Researchers seek deeper understanding on how cells in the body operate
An interdisciplinary team seeks to better understand how the mechanical properties of cells operate in the body and how pathologies can disrupt these processes.
2021-05-25
(Press-News.org) Cells sense and respond to the mechanical properties of the cellular microenvironment in the body. Changes in these properties, which occur in a number of human pathologies, including cancer, can elicit abnormal responses from cells. How the cells adapt to such changes in the mechanical microenvironment is not well understood.
A team of researchers at Texas A&M University are working to understand cellular mechanosensing -- the ability to sense and respond to the mechanical properties of the microenvironment -- in a unique way. Dr. Tanmay Lele, Unocal Professor in the Department of Biomedical Engineering, Department of Chemical Engineering and the Department of Translational Medical Sciences, partnered with Dr. Charles Baer, an evolutionary biologist at the University of Florida. Together they used methods of experimental cellular evolution as a means to understand cellular adaptation to biomaterials of controlled mechanical properties.
The experiments were led by doctoral student Purboja Purkayastha from the Artie McFerrin Department of Chemical Engineering and technical laboratory coordinator Kavya Pendyala from the Department of Biomedical Engineering at Texas A&M.
"Before our work, it was basically unknown if cells would evolve in controlled mechanical environments," Lele said. "We set out to test this possibility."
Cells are products from hundreds of millions of years of evolution, and their response to environments -- whether chemical or mechanical -- has likely evolved through a process of natural selection. Chemical constraints are well known to exert selection pressure on cell populations, but whether the mechanical properties of a cell's environment constitutes a significant agent of natural selection has never been investigated before.
Many types of animal cells exhibit "phenotypic plasticity" -- they look and function differently -- in different mechanical environments. There are two possible explanations for the plasticity of cells in different mechanical environments. First, the phenotypes may be optimal, such that there is no better way for a cell to function in each environment. Alternatively, the plasticity may be a compromise such that the phenotypic trait is optimal for a given mechanical context, but suboptimal in other mechanical contexts.
The team's research demonstrated that cellular mechanosensing is, in fact, not optimal but a tradeoff. Using a combination of experimental cellular evolution on biomaterials of controlled stiffness, genome sequencing, simulations and gene expression analysis, the team showed that cells evolve under selection pressure from biomaterials of controlled mechanical stiffness.
The team's research was recently published in the journal Molecular Biology and Evolution.
Lele said that experimental cell evolution is a good approach to better understand the mechanisms underlying cellular mechanosensing.
"We are currently using experimental cellular evolution to understand how cancer cells, which have great genomic variation, respond to the altered mechanical stiffness and other mechanical properties of tumor microenvironments," Lele said. "Further, the fact that cells can be evolved on biomaterials of controlled properties in vitro opens up new ways to generate engineered cells with properties optimal for those properties."
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-25
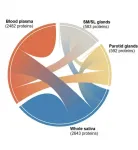
BUFFALO, N.Y. - To improve the development of new saliva-based diagnostic tests and personalized medicine, the National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research (NIDCR) has supported the development of the Human Salivary Proteome Wiki, the first public platform that catalogs and curates data on each of the thousands of proteins within our saliva.
Detailed in an article published on Tuesday, May 25 in the Journal of Dental Research, the wiki provides researchers and clinicians with rich, unbiased evidence from multiple independent studies to help explore the dynamic and complex nature of saliva, as well as analytical tools to search for data by tissue type, disease and more.
"This ...
2021-05-25
New effective compounds, which can be endogenous donors of a signaling molecule - hydrogen sulfide in the body, were synthesized by SUSU scientists. Due to this property, the obtained compounds are potential drugs with a cancer-preventing effect. The research work was published in the Russian Chemical Bulletin (Q3).
Organosulfur compounds with anticancer, antibacterial, and antirheumatic properties have been studied for some years by scientists from South Ural State University and N.D. Zelinsky Institute of Organic Chemistry, Russian Academy of Sciences. In the latest study, they attempted to search for new derivatives of 1,2-dithiol-3-thiones - compounds with various ...
2021-05-25
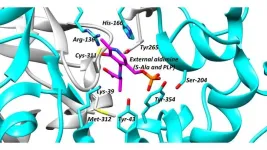
Scientists from the UK's University of Bath explore racemases - an important type of enzyme that is linked to certain cancers and other life-threatening diseases while also being critical to cell function - in a paper published in the prestigious journal Chemical Society Reviews. The scientists also propose new strategies for finding drugs that neutralise these enzymes.
Many racemases and epimerases perform vital roles in human and animal cells, and in disease-causing organisms. They facilitate proper nerve function, the degradation of toxic substances, the formation of bacterial cell walls and the conversion of certain drugs into their active ...
2021-05-25
Alzheimer's disease is the main cause of dementia and current therapeutic strategies cannot prevent, slow down or cure the pathology. The disease is characterized by memory loss, caused by the degeneration and death of neuronal cells in several regions of the brain, including the hippocampus, which is where memories are initially formed. Researchers from the Netherlands Institute for Neuroscience (NIN) have identified a small molecule that can be used to rejuvenate the brain and counteract the memory loss.
New cells in old brains
The presence of adult-born cells in the hippocampus ...
2021-05-25
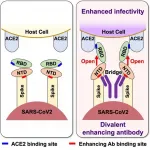
A research group from Osaka University led by Professor Hisashi Arase and consisting of researchers from the Research Institute for Microbial Diseases, the Institute for Protein Research, the Immunology Frontier Research Center, the Center for Infectious Diseases, and the Graduate School of Medicine has discovered for the first time that both neutralizing antibodies that protect against infection as well as infection-enhancing antibodies that increase infectivity are produced after infection with SARS-CoV-2 by analyzing antibodies derived from COVID-19 patients.
Antibodies against the receptor binding site (RBD) of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein play an important function as ...
2021-05-25
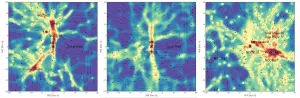
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- A new map of dark matter in the local universe reveals several previously undiscovered filamentary structures connecting galaxies. The map, developed using machine learning by an international team including a Penn State astrophysicist, could enable studies about the nature of dark matter as well as about the history and future of our local universe.
Dark matter is an elusive substance that makes up 80% of the universe. It also provides the skeleton for what cosmologists call the cosmic web, the large-scale structure of the universe ...
2021-05-25
WASHINGTON (May 25, 2021)--A new report summarizes the findings from a national survey of frontline health care workers during the early days of the COVID-19 pandemic, finding that many reported unsafe working conditions and retaliation for voicing their concerns to employers. The survey, launched in May 2020 by staff and student researchers at the George Washington University, provides a snapshot of the experiences of frontline health care workers providing care for millions of Americans during the pandemic.
"This survey gives a voice to US health care workers who have been on the frontlines ...
2021-05-25
Photos and Map
The Paleocene-Eocene Thermal Maximum, or PETM, was a short interval of highly elevated global temperatures 56 million years ago that is frequently described as the best ancient analog for present-day climate warming.
Fish are among the organisms thought to be most sensitive to warming climates, and tropical sea-surface temperatures during the PETM likely approached temperatures that are lethal to some modern marine fish species, according to some estimates.
But newly discovered fish fossils from an eastern Egyptian desert site show that marine fishes thrived in at least ...
2021-05-25
A study by Monash University and Alfred Health found a 70 per cent reduction in one type of human papillomavirus (HPV) in gay and bisexual men after the implementation of the school-based HPV vaccination program.
The HYPER2 study, published in The Lancet Infectious Diseases, and led by Associate Professor Eric Chow, found there was a significant reduction in all four vaccine-preventable genotypes in gay/bisexual men aged 16-20 years following the introduction of the vaccine for boys in 2013.
Australia is one of the first and few countries that have both boys and girls vaccination programs for ...
2021-05-25
It is said that 10 to 15% of the world's agricultural production loss is caused by diseases, which is equivalent of the food for about 500 million people. And since 70-80% of this plant disease is caused by filamentous fungi, protecting crops from filamentous fungi is an important issue in effectively feeding the world population. In order for pathogenic fungi to infect plants, they must break through the epidermal cells of the plant and invade the interior. In other words, plant epidermal cells act as the first barrier to stop the attack of pathogenic fungi in the environment. So what kind of defense functions do ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Researchers seek deeper understanding on how cells in the body operate
An interdisciplinary team seeks to better understand how the mechanical properties of cells operate in the body and how pathologies can disrupt these processes.