depression, along with questions about co-occurring illnesses, including heartburn, regurgitation, indigestion, chronic fatigue, fibromyalgia and nonmigraine headaches.
During the lockdown in Argentina -- one of the longest lockdowns in the world -- the number of patients experiencing severe IBS fell sharply from 65 to 39. The mean Irritable Bowel Syndrome Severity Scale score for the group also fell 66 points, from 278 to 212 on a 500-point scale. IBS symptoms of pain, distention, stool consistency, anxiety, somatization, fibromyalgia and chronic fatigue symptoms all improved during the lockdown.
Patients with functional gastrointestinal disorders experience symptoms even though no structural or biochemical abnormalities are present. The gut-brain connection refers to the role of stress and psychological difficulties in triggering debilitating gut-related symptoms. Headache, heartburn and regurgitation -- all outside the category of functional disorders -- became worse during the study, likely due to the increase in weight that nearly 60 percent of patients reported.
"Our results reinforce the concept that IBS, or functional gastrointestinal disorders, have a connection to psychosocial factors, as well as food and other factors," Dr. Stefanolo said. "The gut-brain axis has a lot of facets."
INFORMATION:
DDW Presentation Details
Dr. Stefanolo will present data from the study, "Gut-brain axis and irritable bowel syndrome during SARS-CoV-2 pandemic. A survey-based study," abstract Su093, on Sunday, May 23, at 1 p.m. EDT.
For more information about featured studies, as well as a schedule of availability for featured researchers, please visit http://www.ddw.org/press.
Digestive Disease Week® (DDW) is the largest international gathering of physicians, researchers and academics in the fields of gastroenterology, hepatology, endoscopy and gastrointestinal surgery. Jointly sponsored by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD), the American Gastroenterological Association (AGA) Institute, the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ASGE) and the Society for Surgery of the Alimentary Tract (SSAT), DDW is a fully virtual meeting from May 21-23, 2021. The meeting showcases more than 2,000 abstracts and hundreds of lectures on the latest advances in GI research, medicine and technology. More information can be found at http://www.ddw.org.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-22
Bethesda, MD (May 22, 2021) -- An artificial intelligence tool under development at Duke University can be added to the standard toilet to help analyze patients' stool and give gastroenterologists the information they need to provide appropriate treatment, according to research that was selected for presentation at Digestive Disease Week® (DDW) 2021. The new technology could assist in managing chronic gastrointestinal issues such as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
"Typically, gastroenterologists have to rely on patient self-reported information about their stool to help determine the cause of their ...
2021-05-22
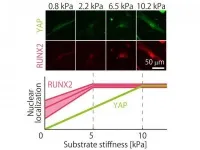
Tokyo, Japan - Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have been quantifying how different batches of mesenchymal stem cells respond to the mechanical stiffness of their environments. They focused on how certain proteins were "localized" in cell nuclei and found key trends in how this changed with stiffness. Their findings explain inconsistencies between previous findings and may guide how scientists control the state of stem cells for research and medical treatments.
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are important "progenitor" cells that can transform into muscle, cartilage, bone or fat cells. In 2006, pioneering work by Engler and coworkers showed that they could control what cell type mesenchymal stem cells ...
2021-05-22
Nearly half a billion people on the planet have diabetes, but most of them aren't getting the kind of care that could make their lives healthier, longer and more productive, according to a new global study of data from people with the condition.
Many don't even know they have the condition.
Only 1 in 10 people with diabetes in the 55 low- and middle-income countries studied receive the type of comprehensive care that's been proven to reduce diabetes-related problems, according to the new findings published in Lancet Healthy Longevity.
That comprehensive package of care ...
2021-05-22
Business shutdowns reduce COVID-19 deaths, though with rapidly diminishing returns, with study of Italian lockdowns estimating they saved over 9,400 lives in under a month.
INFORMATION:
Article Title: Closed for business: The mortality impact of business closures during the Covid-19 pandemic
Funding: The author(s) received no specific funding for this work.
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0251373
...
2021-05-22
Plant diseases don't stop at national borders and miles of oceans don't prevent their spread, either. That's why plant disease surveillance, improved detection systems, and global predictive disease modeling are necessary to mitigate future disease outbreaks and protect the global food supply, according to a team of researchers in a new commentary published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
The idea is to "detect these plant disease outbreak sources early and stop the spread before it becomes a pandemic," says lead-author Jean Ristaino, William Neal Reynolds Distinguished Professor of Plant Pathology at North Carolina State University. Once an epidemic occurs it is difficult to control, Ristaino says, likening the effort to the one undertaken ...
2021-05-22
Neurotic personalities found the pandemic most traumatic, while agreeable and conscientious personalities offered protection from the pandemic's negative impacts.
INFORMATION:
Article Title: Which personality traits can mitigate the impact of the pandemic? Assessment of the relationship between personality traits and traumatic events in the COVID-19 pandemic as mediated by defense mechanisms
Funding: The author(s) received no specific funding for this work.
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0251984
...
2021-05-22
Simon Fraser University researchers have validated a faster, cheaper COVID-19 test that could kickstart the expansion of more widespread rapid testing. Study results have been published in The Journal of Molecular Diagnostics.
"This research offers a cheaper, faster alternative to the most reliable and sensitive test currently used worldwide, without sacrificing sensitivity and reproducibility," says molecular biology and biochemistry professor Peter Unrau, who led the team evaluating the COVID-19 test kit.
The researchers suggest the test could be deployed in remote locations, clinics and airports due to its ease of use and portability.
The microchip real-time PCR test can provide ...
2021-05-21
To meet soaring demand for lightning-quick mobile technology, each year tech giants create faster, more powerful devices with longer-lasting battery power than previous models.
A major reason companies like Apple and Samsung can miraculously pull this off year after year is because engineers and researchers around the world are designing increasingly power-efficient microchips that still deliver high speeds.
To that end, researchers led by a team at Brigham Young University have just built the world's most power-efficient high-speed analog-to-digital converter (ADC) microchip. An ADC is a tiny piece of technology present in almost every electronic piece of equipment that converts analog ...
2021-05-21
For decades scientists have been puzzled by the formation of rare hyper-enriched gold deposits in places like Ballarat in Australia, Serra Palada in Brazil, and Red Lake in Ontario. While such deposits typically form over tens to hundreds of thousands of years, these "ultrahigh-grade" deposits can form in years, month, or even days. So how do they form so quickly?
Studying examples of these deposits from the Brucejack Mine in northwestern British Columbia, McGill Professor Anthony Williams-Jones of the Department of Earth and Planetary Sciences and PhD student Duncan McLeish have discovered that these gold deposits form much like soured milk. When milk goes sour, the butterfat particles clump together to form a jelly.
Q&A with Anthony Williams-Jones and Duncan McLeish
What did you ...
2021-05-21
A team of researchers led by scientists at UC Santa Cruz analyzed data from 3,212 camera traps to show how human disturbance could be shifting the makeup of mammal communities across North America.
The new study, published in the journal Global Change Biology, builds upon the team's prior work observing how wildlife in the Santa Cruz Mountains respond to human disturbance. Local observations, for example, have shown that species like pumas and bobcats are less likely to be active in areas where humans are present, while deer and wood rats become bolder and more active. But it's difficult to generalize findings like these across larger geographic areas because human-wildlife interactions are often regionally unique.
So, to get a continent-wide ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] IBS patients' symptoms improved under COVID-19 lockdown orders
Unexpected reduction in symptoms may result from lower stress and more control over diet at home