Finer touch for tuning stem cell 'fate' with substrates of varying stiffness
Quantitative control over localization of key proteins in mesenchymal stem cells
2021-05-24
(Press-News.org) Tokyo, Japan - Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have been quantifying how different batches of mesenchymal stem cells respond to the mechanical stiffness of their environments. They focused on how certain proteins were "localized" in cell nuclei and found key trends in how this changed with stiffness. Their findings explain inconsistencies between previous findings and may guide how scientists control the state of stem cells for research and medical treatments.
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are important "progenitor" cells that can transform into muscle, cartilage, bone or fat cells. In 2006, pioneering work by Engler and coworkers showed that they could control what cell type mesenchymal stem cells transformed (or "differentiated") into by simply placing them on surfaces with a different mechanical stiffness, or elastic modulus. Ever since, scientists have been trying to identify exactly how this occurs. The trouble is, despite the phenomenon being robust and reproducible, it turns out that they are very sensitive to the exact environment into which they are placed, even which batch they came from. The stakes are high: reliable control over MSC states would mean more research and even potential biomedical applications.
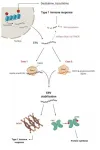
This search inspired a team led by Associate Professor Hiromi Miyoshi of Tokyo Metropolitan University to look at how different batches of MSCs respond to different environments. They focused on two proteins present in MSCs, the YAP protein, which helps cells respond to mechanical environments, and RUNX2, a key player in helping MSCs turn into osteoblasts which eventually become bone. They looked at how different MSC batches have different distributions of YAP and RUNX2 inside their cells. For their "stiff" environments, they chose a specially designed gelatin substrate which had significantly better reproducibility than popular collagen alternatives.
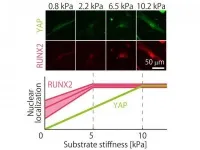
From the beginning, they found that their batches were quite distinct. In basic experiments looking at how they turned into bone-making or fat-making cells, they found that the batches produced very different levels of calcium and fat deposits. But when it came to their mechanoresponsive behavior, it turned out they were not as wildly distinct as initially thought. Firstly, the team found that the proportion of YAP found in the nuclei of cells (or "localization") turns out to vary in a consistent manner between batches, plateauing at the same stiffness. For RUNX2, though the localization varied differently, they still plateaued at a specific stiffness value (a different one to YAP). Even then, the trend in RUNX2 localization was linear up to the plateau.
With this kind of information, anyone could make a gel of a specific stiffness and actively control the level of YAP/RUNX2 in the nucleus of mesenchymal stem cells. By doing so, they could tune when and how their cells differentiate. The team hope this new level of control over cell fate will help accelerate research into MSCs and potentially lead to therapeutic applications.
INFORMATION:
This work was supported by a JSPS KAKENHI Grant-in-Aid of Scientific Research (JP19J13048) and AMED under grant number 18gm5810012h9904.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-24
Press release - Abstract 1394: Alterations in clock genes expression in Eutopic and Ectopic Endometrial Tissue
New research suggests that night shift work is linked to menstrual irregularity and increased chance of developing endometriosis
According to a study being presented at the 23rd European Congress of Endocrinology (e-ECE 2021), on Sunday 23 May at 19:00 CET (http://www.ece2021.org), women working night shifts may be at a greater risk of menstrual irregularity and developing endometriosis. The research found a reduction in the expression of ...
2021-05-24
A natural food supplement reduces anxiety in mice, according to a new Weizmann Institute of Science study. The plant-derived substance, beta-sitosterol, was found to produce this effect both on its own and in synergic combination with an antidepressant known under the brand name Prozac. If these findings, published today in Cell Reports Medicine, are confirmed in clinical trials, they could point the way toward the use of beta-sitosterol as a treatment for relieving anxiety in humans.
Anxiety is not always a bad thing. In fact, in evolutionary terms, feeling anxious about potential threats is critical for survival because it helps us mount an appropriate response. That's precisely why developing antianxiety drugs is so challenging. The circuits for anxiety ...
2021-05-24
New research from Flinders University in Australia indicates people with myopia are more likely to experience poorer sleep quality than people with normal vision.
The study indicates that people with short-sightedness have more delayed circadian rhythms and lower production of melatonin, a hormone secreted in the brain and responsible for regulating sleep at night, compared to people with normal vision.
People affected by myopia or short-sightedness are familiar with the frustration of only being able to clearly see objects up close, but not a far distance.
Optometrist Dr Ranjay Chakraborty , from the Flinders University Caring Futures Institute, says the study adds to the growing evidence of the potential association between disruption of the circadian ...
2021-05-24
Gaping policy shortfalls in the Australian Government's 'Closing the Gap' program have seen it fail to reduce disparities in Indigenous health, income, employment, child removal and incarceration, Flinders University researchers say.
Their five-year study just published in the Australian Journal of Public Administration examined why the targets of Australia's national Closing the Gap strategy to reduce or eliminate inequalities in health, education and employment outcomes between Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people and other Australians have mostly not been met.
"Despite talk of governments 'doing things with and ...
2021-05-24
Our livers work hard to perform an entire range of activities: helping us digest food, maintaining body temperature and serving as an important checkpoint of the immune system for everything that we eat. It is inside the liver that the unique, rich and complex network of immune cells and pathways is set up to decide what is a harmless food particle, and what is a dangerous pathogen that should be neutralized and removed. Liver is therefore very sensitive to the food we consume, and sometimes a bad diet can induce a serious dysregulation of the immune activities within it.
Obesity is an extremely ...
2021-05-24
The chemotherapy drug decitabine is commonly used to treat patients with blood cancers, but its response rate is somewhat low. Researchers have now identified why this is the case, opening the door to more personalized cancer therapies for those with these types of cancers, and perhaps further afield.
Researchers have identified the genetic and molecular mechanisms within cells that make the chemotherapy drug decitabine--used to treat patients with myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) and acute myeloid leukemia (AML) --work for some patients but not others. The findings should assist clinicians in developing more patient-specific treatment strategies.
The findings were published in the Proceedings of the National Academies of Science on March 30.
The chemotherapy drug decitabine, ...
2021-05-24
Recently, Professor YANG Liangbao, from the Institute of Health and Medical Technology, Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS), developed a general surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) method for actively capturing target molecules in small gaps based on nano-capillary pumping model. Relevant results were detailed in the Journal of the American Chemical Society.
SERS is a spectroscopic technique typically used to determine vibrational modes of molecules. It's commonly used in chemistry to provide a structural fingerprint by which molecules can be identified.
In this research, using the principle of capillary suction, they constructed ...
2021-05-24
Talk of a graduate student mental health crisis is abundant in academic and popular media, but a University of Otago study has found no evidence of one in New Zealand.
The study, published in Frontiers in Psychology, used data from the Graduate Longitudinal Study New Zealand to compare the mental wellbeing of students who did, and did not, transition into PhD study after completing their undergraduate degree.
Co-author Dr Damian Scarf, from the Department of Psychology, says the researchers found poor mental health is not an inevitable consequence of PhD study in New Zealand.
This is despite ...
2021-05-24
ATLANTA - MAY 24, 2021 - A new study underscores the importance of health insurance coverage continuity in access to and receipt of care and care affordability in the United States. Researchers found that health insurance coverage disruptions were consistently associated with worse healthcare access and problems with care affordability. The study appears in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine.
Decades of research has demonstrated that health insurance coverage is associated with better access to care and health outcomes in the U.S. However, less research has addressed coverage disruptions ...
2021-05-24
A strange phenomenon happens with modern blue whales, humpback whales and gray whales: they have teeth in the womb but are born toothless. Replacing the teeth is baleen, a series of plates composed of thin, hair- and fingernail-like structures growing from the roof of their mouths that act as a sieve for filter feeding small fish and tiny shrimp-like krill.
The disappearing embryonic teeth are testament to an evolutionary history from ancient whales that had teeth and consumed larger prey. Modern baleen whales on the other hand use their fringed baleen ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Finer touch for tuning stem cell 'fate' with substrates of varying stiffness
Quantitative control over localization of key proteins in mesenchymal stem cells