INFORMATION:
'Rejuvenating' the Alzheimer's brain
2021-05-25
(Press-News.org) Alzheimer's disease is the main cause of dementia and current therapeutic strategies cannot prevent, slow down or cure the pathology. The disease is characterized by memory loss, caused by the degeneration and death of neuronal cells in several regions of the brain, including the hippocampus, which is where memories are initially formed. Researchers from the Netherlands Institute for Neuroscience (NIN) have identified a small molecule that can be used to rejuvenate the brain and counteract the memory loss.
New cells in old brains
The presence of adult-born cells in the hippocampus of old people was recently demonstrated in scientific studies. It suggests that, generally speaking, the so-called process of adult neurogenesis is sustained throughout adulthood. Adult neurogenesis is linked to several aspects of cognition and memory in both animal models and humans, and it was reported to sharply decrease in the brains of patients with Alzheimer's disease. Researchers also found that higher levels of adult neurogenesis in these patients seem to correlate with better cognitive performance before death. "This could suggest that the adult-born neurons in our brain may contribute to a sort of cognitive reserve that could later on provide higher resilience to memory loss", says Evgenia Salta, group leader at the NIN. Therefore, researchers from the NIN investigated if giving a boost to adult neurogenesis could help prevent or improve dementia in Alzheimer's disease.
A small molecule with big potential
Salta: "Seven years ago, while studying a small RNA molecule that is expressed in our brain, called microRNA-132, we came across a rather unexpected observation. This molecule, which we had previously found to be decreased in the brain of Alzheimer's patients, seemed to regulate homeostasis of neural stem cells in the central nervous system". Back then, Alzheimer's was thought to be a disease affecting only mature neuronal cells, so at first glance this finding did not seem to explain a possible role of microRNA-132 in the progression of Alzheimer's.
In this study, the researchers set out to address whether microRNA-132 can regulate adult hippocampal neurogenesis in healthy and Alzheimer's brains. Using distinct Alzheimer's mouse models, cultured human neural stem cells and post-mortem human brain tissue, they discovered that this RNA molecule is required for the neurogenic process in the adult hippocampus. "Decreasing the levels of microRNA-132 in the adult mouse brain or in human neural stem cells in a dish impairs the generation of new neurons. However, restoring the levels of microRNA-132 in Alzheimer's mice rescues neurogenic deficits and counteracts memory impairment related to adult neurogenesis", Sarah Snoeck, technician in the group of Salta, explains.
These results provide a proof-of-concept regarding the putative therapeutic potential of bringing about adult neurogenesis in Alzheimer's. Salta: "Our next goal is to systematically assess the efficacy and safety of targeting microRNA-132 as a therapeutic strategy in Alzheimer's disease".
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
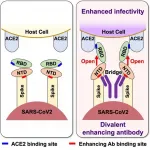
Antibodies that enhance SARS-CoV-2 infection -- A possible factor for severe COVID-19
2021-05-25
A research group from Osaka University led by Professor Hisashi Arase and consisting of researchers from the Research Institute for Microbial Diseases, the Institute for Protein Research, the Immunology Frontier Research Center, the Center for Infectious Diseases, and the Graduate School of Medicine has discovered for the first time that both neutralizing antibodies that protect against infection as well as infection-enhancing antibodies that increase infectivity are produced after infection with SARS-CoV-2 by analyzing antibodies derived from COVID-19 patients.
Antibodies against the receptor binding site (RBD) of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein play an important function as ...
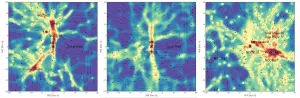
Mapping the local cosmic web
2021-05-25
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- A new map of dark matter in the local universe reveals several previously undiscovered filamentary structures connecting galaxies. The map, developed using machine learning by an international team including a Penn State astrophysicist, could enable studies about the nature of dark matter as well as about the history and future of our local universe.
Dark matter is an elusive substance that makes up 80% of the universe. It also provides the skeleton for what cosmologists call the cosmic web, the large-scale structure of the universe ...
National survey of frontline health care workers finds fear, unsafe working conditions
2021-05-25
WASHINGTON (May 25, 2021)--A new report summarizes the findings from a national survey of frontline health care workers during the early days of the COVID-19 pandemic, finding that many reported unsafe working conditions and retaliation for voicing their concerns to employers. The survey, launched in May 2020 by staff and student researchers at the George Washington University, provides a snapshot of the experiences of frontline health care workers providing care for millions of Americans during the pandemic.
"This survey gives a voice to US health care workers who have been on the frontlines ...
Egyptian fossil surprise: Fishes thrived in tropics in ancient warm period, despite high ocean tempe
2021-05-25
Photos and Map
The Paleocene-Eocene Thermal Maximum, or PETM, was a short interval of highly elevated global temperatures 56 million years ago that is frequently described as the best ancient analog for present-day climate warming.
Fish are among the organisms thought to be most sensitive to warming climates, and tropical sea-surface temperatures during the PETM likely approached temperatures that are lethal to some modern marine fish species, according to some estimates.
But newly discovered fish fossils from an eastern Egyptian desert site show that marine fishes thrived in at least ...
HPV vaccine shows success in gay, bisexual men
2021-05-25
A study by Monash University and Alfred Health found a 70 per cent reduction in one type of human papillomavirus (HPV) in gay and bisexual men after the implementation of the school-based HPV vaccination program.
The HYPER2 study, published in The Lancet Infectious Diseases, and led by Associate Professor Eric Chow, found there was a significant reduction in all four vaccine-preventable genotypes in gay/bisexual men aged 16-20 years following the introduction of the vaccine for boys in 2013.
Australia is one of the first and few countries that have both boys and girls vaccination programs for ...
Immune function of small chloroplasts in the epidermal cells of plants
2021-05-25
It is said that 10 to 15% of the world's agricultural production loss is caused by diseases, which is equivalent of the food for about 500 million people. And since 70-80% of this plant disease is caused by filamentous fungi, protecting crops from filamentous fungi is an important issue in effectively feeding the world population. In order for pathogenic fungi to infect plants, they must break through the epidermal cells of the plant and invade the interior. In other words, plant epidermal cells act as the first barrier to stop the attack of pathogenic fungi in the environment. So what kind of defense functions do ...
As water sources become scarce, understanding emerging subsurface contaminants is key
2021-05-25
In the last year, one thing has become clear: we cannot live life without risk. In fact, every part of our daily routines became subject to analysis: How risky is the action and is its value worth the potential cost?
Risk analysis, though seemingly more ever-present in our thoughts today, has always been a part of how we operate and how the systems around us work. As new pressures, such as climate change, deepen, the accuracy and reliability of risk analysis models regarding issues as basic as the cleanliness of our drinking water have become more important than ever.
USC ...
Conservation success leads to new challenges for endangered mountain gorillas
2021-05-25
A study published today in Scientific Reports suggests that new health challenges may be emerging as a result of conservationists' success in pulling mountain gorillas back from the brink of extinction.
The study, the first species-wide survey of parasite infections across the entire range of the mountain gorilla, was conducted by an international science team led by the Institute of Vertebrate Biology, Czech Academy of Sciences; University of Veterinary Sciences Brno, Czech Republic; Gorilla Doctors; and the Dian Fossey Gorilla Fund. The work was conducted in collaboration with the protected area authorities of Rwanda, Uganda and the Democratic Republic of Congo (the Rwanda Development Board, the Uganda Wildlife Authority and l'Institut Congolais pour la Conservation de la Nature, respectively).
All ...
'Slow slip' earthquakes' hidden mechanics revealed
2021-05-25
Slow slip earthquakes, a type of slow motion tremor, have been detected at many of the world's earthquake hotspots, including those found around the Pacific Ring of Fire, but it is unclear how they are connected to the damaging quakes that occur there. Scientists at The University of Texas at Austin have now revealed the earthquakes' inner workings using seismic CT scans and supercomputers to examine a region off the coast of New Zealand known to produce them.
The insights will help scientists pinpoint why tectonic energy at subduction zones such as New Zealand's Hikurangi subduction ...
Low blood flow in the brain may be an early sign of Parkinson's disease
2021-05-25
Patients who suffer from REM sleep behaviour disorder have altered blood flow in the brain, which can lead to a lack of oxygen in the brain tissue. In the long term, this may cause symptoms of Parkinson's disease. This is shown by research from Aarhus University and Aarhus University Hospital.
Do you sleep restlessly and flail your arms and kick out in your sleep? This could be a sign of a disorder associated with diseases of the brain. Researchers from AU and AUH have examined whether the sleep disorder RBD - which is also known as Rapid Eye Movement Sleep Behaviour Disorder - may ...